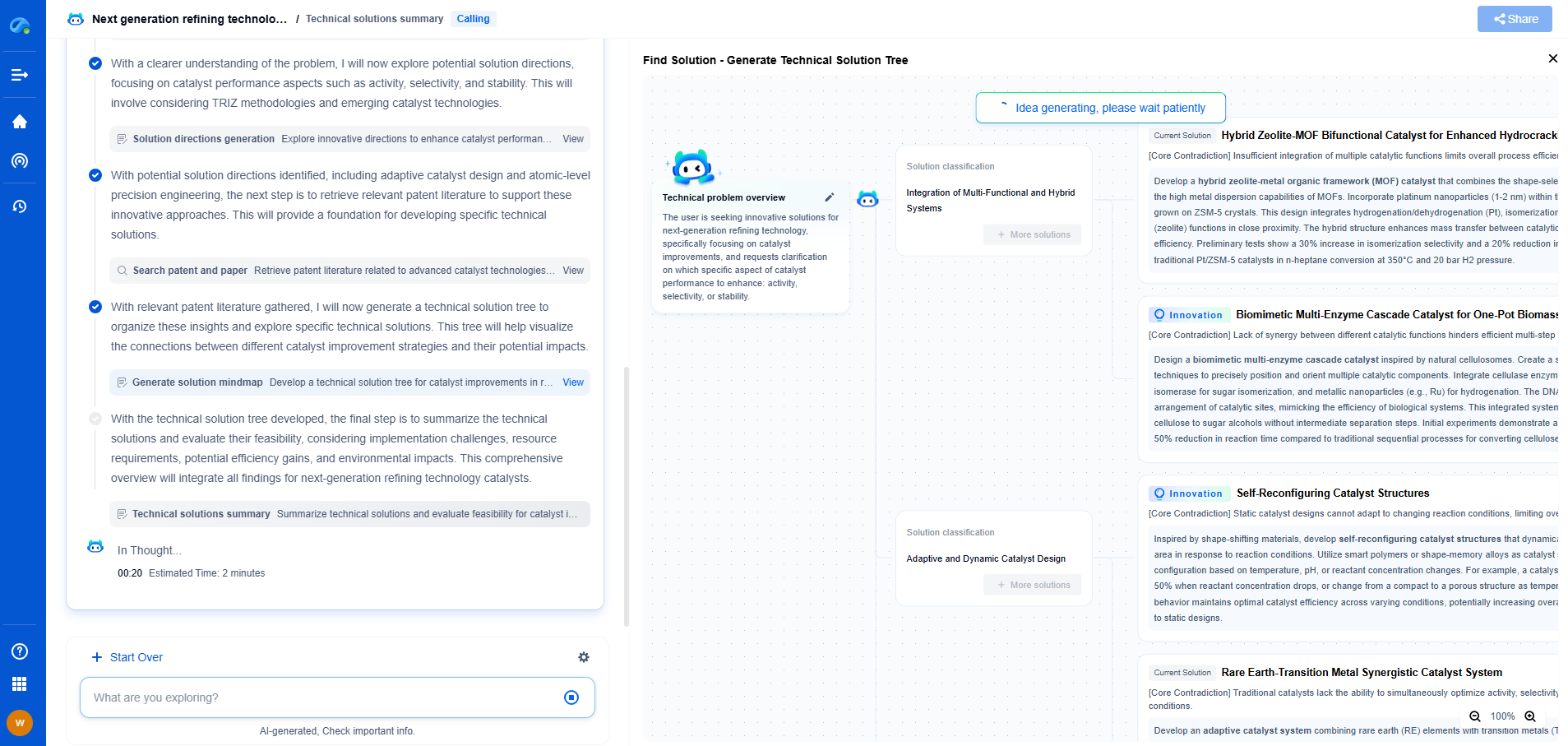
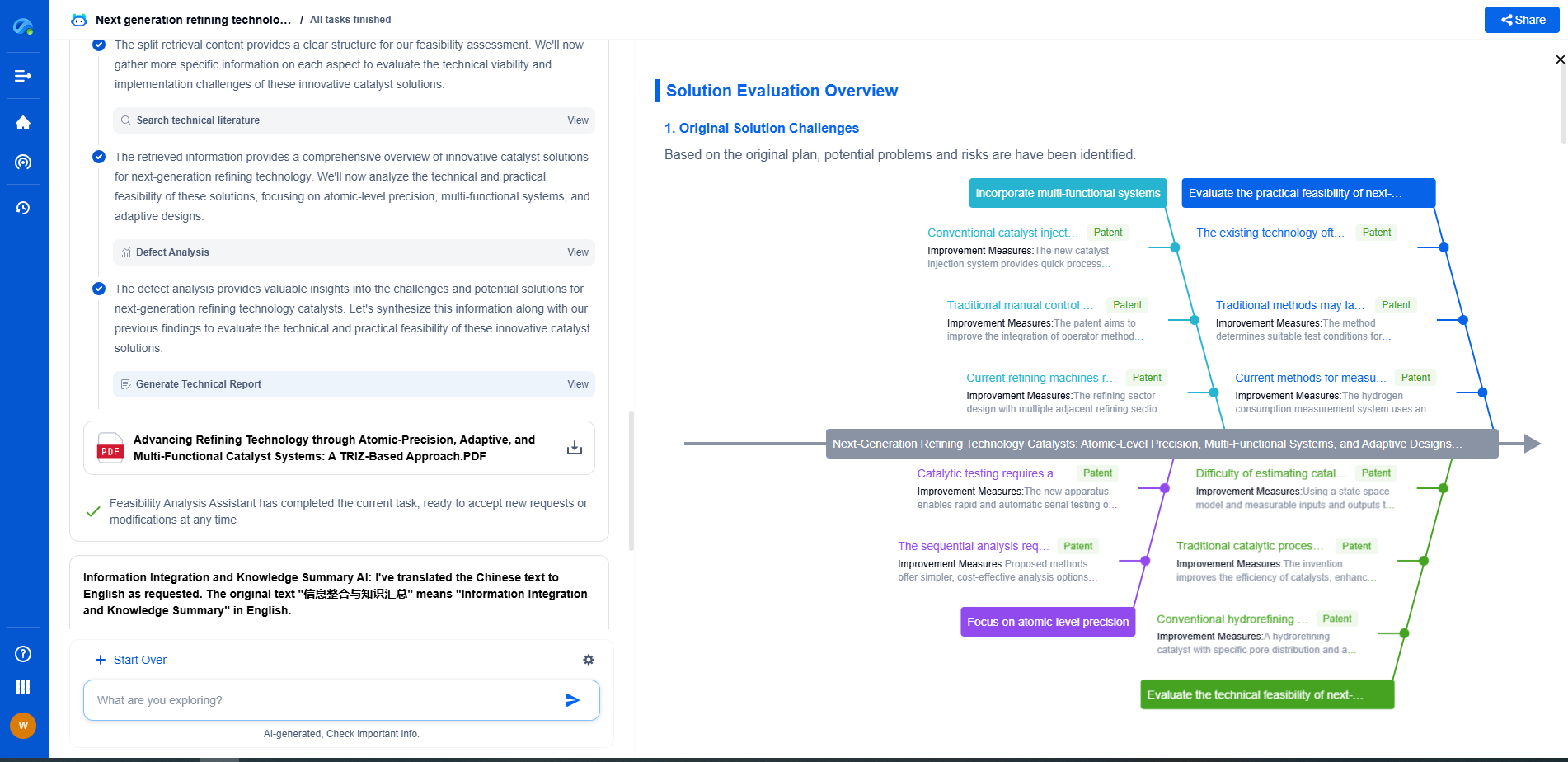
WASNs vs. Wired Acoustic Systems: A Comparison of Scalability and Cost
JUL 16, 2025 |
In the realm of acoustic monitoring and sensing, technology is evolving at a remarkable pace. Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks (WASNs) and wired acoustic systems are two prominent solutions that have emerged to address the needs of various industries, from environmental monitoring to industrial applications. Both systems offer unique benefits and come with their own set of challenges, especially when it comes to scalability and cost. This article delves into these aspects, providing a comprehensive comparison of WASNs and wired acoustic systems.
Understanding WASNs and Wired Acoustic Systems
Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks (WASNs) consist of numerous distributed nodes equipped with microphones and communication capabilities. These nodes collect acoustic data and transmit it wirelessly to a central hub for analysis. WASNs are renowned for their flexibility and ease of deployment in diverse environments.
In contrast, wired acoustic systems rely on physical cables to connect sensors to their processing units. They are typically used in settings where stable and consistent power supply and data transmission are paramount. Wired systems have been the traditional choice, particularly in environments where wireless communication may face interference or reliability issues.
Scalability: The Flexibility Factor
Scalability is a critical consideration in choosing between WASNs and wired systems. WASNs, by design, offer superior scalability. Their wireless nature allows for easy expansion of the network by simply adding more nodes without the need for complex cabling infrastructure. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in large-scale applications such as environmental monitoring over vast areas or in urban soundscaping projects.
On the other hand, wired systems pose significant challenges in terms of scalability. Expanding a wired network often involves extensive labor and costs associated with laying new cables and ensuring secure and stable connections. In scenarios where the monitoring area is expected to grow, WASNs provide a more viable and cost-effective solution.
Cost Considerations: Initial Investment and Maintenance
