Steel vs tungsten carbide: which is better for wear-resistant drilling tools?
JUN 20, 2025 |
In the world of drilling, the longevity and efficiency of tools are paramount. Choosing the right material can significantly influence the performance and cost-effectiveness of drilling operations. Among the most popular materials for wear-resistant drilling tools are steel and tungsten carbide. Each material has its unique properties, making it suitable for different applications. This article explores the characteristics of steel and tungsten carbide, comparing their suitability for wear-resistant drilling tools.
Understanding Steel as a Wear-Resistant Material
Steel is one of the most widely used materials in the manufacturing of drilling tools. Known for its toughness and versatility, steel offers several advantages in various drilling applications. Its ability to withstand high tensile and shear stresses makes it an excellent choice for many industries.
1. Strength and Toughness
Steel is renowned for its strength and toughness. It can withstand heavy impacts and extreme pressure, which is essential for drilling through hard surfaces. Its ductility allows it to absorb shock without fracturing, which is a critical factor in many drilling applications.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
Steel is generally more cost-effective than tungsten carbide. Its abundance and relatively simple manufacturing processes contribute to its affordability. For projects where budget constraints are a concern, steel is often the preferred choice.
3. Versatility
The versatility of steel is unmatched. It can be alloyed with various elements to enhance specific properties such as hardness, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. This flexibility allows manufacturers to create steel tools tailored to specific drilling conditions.
Exploring Tungsten Carbide for Wear Resistance
Tungsten carbide is a compound made from tungsten and carbon atoms. Known for its hardness and wear resistance, tungsten carbide is often used in high-demand applications requiring durability and longevity.
1. Superior Hardness
Tungsten carbide is significantly harder than steel, ranking close to diamonds on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. This makes it exceptionally wear-resistant, ideal for drilling in abrasive environments where tools are subjected to constant friction and wear.
2. Longevity and Durability
The durability of tungsten carbide tools is unparalleled. They often outlast steel counterparts, reducing the frequency of tool replacements. This longevity translates to lower downtime and maintenance costs, making tungsten carbide a cost-effective option in the long run.
3. Resistance to Corrosion
Tungsten carbide is highly resistant to corrosion and oxidation, even at high temperatures. This property is crucial in drilling environments exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme conditions, ensuring the tools maintain their integrity and performance over time.
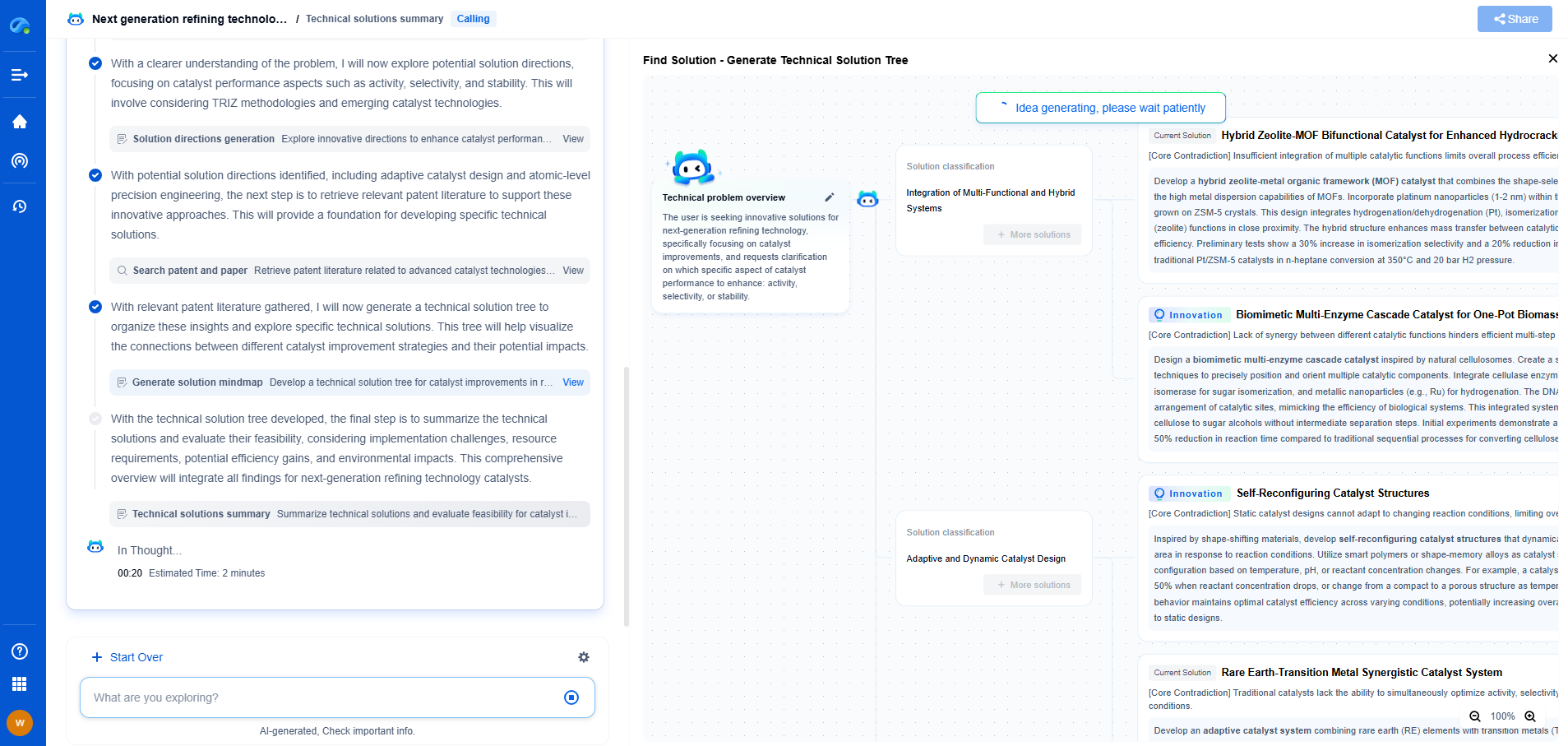
Comparative Analysis: Steel vs. Tungsten Carbide
When comparing steel and tungsten carbide for wear-resistant drilling tools, several factors come into play. The choice between the two often depends on the specific requirements of the drilling operation.
