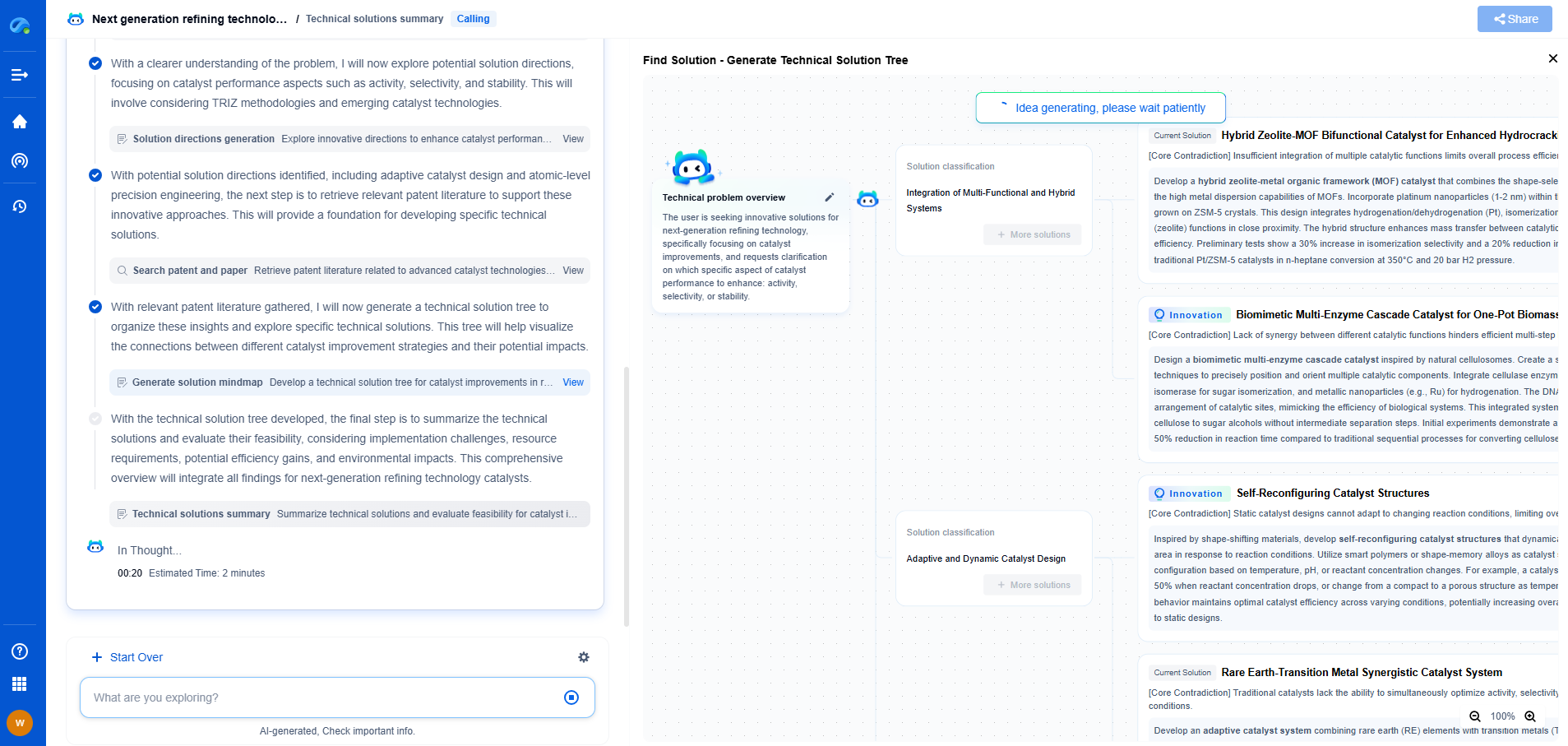
Thin-Film vs. Crystalline Solar Panels: Pros, Cons, and Use Cases
JUL 22, 2025 |
The quest for renewable energy solutions has led to significant advancements in solar panel technologies. Among the leading types, thin-film and crystalline solar panels have emerged as popular choices for different applications. Each type has its unique advantages and limitations, making them suitable for specific use cases. In this article, we will delve into the pros, cons, and typical applications of thin-film and crystalline solar panels, helping you make informed decisions for your solar energy needs.
