Voltage Rating Demystified: How to Avoid Overvoltage Failures
JUL 9, 2025 |
When dealing with electrical and electronic equipment, understanding voltage ratings is crucial. Voltage rating refers to the maximum voltage that a component, device, or system can handle safely. This rating is essential because it determines the operational limits of electrical equipment and helps in preventing overvoltage failures, which can lead to severe damage or even catastrophic failure.
The Importance of Adhering to Voltage Ratings
Voltage ratings are not just arbitrary numbers; they are carefully calculated limits set by manufacturers based on rigorous testing. Adhering to these ratings is essential for several reasons:
1. Safety: Operating beyond the rated voltage can result in overheating, short circuits, and even fires. This poses serious safety hazards to both individuals and property.
2. Longevity: Components exposed to voltages higher than their ratings can suffer from accelerated wear and tear, reducing their lifespan significantly.
3. Performance: Devices may not perform optimally when subjected to overvoltages, leading to inefficiencies and potential malfunctions.
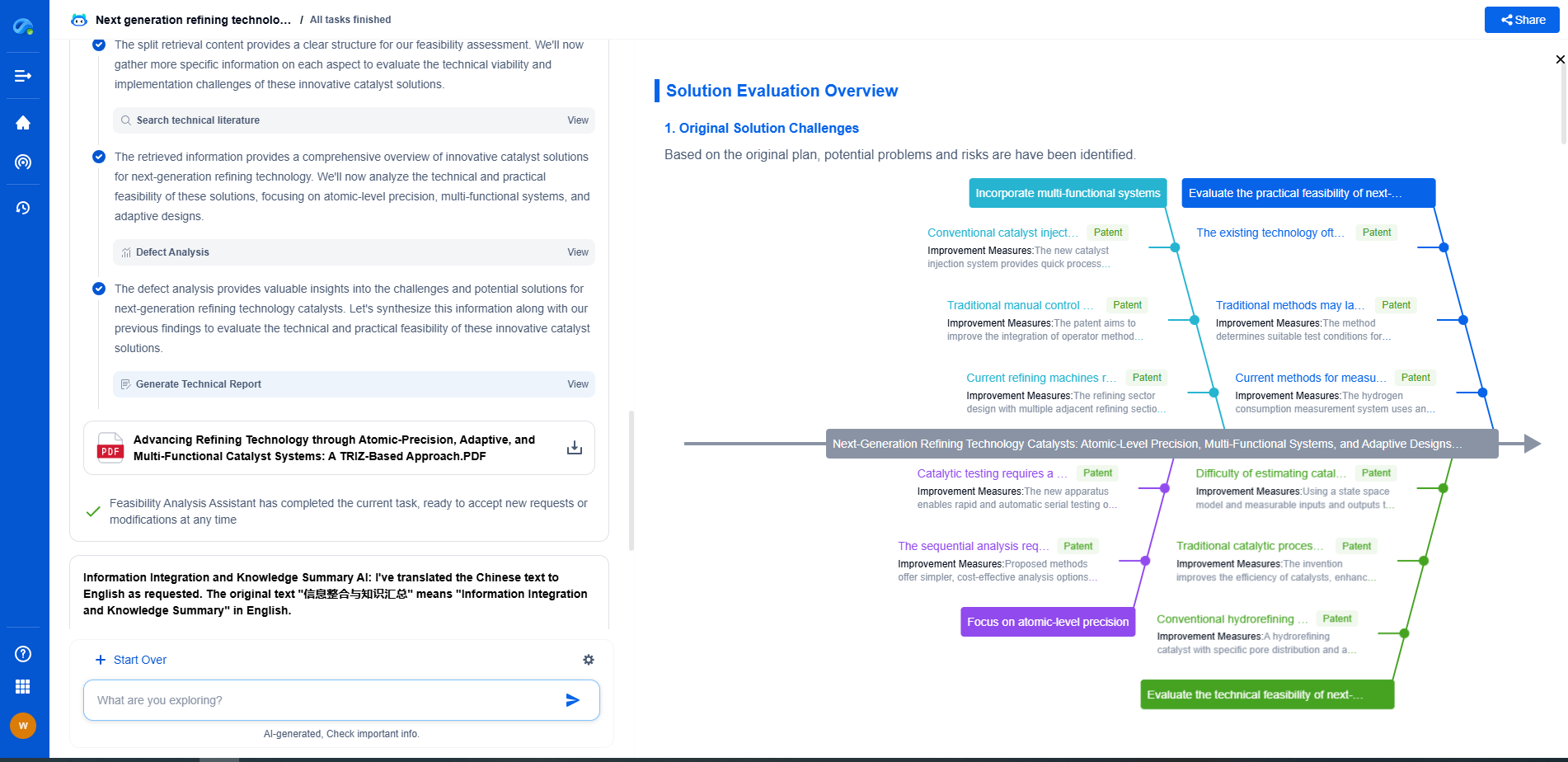
Causes of Overvoltage
Understanding what causes overvoltage is the first step in preventing it. Here are some common causes:
1. Lightning Strikes: One of the most potent natural causes of overvoltage, lightning can induce high voltages in electrical systems, leading to instant damage.
