Trends in Pipeline Transport of Ammonia for Energy Storage
JUN 20, 2025 |
Introduction to Pipeline Transport of Ammonia
In recent years, the global energy sector has witnessed a paradigm shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. Amidst this transition, ammonia has emerged as a promising candidate for energy storage and transport due to its high energy density and carbon-free nature. As countries strive to achieve climate targets, the role of ammonia in the energy landscape continues to rise, and pipeline transport of ammonia has become a focal point for innovation and development.
Advantages of Ammonia as an Energy Carrier
Ammonia, composed of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen atoms (NH3), serves as a potential energy carrier with several advantages. Firstly, it is carbon-free, meaning its use does not contribute to CO2 emissions, aligning with global climate goals. Secondly, ammonia has a higher energy density compared to hydrogen, which makes it easier to transport and store. This positions ammonia as an attractive option for renewable energy storage and transportation, particularly in situations where hydrogen may face logistical challenges.
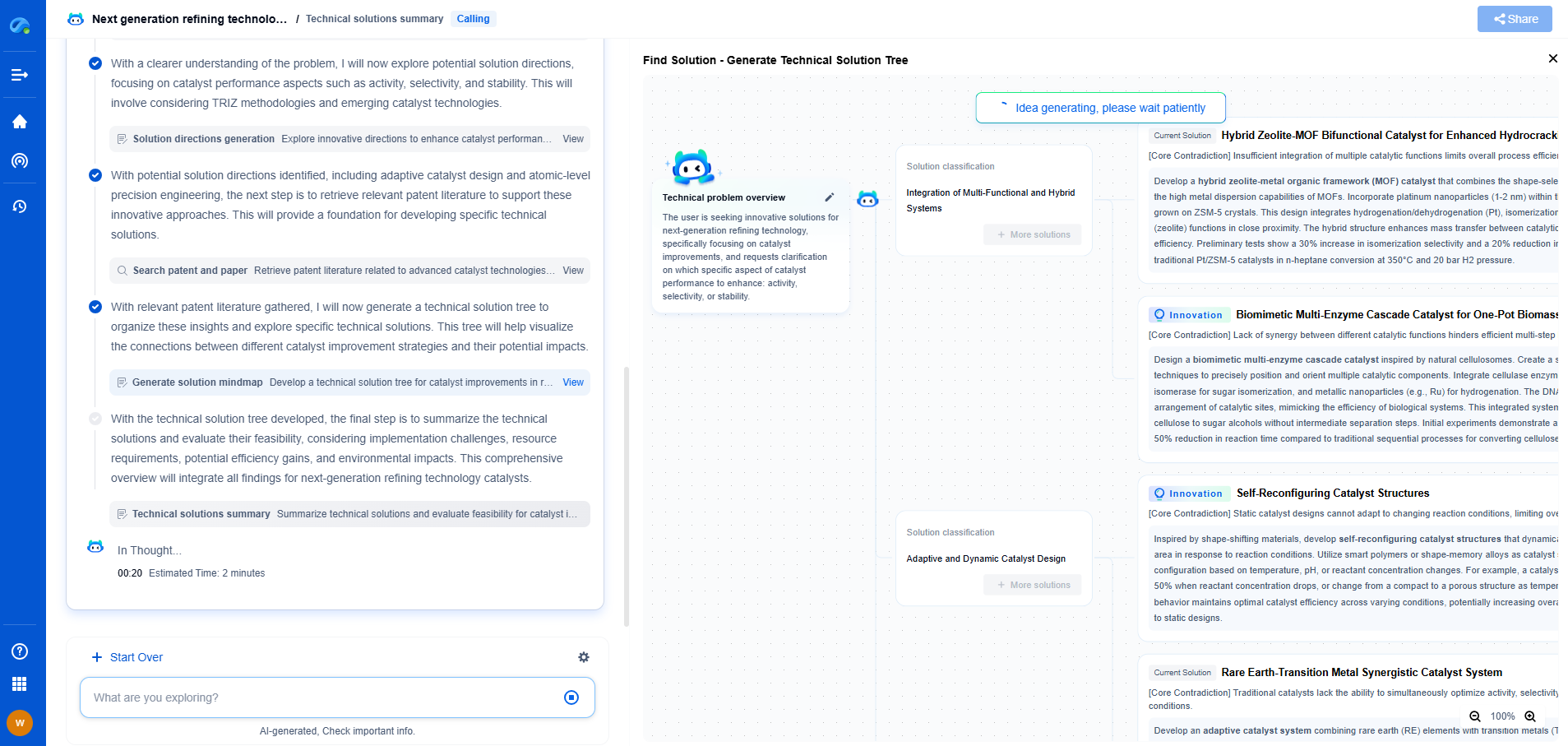
Current Trends in Pipeline Transport of Ammonia
The development of ammonia pipelines is gaining traction as industries recognize the need for reliable and efficient transportation methods. Traditional routes have relied on shipping for international distribution, but pipelines offer a more direct and cost-effective solution for large-scale movement. Recent advancements in materials and engineering have improved the safety and feasibility of ammonia pipelines, making them a viable alternative to other transportation methods.
Innovations in Pipeline Infrastructure
One of the critical areas of innovation in ammonia transport is the enhancement of pipeline infrastructure. Modern pipelines are being designed to withstand the specific chemical properties of ammonia, including its corrosive nature. High-grade alloys and coatings are employed to ensure the longevity and integrity of the pipelines. Furthermore, smart monitoring technologies are being integrated into pipeline systems to provide real-time data on flow rates, pressure levels, and potential leakages, thus enhancing safety and operational efficiency.
