Vibration Isolators: Rubber vs. Spring vs. Air Mounts for Different Frequencies
JUL 16, 2025 |
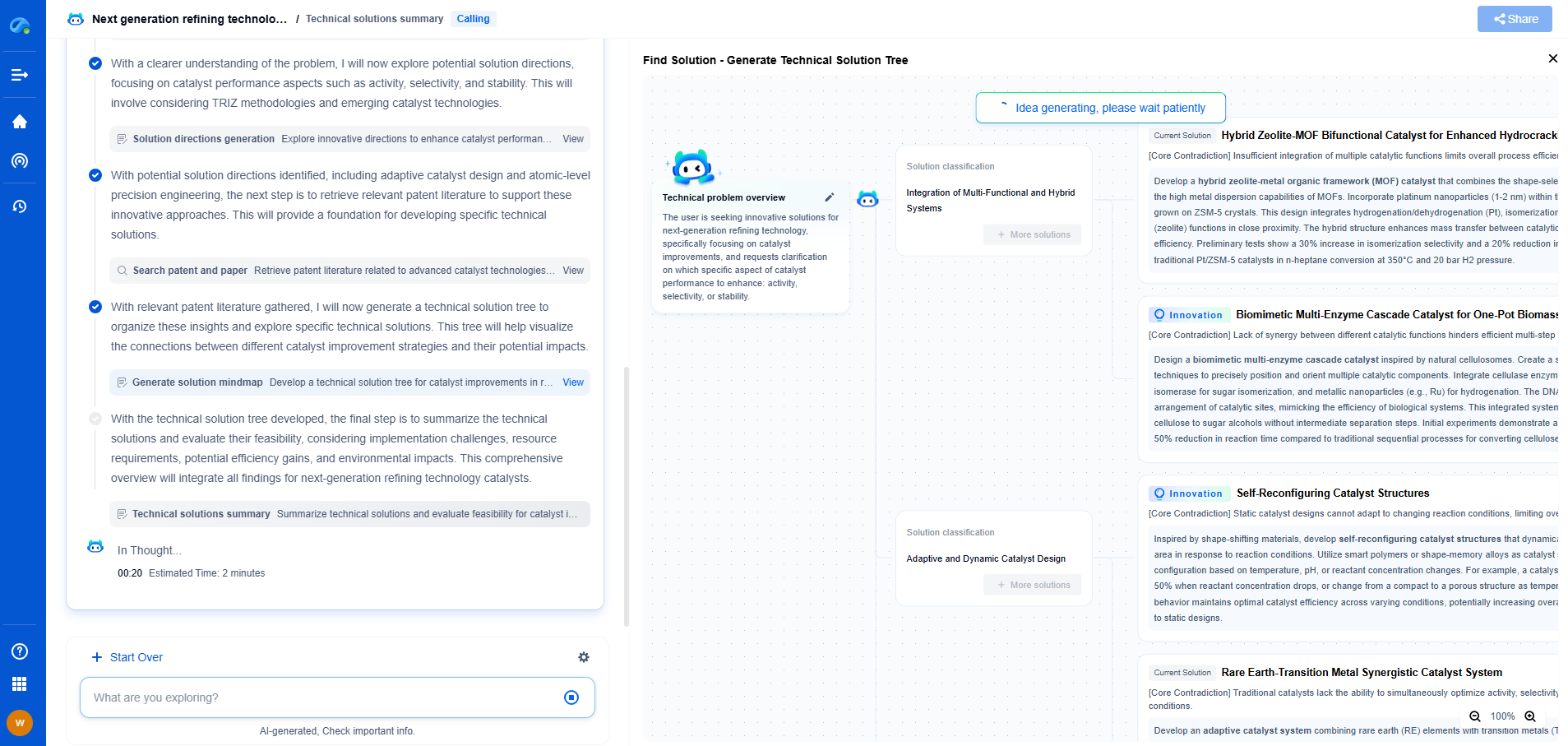
Understanding Vibration Isolation
Before diving into the specific types of isolators, it's important to understand the basic principles of vibration isolation. Vibrations are oscillatory motions that can result from machinery operations, environmental factors, or human activity. If not properly managed, these vibrations can lead to noise, wear, and even structural damage. Vibration isolators work by reducing the amplitude and frequency of these oscillations, ensuring smoother operation and extending the lifespan of equipment.
Rubber Isolators: The Flexible Solution
Rubber isolators are widely used due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. They are particularly effective in damping high-frequency vibrations, making them ideal for applications where noise reduction is a priority. The inherent material properties of rubber allow it to absorb energy and provide both isolation and damping simultaneously.
However, rubber isolators are not without limitations. At lower frequencies, their effectiveness diminishes, and they may not provide the necessary level of isolation. Additionally, rubber can degrade over time due to environmental factors such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to oils or chemicals. Nevertheless, for applications where high-frequency isolation is crucial and the operational environment is controlled, rubber isolators offer a practical solution.
Spring Isolators: The Heavy-Duty Choice
Spring isolators are characterized by their ability to handle heavy loads and provide isolation across a broader range of frequencies. They are commonly used in industrial settings where equipment produces low to medium frequency vibrations. The mechanical properties of springs allow them to support substantial weights while maintaining flexibility to absorb vibrations.
One of the key advantages of spring isolators is their durability. Made from materials such as steel, they are resistant to environmental degradation and can operate effectively over long periods. However, spring isolators are not as effective at damping high-frequency vibrations compared to rubber isolators. This limitation can be mitigated by incorporating additional damping materials or devices in conjunction with the springs.