Understanding Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are created by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic materials onto a substrate. The main types of thin-film technologies include amorphous silicon (a-Si), cadmium telluride (CdTe), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS). These panels are known for their flexibility, lightweight nature, and adaptability to various surfaces.
Pros of Thin-Film Solar Panels
1. Flexibility and Versatility: Thin-film panels can be applied to a wide range of surfaces, including those with irregular shapes, making them ideal for unconventional installations, such as curved rooftops or facades.
2. Lightweight: Their lightweight nature makes installation easier and reduces the structural load on buildings, which is particularly beneficial for retrofitting or temporary setups.
3. Better Performance in Low-Light Conditions: Thin-film panels generally perform better in low-light or diffuse-light conditions compared to crystalline panels, making them suitable for regions with frequent overcast weather.
Cons of Thin-Film Solar Panels
1. Lower Efficiency: Thin-film panels typically have lower energy conversion efficiency compared to crystalline panels, requiring more space to produce the same amount of power.
2. Shorter Lifespan: These panels often have a shorter lifespan, which may lead to more frequent replacements and higher long-term costs.
3. Degradation: Some thin-film technologies experience significant degradation over time, affecting their performance and reliability.
Understanding Crystalline Solar Panels
Crystalline solar panels are made from silicon and are divided into two main categories: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. These panels are known for their high efficiency and durability, making them the most widely used solar technology today.
Pros of Crystalline Solar Panels
1. High Efficiency: Crystalline panels are known for their high energy conversion efficiency, meaning they can generate more power from a smaller surface area.
2. Longevity: They have a longer lifespan compared to thin-film panels, often lasting 25 years or more with minimal degradation.
3. Proven Track Record: With decades of development and usage, crystalline panels have a proven track record of reliability and performance.
Cons of Crystalline Solar Panels
1. Rigidity: These panels are rigid and not as adaptable to non-flat surfaces, limiting their use in certain applications.
2. Heavier: Crystalline panels are typically heavier, which can complicate installation and increase the structural load on buildings.
3. Higher Initial Cost: While their efficiency is higher, the initial cost of crystalline panels is generally greater than that of thin-film options.
Use Cases for Thin-Film Solar Panels
Due to their flexibility and lightweight nature, thin-film solar panels are often used in applications where traditional panels may be unsuitable. They are ideal for:
1. Large-scale Solar Farms: In projects where land area is not a constraint, the lower efficiency of thin-film panels can be offset by installing more panels.
2. Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV): Their adaptability makes thin-film panels perfect for integration into building materials like windows, roofs, and facades.
3. Portable and Mobile Applications: Their lightweight and flexible nature makes them suitable for portable solar solutions, such as backpacks, tents, and vehicles.
Use Cases for Crystalline Solar Panels
Crystalline solar panels are preferred for applications where high efficiency and reliability are crucial. Common use cases include:
1. Residential Rooftops: The high efficiency and long lifespan of crystalline panels make them ideal for residential installations where space is limited.
2. Commercial and Industrial Roofs: Businesses seeking to maximize energy production with limited roof space often choose crystalline panels for their projects.
3. Off-grid Systems: For off-grid applications where reliability and maximum energy output are essential, crystalline panels are often the preferred choice.
Conclusion
The decision between thin-film and crystalline solar panels depends largely on the specific requirements of your project. Thin-film panels offer flexibility and versatility, making them ideal for unconventional installations and large-scale projects where land is abundant. On the other hand, crystalline panels provide high efficiency and reliability, making them suitable for space-constrained installations and applications demanding long-term performance. By understanding the characteristics of each panel type, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your energy needs and project goals.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com