Triaxial Accelerometers vs. Uniaxial: Which One Should You Use?
JUL 16, 2025 |
Accelerometers are essential tools in various industries, ranging from automotive to consumer electronics, enabling the measurement of acceleration forces. These devices help in determining orientation, detecting motion, and even enhancing user experience in gadgets. There are two main types of accelerometers: triaxial and uniaxial. Choosing the right one can significantly impact the performance and accuracy of your application.
**What is a Uniaxial Accelerometer?**
A uniaxial accelerometer measures acceleration along a single axis. This simplicity makes it cost-effective and straightforward, especially for applications that only need acceleration data in one direction. Common uses include basic motion detection, structural health monitoring, and applications where space is constrained, and only single-axis data is required.
The advantage of uniaxial accelerometers lies in their simplicity and lower cost. They are easier to install and integrate, particularly when the application demands focus on specific directional measurements. However, their limitation is evident in applications requiring a comprehensive understanding of motion in multiple directions.
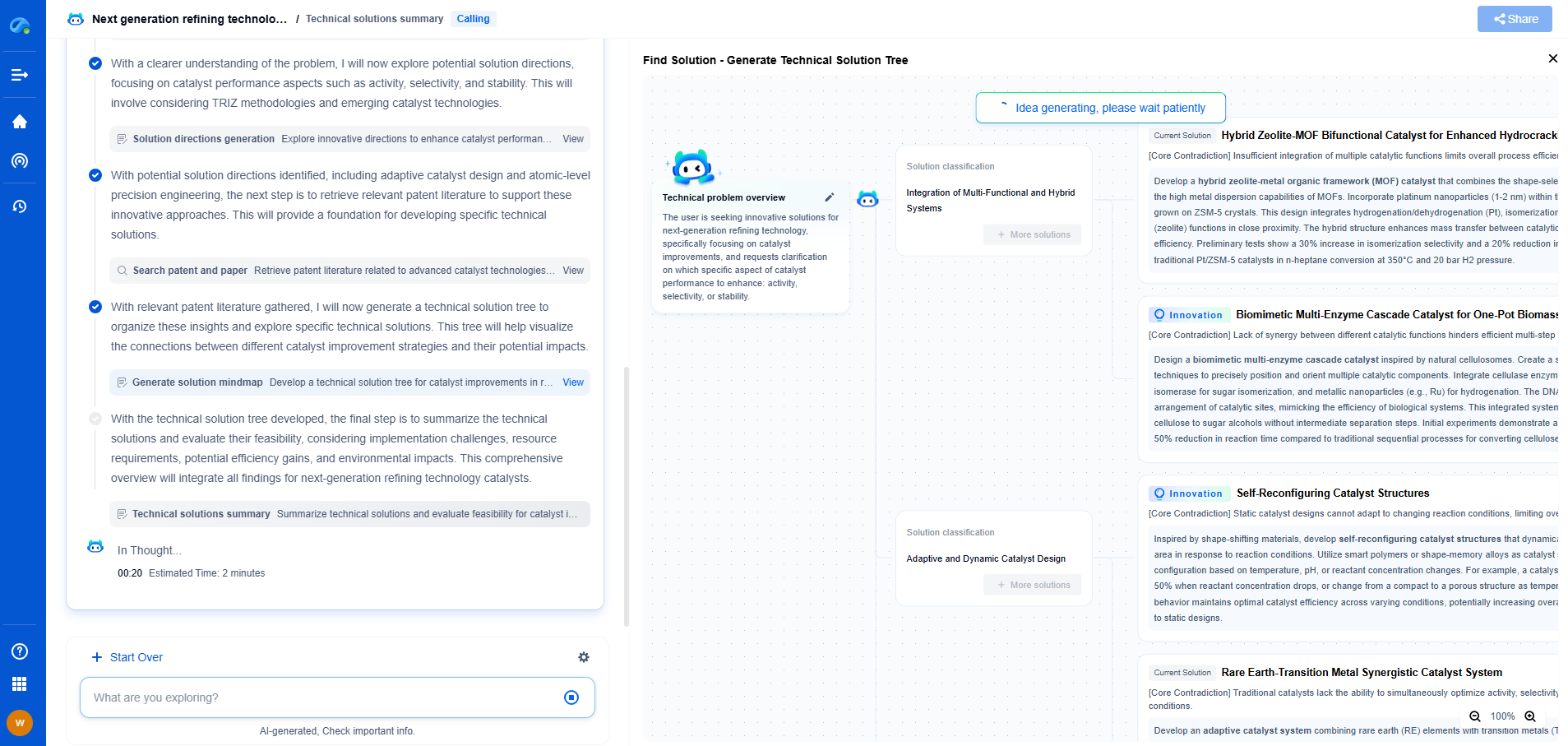
**Exploring Triaxial Accelerometers**
Triaxial accelerometers measure acceleration along three perpendicular axes: X, Y, and Z. This capability allows for a more comprehensive analysis of motion, making them indispensable in applications requiring detailed motion tracking and orientation detection.
Triaxial accelerometers find their usage in more complex applications such as smartphones, wearable technology, and advanced industrial equipment. They provide richer data, enabling more robust analysis and decision-making. Despite their higher cost compared to uniaxial accelerometers, the depth of information they provide justifies the investment in applications where multidirectional data is necessary.
**When to Use Uniaxial Accelerometers**
Uniaxial accelerometers are ideal for situations where only a single plane of motion needs to be monitored. They are suitable for cost-sensitive projects or applications with limited space for installation. If your application involves straightforward motion detection, such as monitoring vibrations in machinery along one axis or tracking linear movement in a constrained path, a uniaxial accelerometer might be the appropriate choice.