Cost is a decisive factor when evaluating technology solutions. WASNs tend to have a lower initial cost due to the absence of extensive cabling infrastructure. The deployment of wireless nodes is generally quicker and less labor-intensive. However, the total cost of ownership for WASNs can vary depending on factors such as battery life, maintenance needs, and the potential need for periodic upgrades to wireless protocols to ensure reliable communication.
Wired systems, while potentially more costly upfront due to cabling and installation fees, may offer a more stable and predictable maintenance cost structure. They are often favored in applications where long-term data transmission reliability is crucial, and the environment is less conducive to wireless communication, such as in industrial settings with significant electromagnetic interference.
Reliability and Performance
When considering reliability and performance, both WASNs and wired systems have their strengths and weaknesses. WASNs offer flexibility and ease of reconfiguration, which can be crucial in dynamic environments. However, they can be susceptible to interference, signal loss, and battery-related downtimes, which may affect their consistent performance.
Wired systems typically provide more reliable data transmission with minimal latency and interference. Their performance is less likely to be affected by environmental variables, making them a suitable choice for critical applications where data integrity and reliability are paramount.
Conclusion
Choosing between Wireless Acoustic Sensor Networks and wired acoustic systems requires a careful evaluation of scalability and cost, alongside other factors such as reliability, performance, and specific application needs. WASNs offer unparalleled scalability and flexibility, making them an ideal choice for rapidly expanding or geographically dispersed projects. However, wired systems provide robust, reliable data transmission in environments where wireless solutions may struggle.
Ultimately, the decision should be guided by the specific requirements of the application, the available budget, and the long-term goals of the project. By weighing the pros and cons of each system, organizations can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and objectives.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com