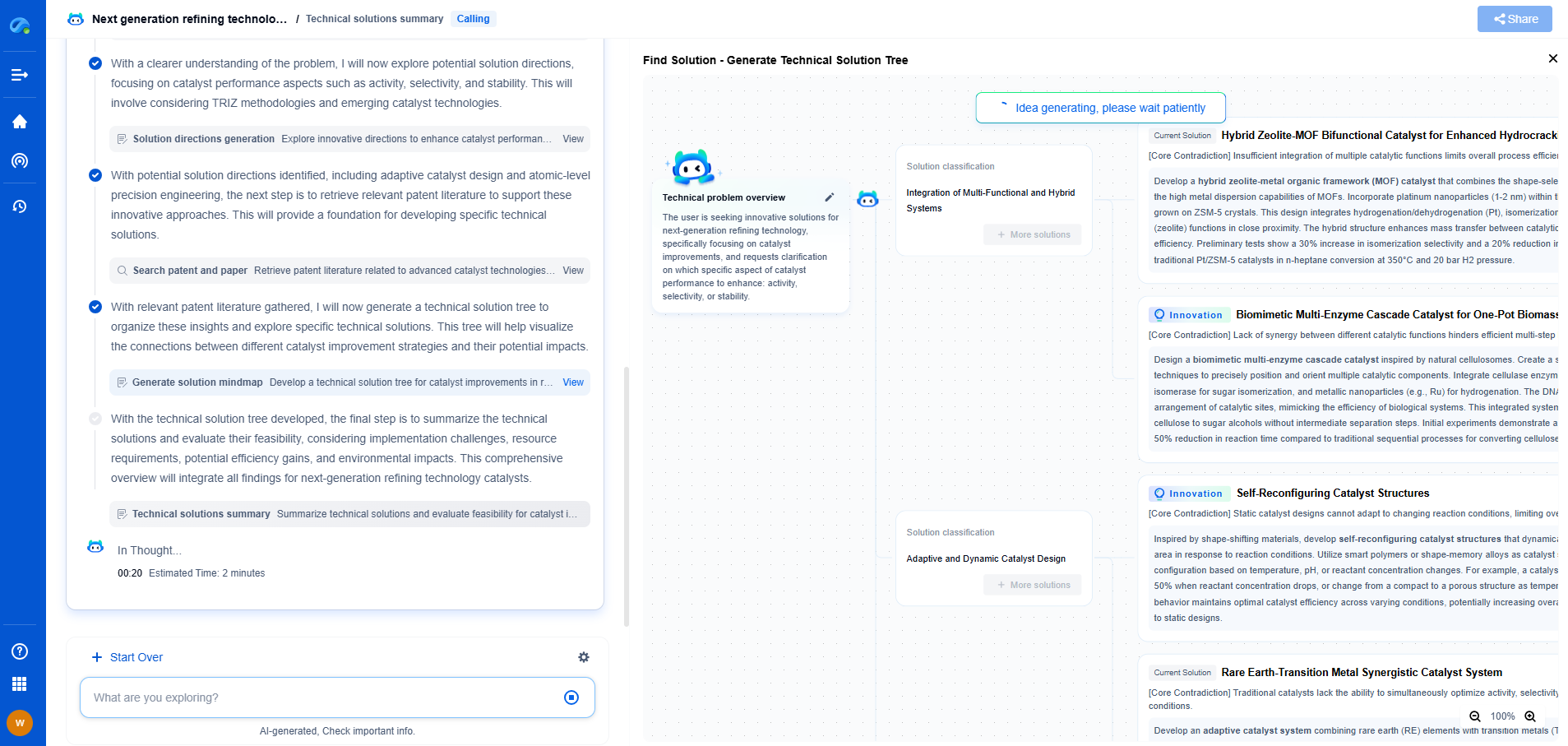
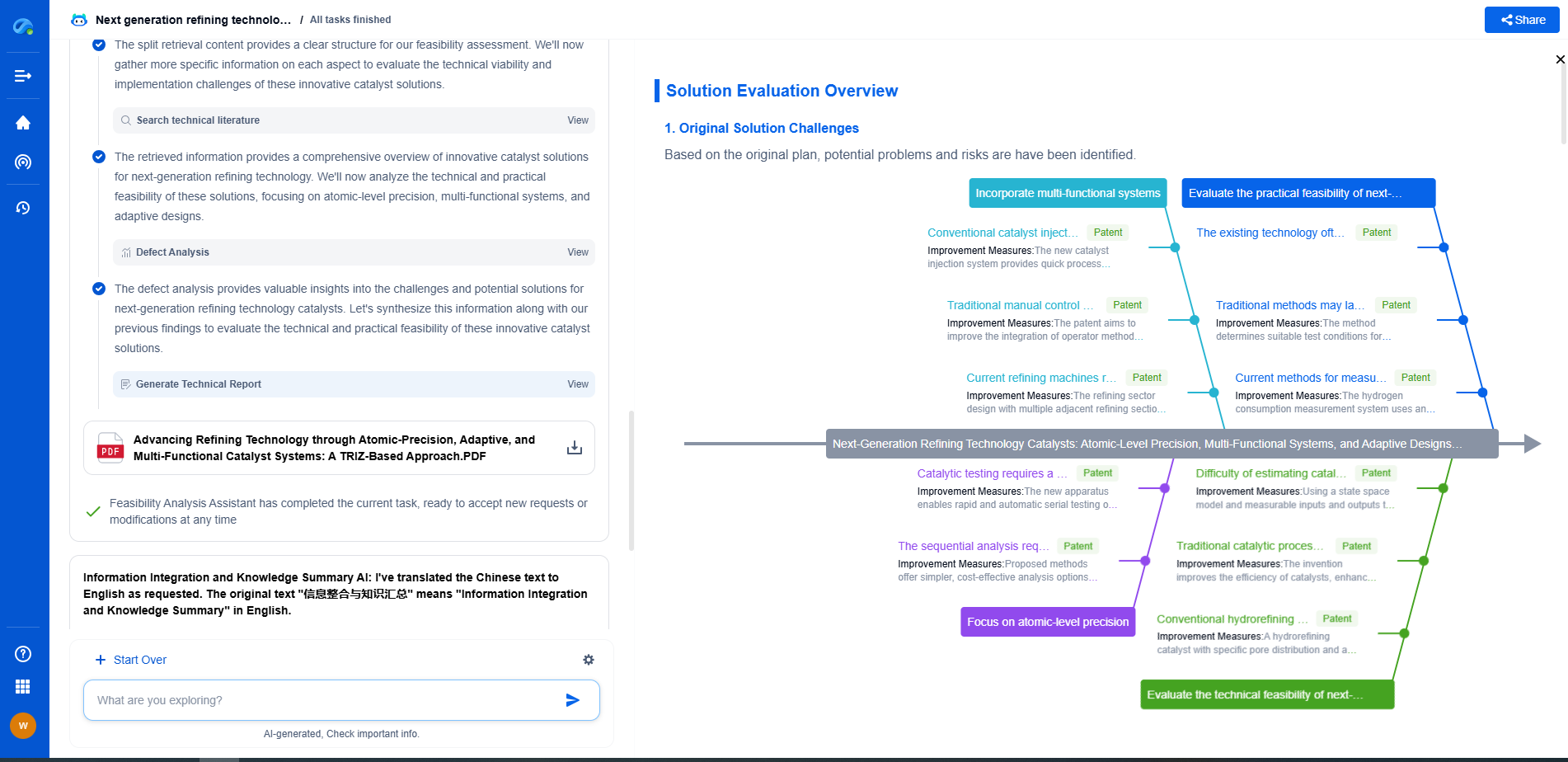
UL 61730 vs. IEC 61730: Global Solar Module Safety Requirements Compared
JUL 22, 2025 |
In the rapidly evolving world of solar energy, safety and reliability are paramount. As solar power systems become more widespread, ensuring the safety of solar modules is critical. Two primary standards guide the safety requirements for solar modules: UL 61730 and IEC 61730. While both serve the same fundamental purpose—ensuring the safety and performance of photovoltaic (PV) modules—they are applied in different regions and exhibit some differences. Understanding these standards is crucial for manufacturers, installers, and stakeholders in the solar industry.