1. Application Suitability
For applications involving extreme hardness and abrasive conditions, tungsten carbide is the superior choice due to its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. Conversely, steel is better suited for general-purpose drilling where cost and toughness are primary considerations.
2. Cost Implications
While tungsten carbide tools have a higher upfront cost, their durability often results in lower operational costs over time due to reduced replacement frequency. Steel tools, while cheaper initially, may require more frequent replacements, impacting long-term expenses.
3. Manufacturing and Design Flexibility
Steel offers greater flexibility in terms of manufacturing and design. It can be easily machined and modified to meet specific requirements, whereas tungsten carbide is more challenging to work with due to its hardness.
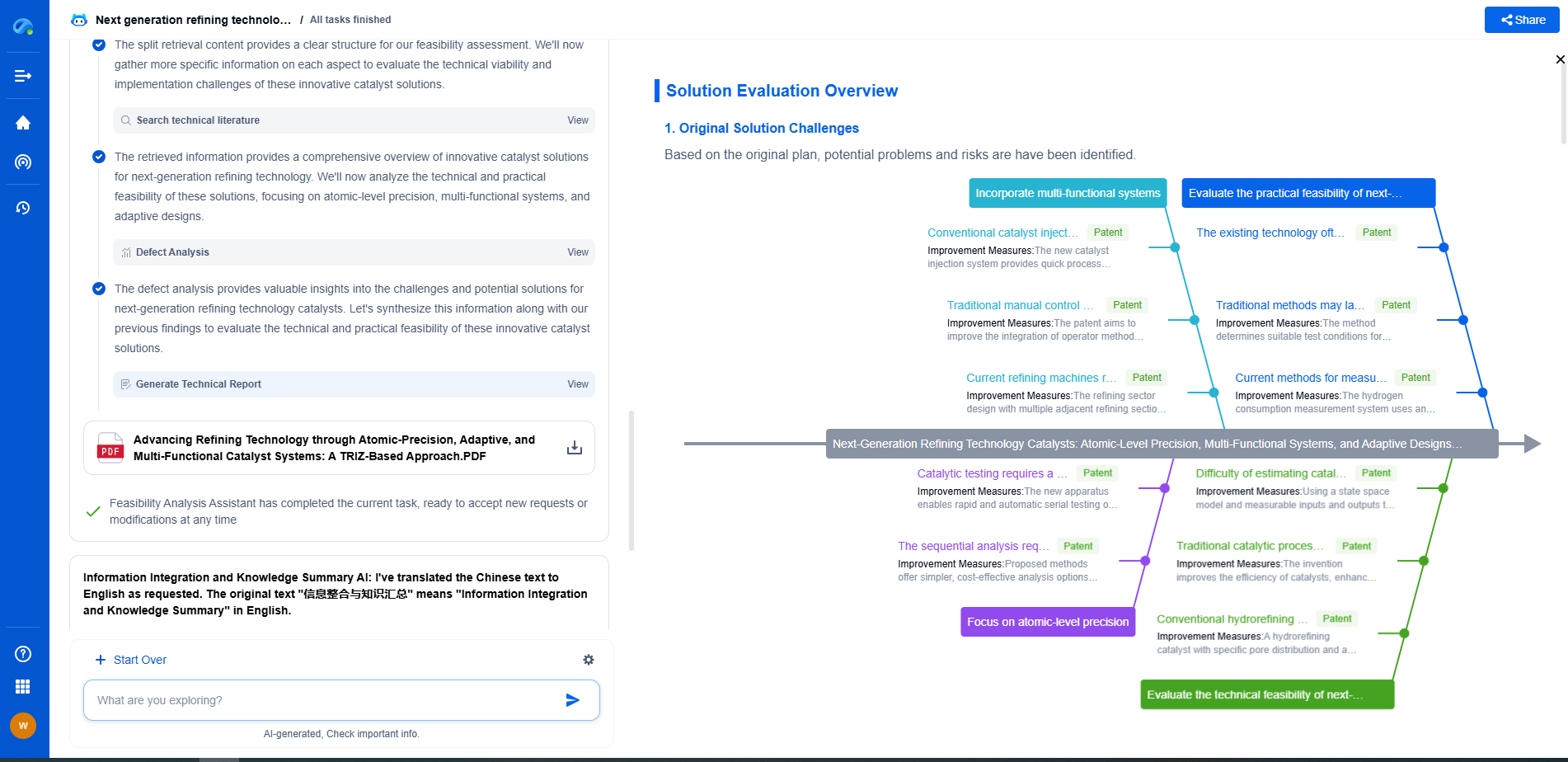
Conclusion
Both steel and tungsten carbide have their distinct advantages as materials for wear-resistant drilling tools. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the application, budget considerations, and the operational environment. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each material can help make informed decisions, optimizing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of drilling operations. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on balancing these factors to meet the demands of the task at hand.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com