2. Switching Surges: Sudden changes in load or the switching on/off of devices can create transient overvoltages.
3. Equipment Malfunctions: Faulty equipment within the system can generate overvoltages.
4. Poor System Design: Inadequate system design or incorrect component selection can lead to overvoltage conditions.
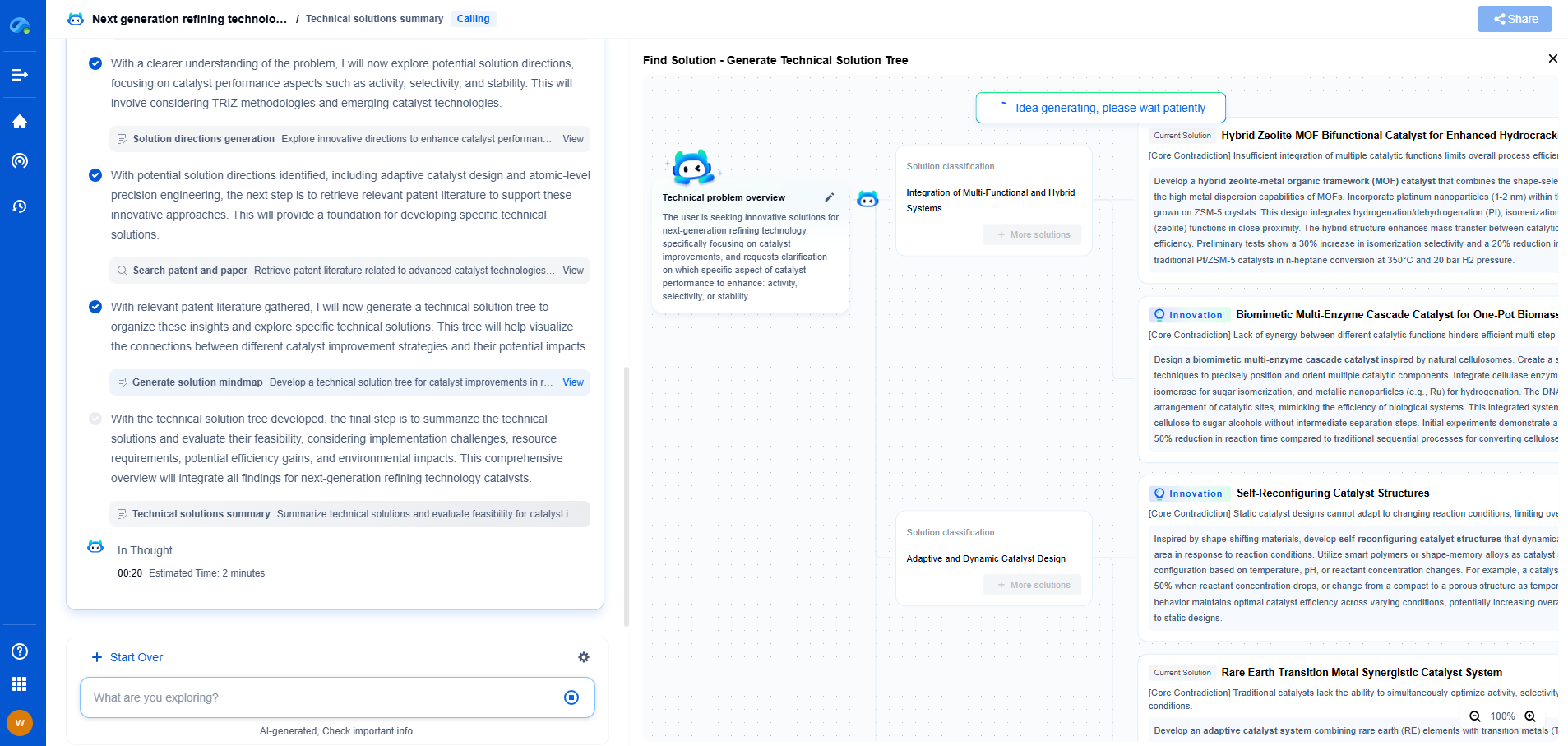
How to Avoid Overvoltage Failures
Avoiding overvoltage failures involves a combination of proper planning, equipment selection, and protection strategies:
1. Proper Equipment Sizing: Ensure that all components and devices in your system are rated for the voltages they will encounter. This includes considering both normal operating conditions and potential transient events.
2. Use of Surge Protection Devices: Surge protectors can absorb excess voltage and prevent it from reaching sensitive components. They are especially useful in areas prone to lightning strikes or frequent power surges.
3. Regular Maintenance and Testing: Regularly inspect and test electrical systems to ensure that all components are functioning correctly and are within their rated parameters.
4. System Design: Invest time in designing your electrical system to handle potential overvoltage scenarios. This may include using devices with higher voltage ratings or incorporating additional protective measures.
5. Education and Training: Ensure that personnel who work with electrical systems are well-trained in recognizing overvoltage conditions and implementing preventive measures.
Conclusion
Understanding and respecting voltage ratings is essential for the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. By adhering to these ratings, implementing protective measures, and ensuring proper system design, you can significantly reduce the risk of overvoltage failures. Remember, a proactive approach to managing electrical systems not only enhances safety but also extends the life and performance of your equipment. Embrace the knowledge of voltage ratings and make informed decisions to safeguard your technology investments.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com