Troubleshooting Gear Grinding Errors: Burn Marks, Pitting & More
JUL 2, 2025 |
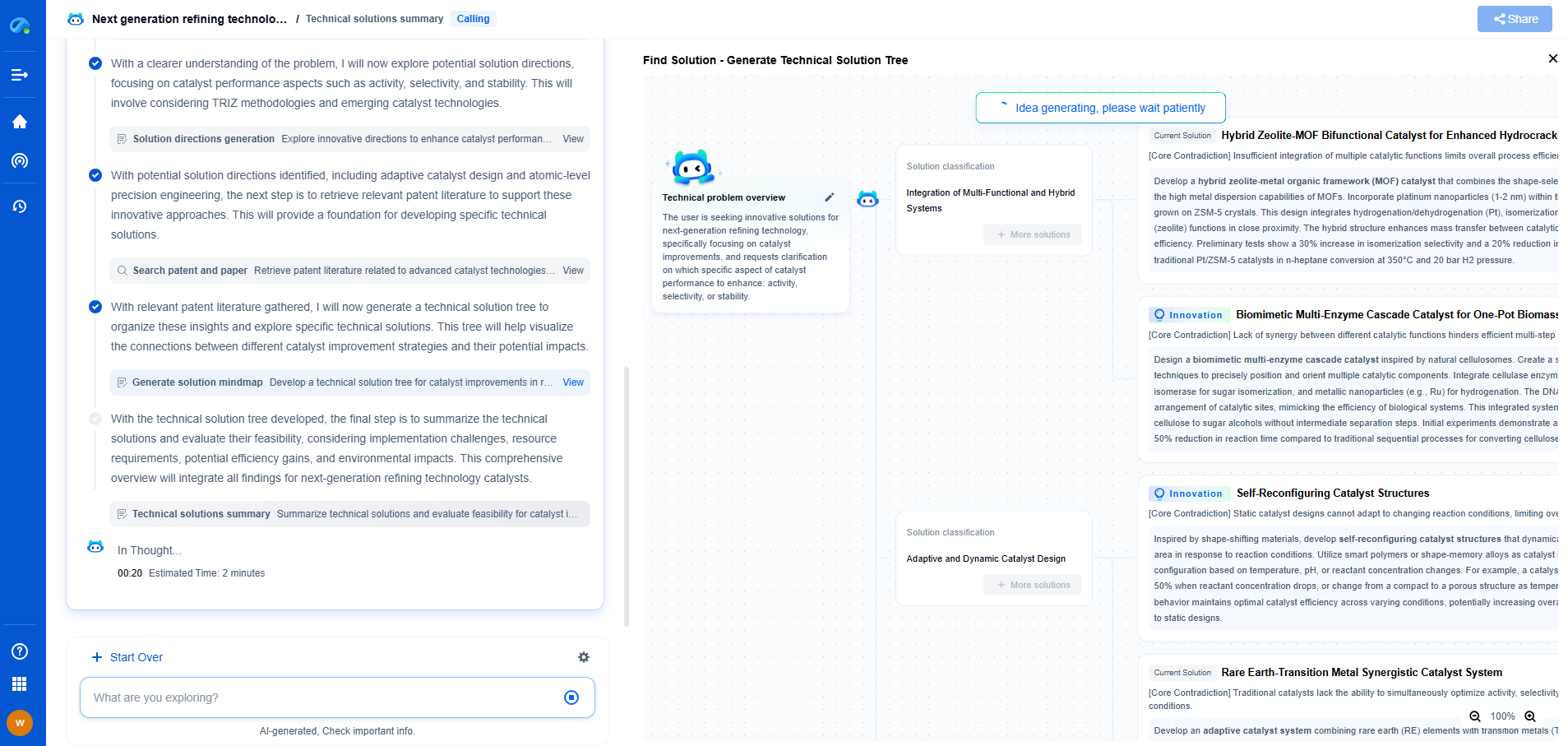
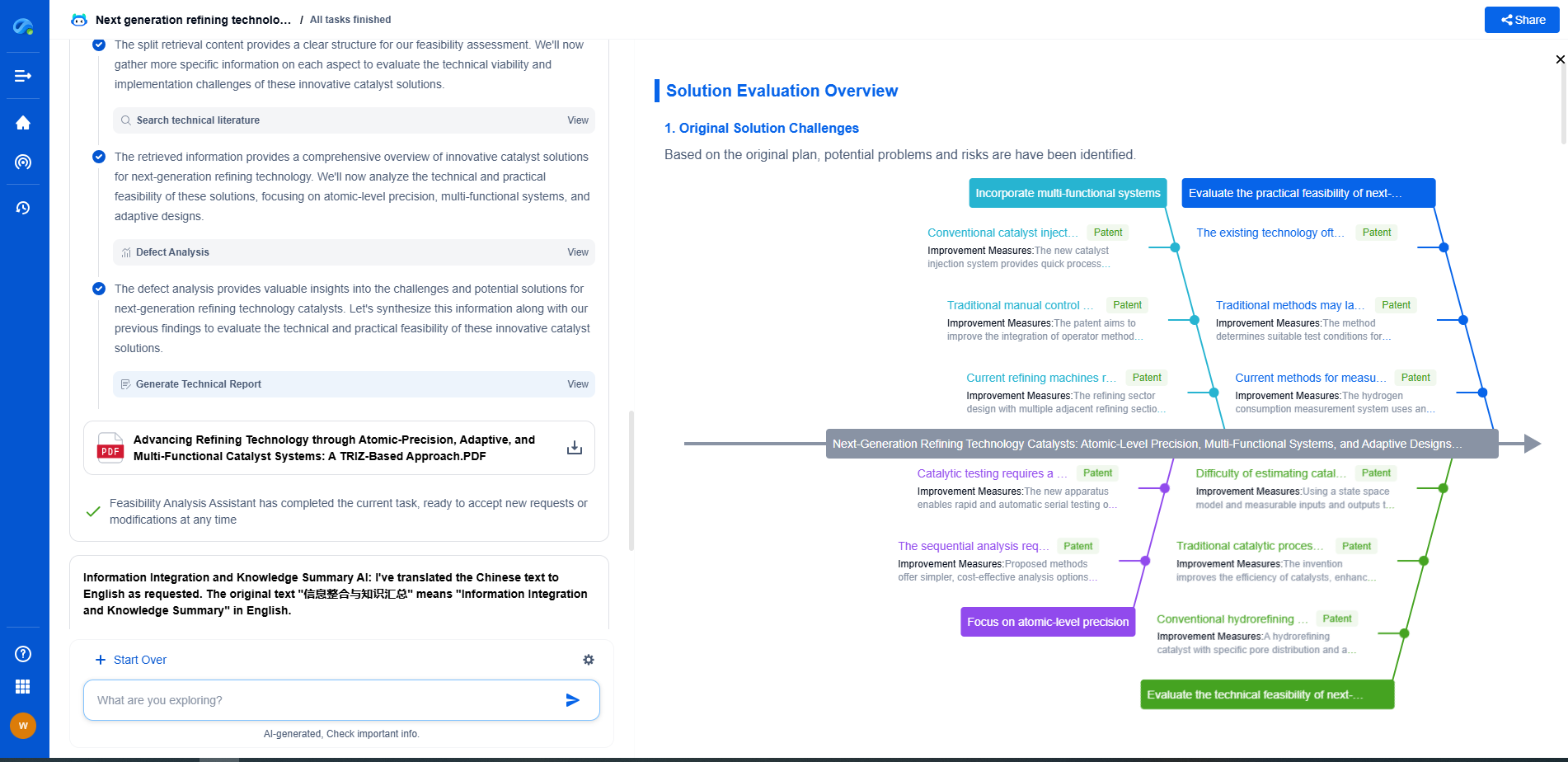
Gear grinding is a critical process in the manufacturing of gears, which ensures precision and smooth operation in various machinery systems. However, like any manufacturing process, it is prone to errors. Common issues such as burn marks, pitting, and more can arise, leading to compromised gear quality and performance. Understanding these errors and knowing how to troubleshoot them is essential for maintaining efficient operations. This article delves into the common gear grinding errors, their causes, and effective troubleshooting methods.
