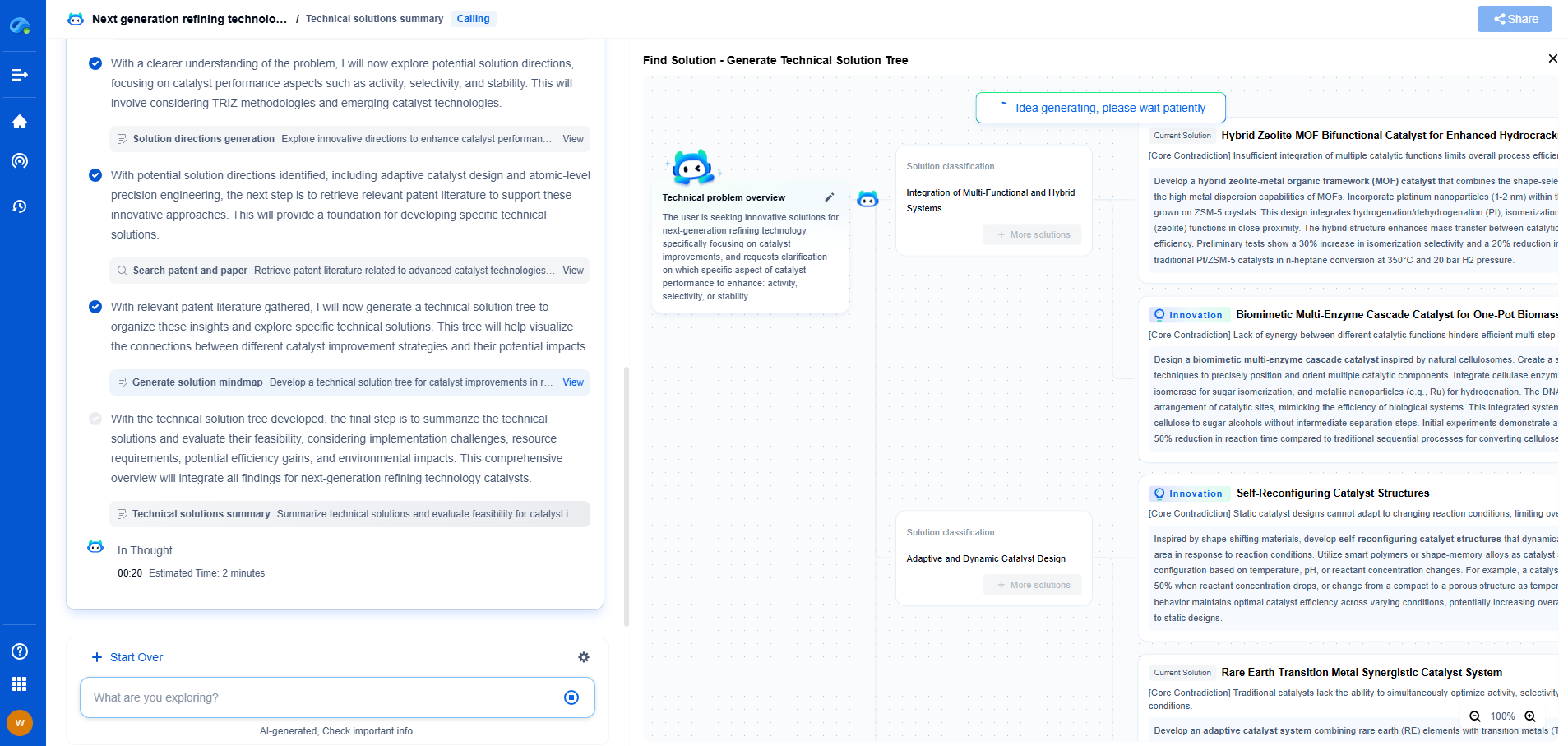
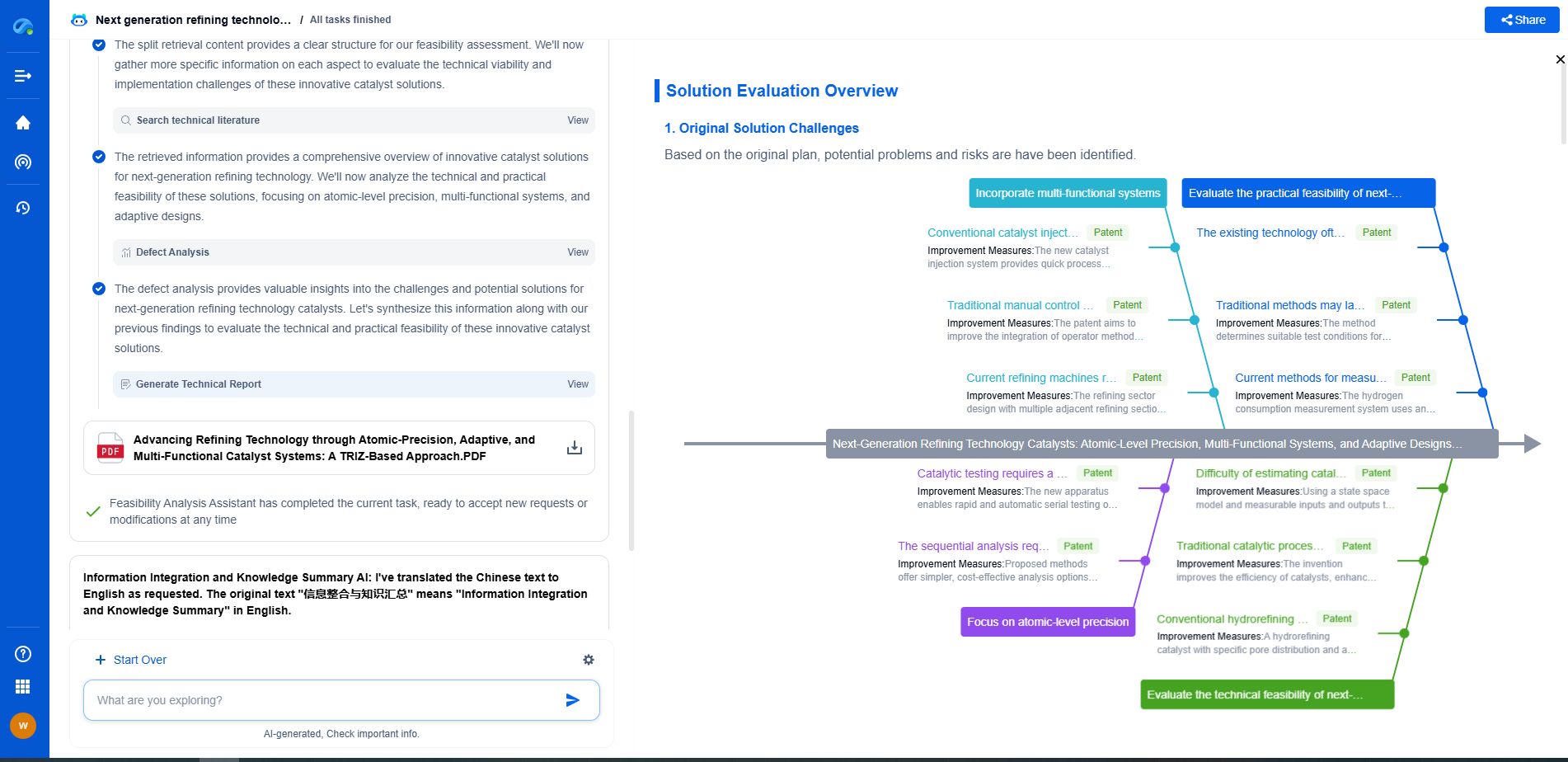
Topological Data Analysis (TDA): Persistent Homology for Detecting Model Overfitting
JUN 26, 2025 |
Topological Data Analysis (TDA) is a rapidly emerging field that leverages concepts from topology, the mathematical study of shapes and spaces, to analyze complex datasets. Unlike traditional methods that focus on individual data points, TDA considers the overall shape of data, which can reveal insights into the structure and features that are not easily captured by conventional techniques. Central to TDA is the concept of persistent homology, a tool that allows us to study the multi-scale topology of data.
What is Persistent Homology?
Persistent homology is a computational method used within TDA to compute topological features of data across various spatial resolutions. It involves building a series of simplicial complexes at different scales, which can be thought of as higher-dimensional generalizations of graphs. By examining how these complexes change as the scale varies, persistent homology identifies features such as connected components, loops, and voids that persist across multiple scales. These features are quantified using persistence diagrams or barcodes, which provide a concise summary of the data's topological structure.
Persistent Homology in Machine Learning
In the context of machine learning, persistent homology offers a novel approach to understanding the behavior of models, particularly in the realm of model evaluation and diagnostics. Traditional metrics, like accuracy or loss, often fail to capture the subtleties of model performance, especially when it comes to issues like overfitting. Overfitting occurs when a model learns the noise in the training data rather than the underlying pattern, resulting in poor generalization to new data.
Detecting Model Overfitting with Persistent Homology
One of the key challenges in machine learning is detecting and mitigating overfitting. Persistent homology can play a crucial role in this regard by providing a topological perspective. When a model is overfitting, it typically captures too much detail, reflecting noise in the training data rather than the true structure. By applying persistent homology to the model's decision boundary or feature space, we can observe these effects in terms of topological complexity.