The Purpose of Safety Standards in Solar Modules
Before diving into the specific standards, it's essential to understand why these safety guidelines are necessary. Solar modules are exposed to various environmental conditions, including high temperatures, humidity, mechanical stress, and ultraviolet radiation. These factors can affect the performance and longevity of the modules. Safety standards help ensure that modules can withstand these conditions without posing risks such as electrical shock, fire hazards, or mechanical failure. By adhering to established safety guidelines, manufacturers can produce reliable and durable solar products, ultimately protecting consumers and their investments.
UL 61730: The North American Standard
UL 61730 is a safety standard developed by Underwriters Laboratories (UL), primarily used in North America. It is part of the UL's suite of standards aimed at ensuring the safety and performance of electrical and electronic products. UL 61730 is aligned with the international standard IEC 61730 but includes additional requirements to meet specific North American regulations and market needs.
Key aspects of UL 61730 include:
1. Fire Safety: UL 61730 addresses fire safety requirements to minimize the risk of module ignition and fire spread. This is crucial in regions prone to wildfires or where rooftop solar installations are common.
2. Electrical Safety: The standard specifies requirements for insulation, grounding, and protection against electric shock. These measures ensure that the solar modules operate safely under various conditions.
3. Mechanical Stress: UL 61730 includes tests for mechanical stress to ensure that modules can withstand wind, snow loads, and other physical forces without compromising their structural integrity.
4. Environmental Testing: The standard includes rigorous environmental testing to guarantee that modules perform reliably in diverse climatic conditions.
IEC 61730: The International Standard
IEC 61730 is developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), making it a globally recognized standard. It serves as the basis for solar module safety requirements in many countries worldwide. IEC 61730 emphasizes a systematic approach to safety, ensuring that PV modules are designed and tested to handle typical environmental and operational stresses.
Key aspects of IEC 61730 include:
1. Harmonization: IEC 61730 aims to harmonize safety requirements internationally, facilitating global trade and ensuring consistency across markets.
2. Safety Classes: The standard defines different safety classes based on the intended application, such as residential, commercial, or utility-scale installations. Each class has specific safety requirements tailored to its use scenario.
3. Comprehensive Testing: IEC 61730 includes a broad range of tests, including impact resistance, thermal cycling, damp heat, and more. These tests simulate real-world conditions to verify module performance and durability.
4. Compatibility: The standard considers compatibility with other electrical systems, ensuring that modules operate safely alongside other components in a solar power system.
Comparative Analysis: UL 61730 vs. IEC 61730
While UL 61730 and IEC 61730 share many similarities, their differences are worth noting:
1. Regional Focus: UL 61730 is tailored to North American regulations, whereas IEC 61730 is designed for international applicability. This distinction can affect the certification process for manufacturers targeting different markets.
2. Fire Safety Emphasis: UL 61730 places a stronger emphasis on fire safety, reflecting the specific concerns and regulatory requirements in North America.
3. Testing Procedures: While both standards include rigorous testing procedures, there may be variations in the specifics of the tests conducted, reflecting regional differences in environmental conditions and safety priorities.
4. Market Access: Compliance with IEC 61730 can ease entry into international markets, while UL 61730 certification is often essential for the North American market. Manufacturers may choose to certify modules under both standards to maximize their market reach.
Conclusion: Navigating the Path to Solar Safety
Understanding the nuances of UL 61730 and IEC 61730 is crucial for stakeholders in the solar industry. While both standards aim to ensure the safety and reliability of solar modules, their regional focus and specific requirements necessitate careful consideration by manufacturers and installers. By adhering to these standards, the solar industry can continue to grow sustainably, providing safe and efficient renewable energy solutions worldwide.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com