Global Developments and Collaborations
Several countries are embarking on ambitious projects to establish ammonia pipeline networks. In Europe, initiatives are underway to connect key industrial hubs with ammonia supply chains, fostering collaboration across borders. Similarly, in Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea are investing in ammonia infrastructure to support their energy transition goals. These developments are being bolstered by international partnerships that aim to standardize regulations and promote best practices in ammonia transport.
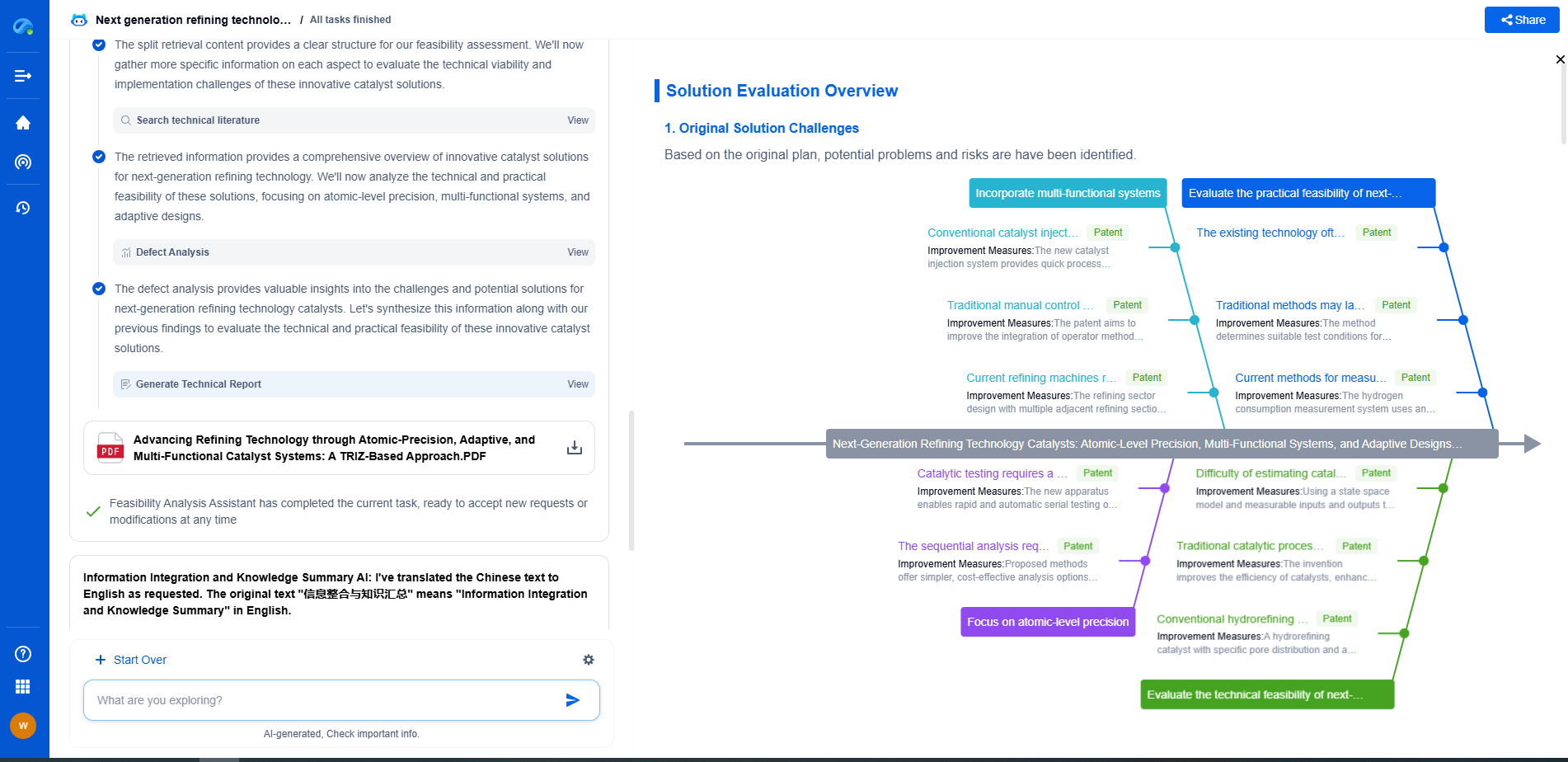
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the potential benefits, pipeline transport of ammonia presents certain challenges. The handling of ammonia requires rigorous safety measures due to its toxicity and potential environmental impact. Establishing comprehensive safety protocols and emergency response strategies is crucial to mitigate risks. Additionally, the economic feasibility of extensive ammonia pipeline networks must be carefully evaluated, taking into account the initial capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the future of ammonia pipeline transport appears promising, given the global momentum towards sustainable energy solutions. As technology evolves and infrastructure expands, ammonia could play a significant role in bridging the gap between renewable energy production and consumption. Moreover, ammonia’s versatility in energy applications—from fuel cells to power generation—underscores its potential as a cornerstone of the future energy system.
Conclusion
The pipeline transport of ammonia represents a pivotal trend in the ongoing quest for renewable energy solutions. By leveraging its inherent advantages and overcoming associated challenges, ammonia can become a key player in the energy transition. As industries and governments continue to invest in infrastructure and innovation, ammonia pipelines will likely become an integral component of the global energy landscape, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
---
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com