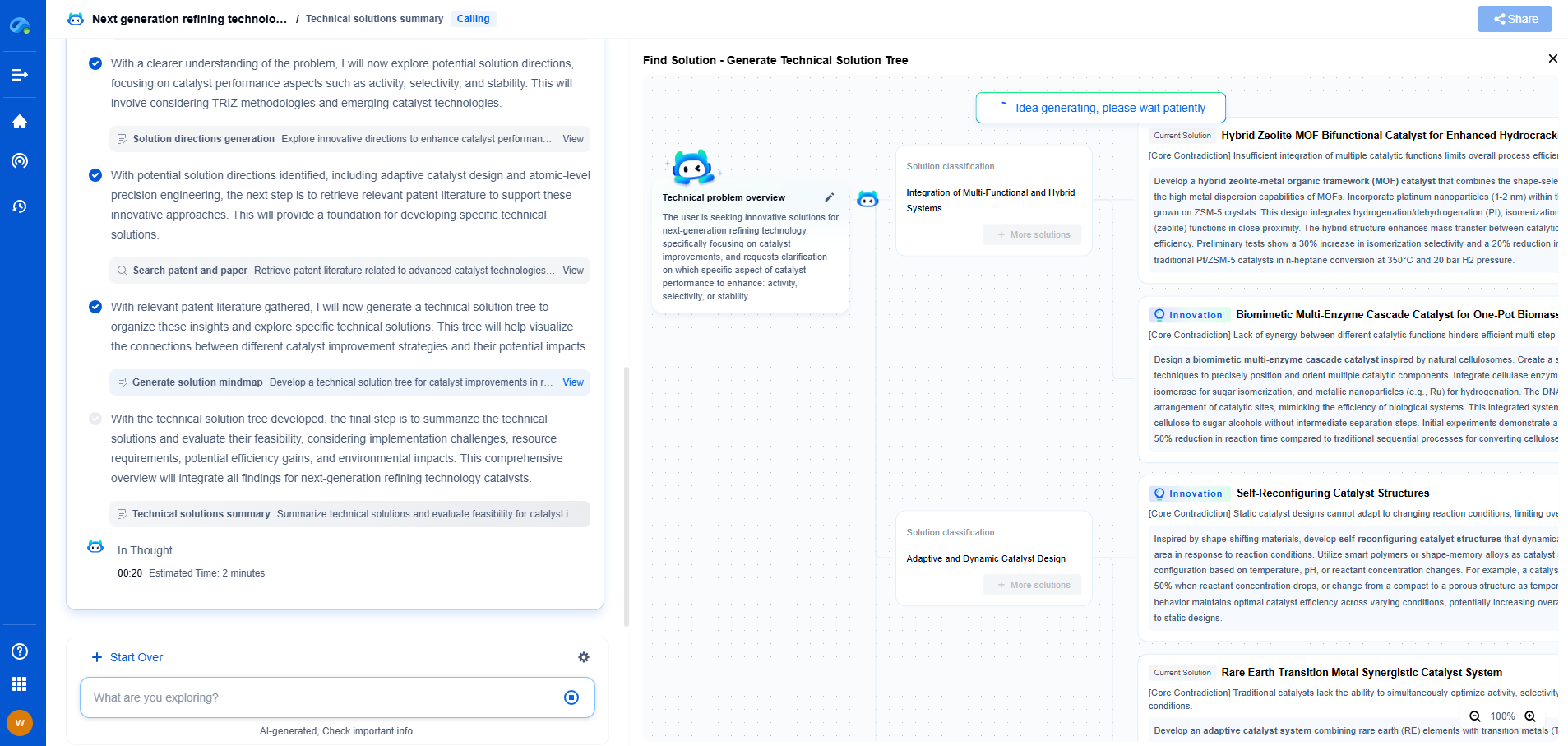
Variable Capacitors vs. Fixed Capacitors: When to Use Each?
JUL 9, 2025 |
Capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, serving various critical functions such as energy storage, signal filtering, and tuning circuits. Their primary characteristic is their ability to store and release electrical energy, which makes them invaluable in different applications. Broadly, capacitors can be categorized into two types: variable capacitors and fixed capacitors. Each type has its specific uses, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding when to use each type is crucial for designing effective electronic systems.
Fixed Capacitors: Reliability and Consistency
Fixed capacitors have a set capacitance value that cannot be changed during operation. This predetermined capacitance makes them ideal for applications where a stable and unchanging capacitance is required. Common types of fixed capacitors include ceramic, electrolytic, tantalum, and film capacitors, each serving different circuit needs based on their properties.
**Applications of Fixed Capacitors**
1. **Power Supply Smoothing**: Fixed capacitors are often used in power supply circuits to smooth out voltage fluctuations. Electrolytic capacitors, for instance, are ideal for filtering out the noise in DC power supplies due to their high capacitance values.
2. **Signal Filtering**: In audio and radio frequency circuits, fixed capacitors act as filters, blocking certain frequencies while allowing others to pass, thus ensuring clear signal transmission.
3. **Timing Circuits**: Fixed capacitors can be used in combination with resistors to create timing circuits, such as those found in oscillators and timers.
4. **Energy Storage**: They are also employed in applications requiring a steady energy release, such as in flash photography or to provide backup power in small devices.
**Advantages of Fixed Capacitors**
- **Stability**: Their fixed capacitance value offers stability and predictability in electronic circuits.
- **Cost-effective**: Generally cheaper than variable capacitors, making them suitable for mass production.
- **Variety**: Available in numerous capacitance values and types, offering versatility for different needs.
Variable Capacitors: Flexibility in Tuning
Unlike fixed capacitors, variable capacitors can change their capacitance value during operation. This adjustability makes them indispensable in applications needing precise tuning and calibration. Variable capacitors are commonly used in radio frequency applications, such as tuning circuits in radios.
**Applications of Variable Capacitors**
1. **Tuning Circuits**: They are extensively used in radio receivers and transmitters to tune circuits to the desired frequency. By adjusting the capacitance, users can select different frequency channels.
2. **Antenna Matching**: Variable capacitors help match antenna impedance to transmitter or receiver circuitry, maximizing signal strength and clarity.
3. **Oscillators**: In oscillator circuits, variable capacitors allow for frequency adjustment, aiding in generating signals with varying frequencies.
4. **Experimentation and Prototyping**: They offer flexibility in experimental setups and prototypes, where circuit parameters need frequent adjustments.
**Advantages of Variable Capacitors**
- **Adjustability**: Their ability to vary capacitance makes them ideal for applications requiring fine-tuning.
- **Versatility**: Suitable for a range of applications from simple tuning to complex impedance matching.
- **Convenience**: Allow real-time adjustments without the need to modify the entire circuit.
Choosing Between Variable and Fixed Capacitors
When deciding between variable and fixed capacitors, consider the specific needs of your application. For stable, cost-effective solutions where capacitance does not need adjustment, fixed capacitors are the better choice. However, if your project requires frequent tuning and adaptability, particularly in RF applications, variable capacitors are indispensable.
Ultimately, both types of capacitors have their place in electronics, each fulfilling roles that complement the other. Understanding their specific characteristics and applications ensures efficient and effective circuit designs, enhancing functionality and performance.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com