Air Mounts: Precision and Adaptability
Air mounts, or pneumatic isolators, offer excellent vibration isolation, particularly at low frequencies. These isolators utilize air pressure to support the load and isolate vibrations, providing a smooth and adaptable system. Air mounts are highly effective in environments where precision is critical, such as in optical equipment, laboratory settings, or highly sensitive manufacturing processes.
The primary advantage of air mounts is their ability to adapt to varying loads and conditions. By adjusting the air pressure, users can fine-tune the isolation performance to match specific requirements. However, air mounts require a constant source of compressed air, which can be a logistical challenge in some settings. Additionally, while they excel at low-frequency isolation, their high-frequency damping capabilities are limited without additional measures.
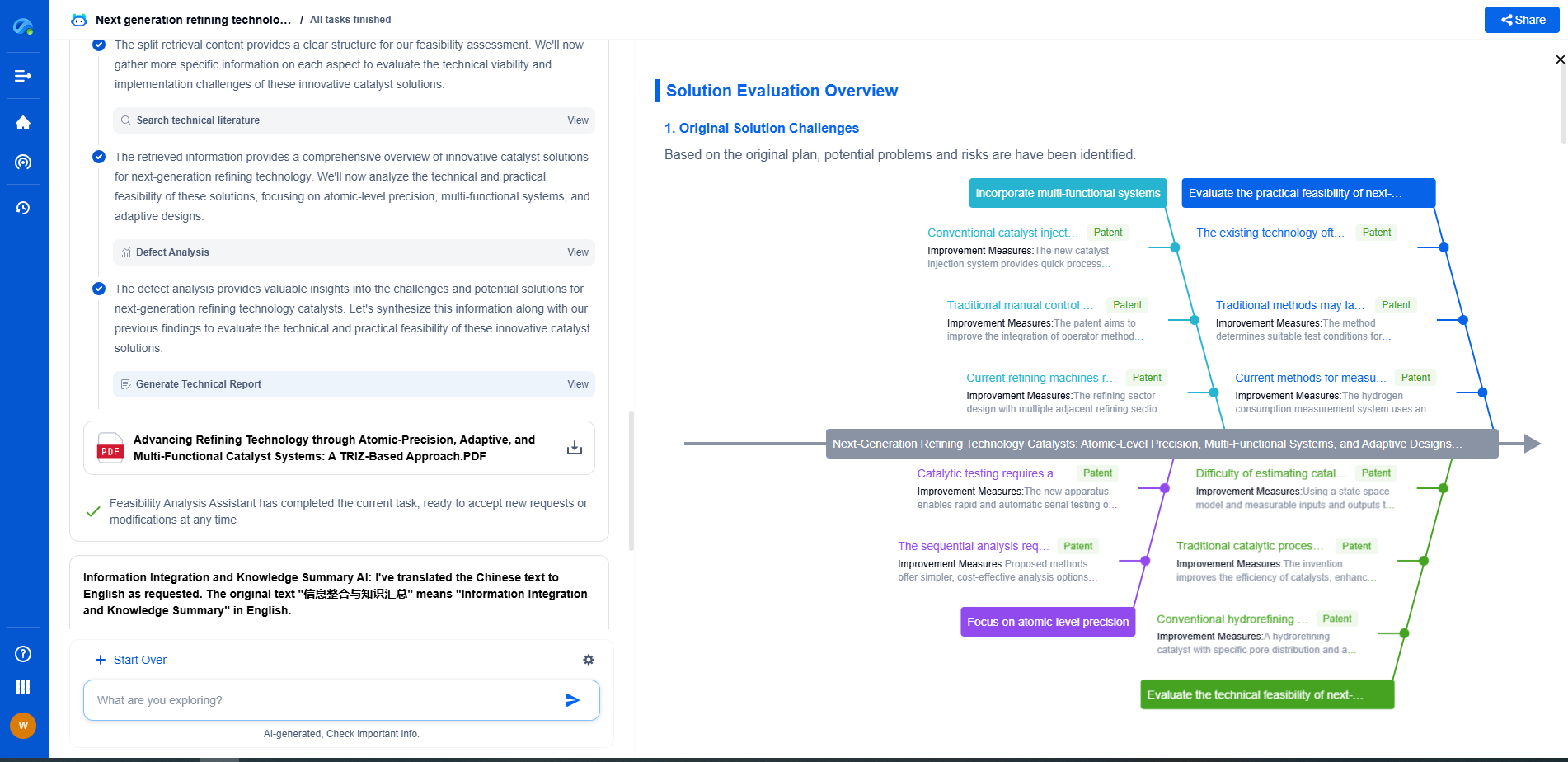
Choosing the Right Isolator
Selecting the appropriate vibration isolator depends on several factors, including the frequency and amplitude of the vibrations, the load capacity, and the environmental conditions. For applications dealing with high-frequency vibrations and noise reduction, rubber isolators are often the ideal choice. In industrial settings with heavy equipment producing low to medium frequency vibrations, spring isolators provide a robust solution. Meanwhile, in laboratories or precision-focused environments, air mounts offer the adaptability and performance necessary for optimal isolation.
In conclusion, understanding the strengths and limitations of each type of isolator is critical for ensuring effective vibration management. By aligning the isolator choice with the specific needs of the application, you can significantly enhance the performance and longevity of your equipment.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com