For instance, a model that fits the training data too closely might exhibit a large number of short-lived topological features, which correspond to the noise it has captured. Conversely, a well-generalized model will likely show fewer, longer-lived topological features, indicating that it captures the essential structure of the data. By comparing the persistence diagrams of different models, we can assess the level of overfitting and guide model selection or hyperparameter tuning.
Practical Applications and Examples
The use of persistent homology for detecting overfitting is not merely theoretical but has practical implications. In fields such as image recognition, natural language processing, and bioinformatics, where datasets are often high-dimensional and complex, TDA can provide critical insights. For example, in image classification tasks, persistent homology can help in analyzing the decision boundaries of convolutional neural networks, offering a deeper understanding of how these models generalize beyond the training data.
Researchers have also employed TDA to understand the latent space in generative models like Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). By examining the topological structure of these latent spaces, persistent homology can identify whether the models are generating realistic or overfitted representations of the data.
Conclusion: The Future of TDA in Machine Learning
As machine learning models continue to grow in complexity and application, the need for robust evaluation methodologies becomes ever more critical. Topological Data Analysis, and persistent homology in particular, offers powerful tools for gaining a deeper understanding of model behavior, especially in detecting overfitting. By incorporating these techniques, data scientists and researchers can enhance their models' reliability and performance, leading to more accurate and generalizable predictions. As TDA techniques further develop and become more accessible, we can expect their integration into mainstream machine learning workflows, paving the way for more nuanced and sophisticated data analysis strategies.
Unleash the Full Potential of AI Innovation with Patsnap Eureka
The frontier of machine learning evolves faster than ever—from foundation models and neuromorphic computing to edge AI and self-supervised learning. Whether you're exploring novel architectures, optimizing inference at scale, or tracking patent landscapes in generative AI, staying ahead demands more than human bandwidth.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
👉 Try Patsnap Eureka today to accelerate your journey from ML ideas to IP assets—request a personalized demo or activate your trial now.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com