Burn Marks in Gear Grinding
Burn marks are a frequent issue in gear grinding, often resulting from excessive heat generation during the process. These marks not only affect the aesthetic quality of the gears but can also lead to structural weaknesses. Burn marks are typically caused by incorrect grinding parameters, such as unsuitable wheel speed, inappropriate coolant flow, or excessive pressure.
To troubleshoot burn marks, first assess the grinding wheel speed. Ensure that it is set according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Adjusting the speed can help in reducing the friction and heat generation. Next, evaluate the coolant flow rate. Proper coolant application is vital in dissipating heat and preventing burn marks. Ensure that the coolant nozzles are correctly aligned and delivering sufficient flow to the grinding zone. Lastly, consider the grinding pressure. Reducing the pressure can minimize heat build-up, but it should be balanced to maintain the efficiency of the grinding process.
Pitting and Surface Fatigue
Pitting is another common issue in gear grinding. It appears as small, shallow depressions on the gear surface and is usually a result of material fatigue. Pitting can decrease the gear's lifespan and lead to failure if not addressed promptly. Several factors contribute to pitting, including unsuitable grinding techniques, poor material quality, and inadequate lubrication.
To address pitting, begin by examining the grinding technique. Ensure that the correct grinding wheel is used for the specific material and hardness of the gear. Additionally, check the consistency and quality of the material being used. High-quality materials with uniform hardness can significantly reduce the risk of pitting. Lubrication is also crucial; ensure that the lubricant is applied correctly and is suitable for the gear material, as this reduces friction and the likelihood of surface fatigue.
Inconsistent Gear Profiles
Inconsistent gear profiles can lead to improper meshing and increased wear during operation. This error often stems from incorrect machine alignment or issues with the grinding wheel. Variations in the gear profile can cause vibrations, noise, and premature wear in gear systems.
To troubleshoot inconsistent gear profiles, start by inspecting machine alignment. Proper alignment of the grinding machine is essential to achieve uniform gear profiles. Regular calibration and maintenance of the machine can prevent alignment issues. Additionally, evaluate the condition of the grinding wheel. A worn or unbalanced wheel can cause profile irregularities. Regularly dressing the wheel and checking for balance can help maintain consistency in gear profiles.
Chatter Marks and Surface Roughness
Chatter marks are wavy patterns on the gear surface caused by vibrations during grinding. These marks not only affect the surface finish but can also lead to increased noise and reduced component life. Surface roughness, on the other hand, affects the gear's contact performance and may result from inappropriate grinding parameters or a worn grinding wheel.
To reduce chatter marks and improve surface roughness, first ensure that the grinding machine is stable and vibration-free. Check the machine's foundation and mounting for any loose components. Optimizing the grinding parameters, such as wheel speed and feed rate, can also help in minimizing vibrations. For surface roughness, regularly inspect and dress the grinding wheel to maintain its cutting ability and sharpness.
Conclusion
Gear grinding errors like burn marks, pitting, inconsistent profiles, and chatter marks can significantly impact the performance and longevity of gears. Identifying the root causes and implementing effective troubleshooting techniques are crucial steps in maintaining high-quality gear production. Regular monitoring, maintenance, and adjustments of the grinding process play a vital role in preventing these errors and ensuring the reliability of gear systems. By addressing these issues proactively, manufacturers can enhance gear quality, reduce downtime, and improve overall machinery performance.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com