**When to Opt for Triaxial Accelerometers**
On the other hand, triaxial accelerometers excel in scenarios demanding detailed spatial analysis. They are perfect for applications that require high precision and the ability to track movement across multiple planes. Whether it's monitoring athletes' movements in sports science, enhancing user experiences in mobile devices, or enabling more accurate inertial navigation systems, the triaxial accelerometer is the go-to solution.
**Comparing Advantages and Disadvantages**
The primary advantage of uniaxial accelerometers is their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them easier to implement for basic tasks. However, their major limitation is the inability to provide comprehensive motion analysis.
Triaxial accelerometers, while more expensive, offer a complete picture of movement, making them indispensable for applications necessitating detailed orientation and motion data. The increased complexity in data processing and higher cost are notable drawbacks but are often outweighed by their capabilities in sophisticated applications.
**Conclusion: Making the Right Choice**
Choosing between a triaxial and a uniaxial accelerometer boils down to understanding the specific needs of your application. Consider the complexity of motion you need to measure and the level of detail required in your data. For projects with straightforward requirements and budget constraints, uniaxial accelerometers provide a practical solution. Conversely, if your application demands multidirectional analysis and precision, investing in a triaxial accelerometer is worthwhile.
Ultimately, the decision should align with your project's objectives, budget, and technical requirements. Both types of accelerometers have their strengths, and choosing the right one ensures optimal performance and accuracy in your applications.
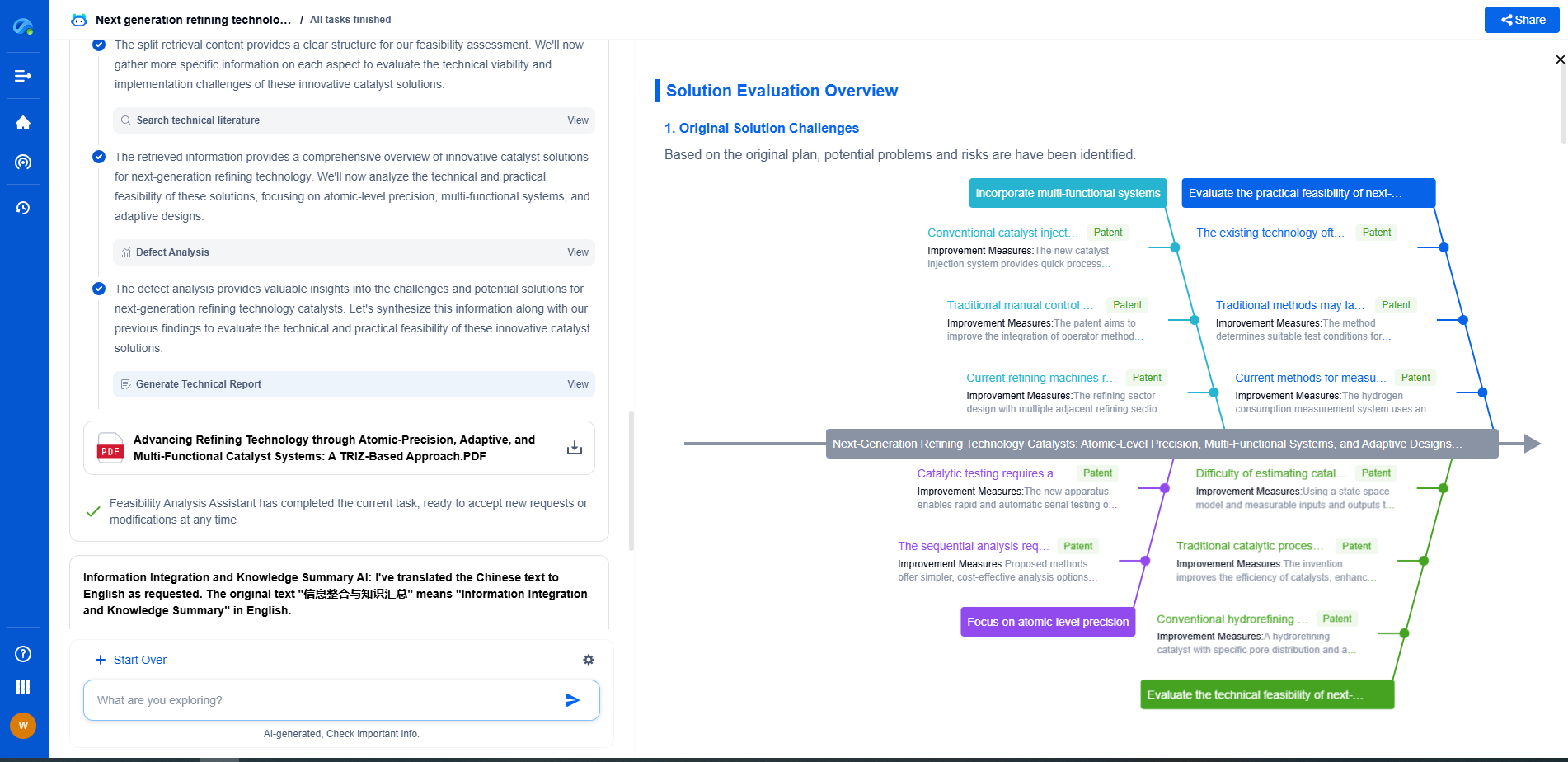
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com