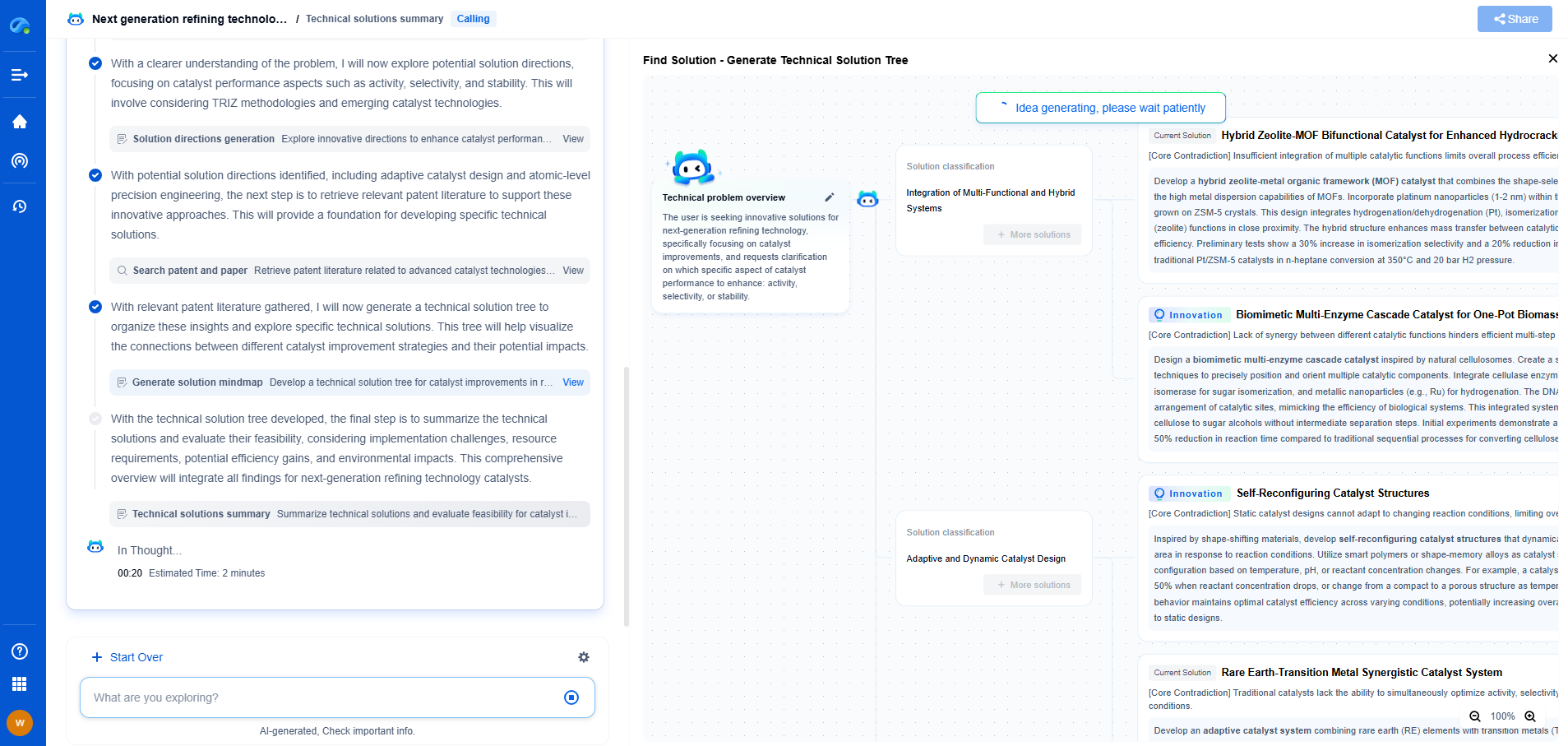
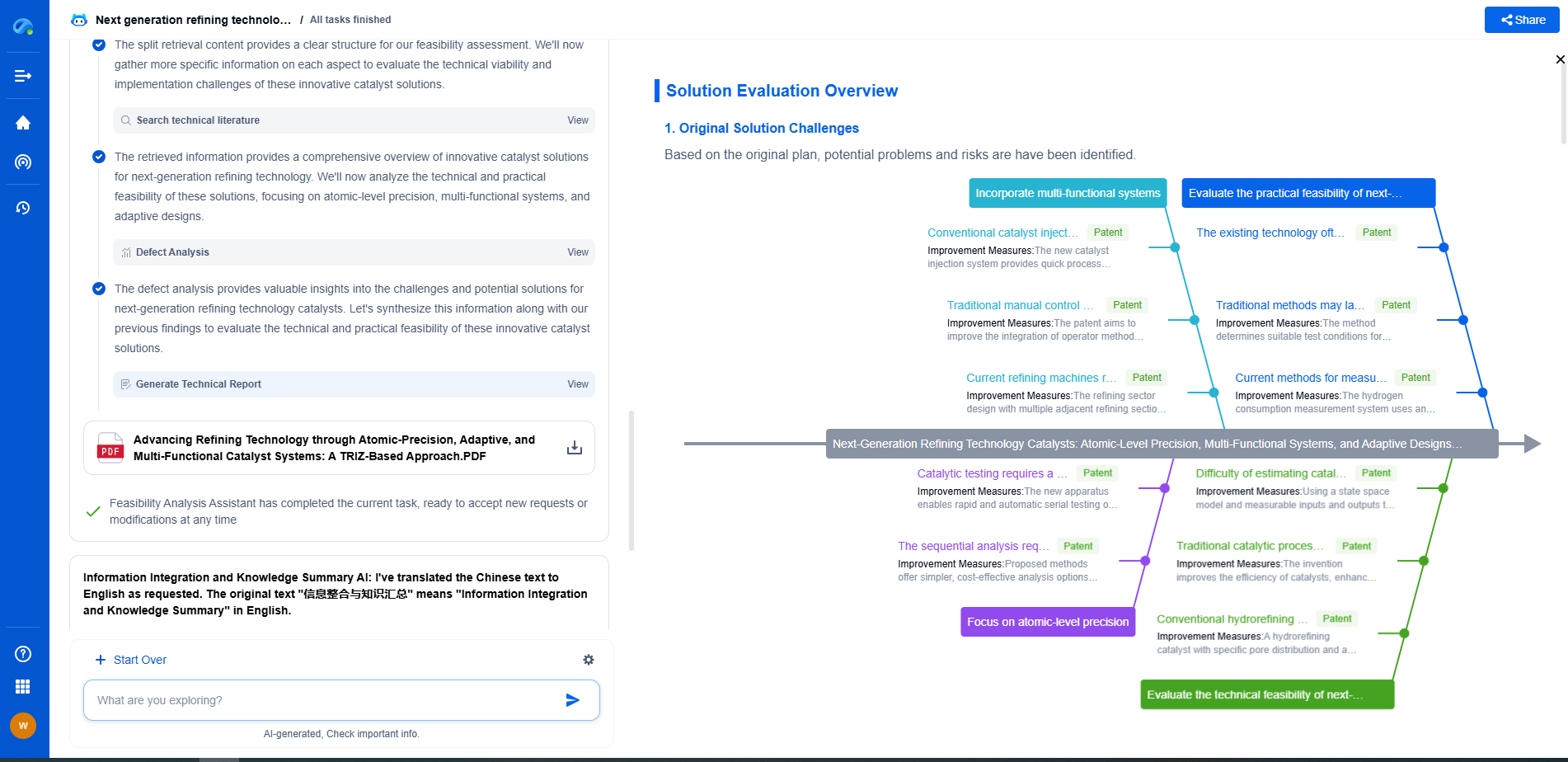
Water-Based Mud (WBM) vs. Oil-Based Mud (OBM): Core Differences
JUN 20, 2025 |
In the realm of drilling fluids, two primary categories dominate the scene: Water-Based Mud (WBM) and Oil-Based Mud (OBM). Both serve the essential purpose of lubricating the drill bit, stabilizing the wellbore, and carrying cuttings to the surface. However, their composition, performance, environmental impact, and cost vary significantly. Understanding these differences is vital for choosing the right drilling fluid for specific conditions.
Composition Differences
Water-Based Mud (WBM)
WBM is primarily composed of water and a variety of additives that enhance its properties. These additives can include clays like bentonite, polymers, and other chemicals to control fluid loss, viscosity, and pH levels. The water component makes WBM more environmentally friendly and easier to dispose of compared to OBM. Additionally, WBM is typically less expensive and easier to formulate on-site.
Oil-Based Mud (OBM)
OBM, on the other hand, uses oil or synthetic oil as its continuous phase, with water being a dispersed phase. The oil component can be either diesel, mineral oil, or synthetic oil, leading to variations like Invert Emulsion Mud. OBM includes emulsifiers, wetting agents, and organophilic clays to maintain its stability and performance. This type of mud is prized for its superior lubricating properties and stability in high-temperature and high-pressure environments.
Performance Differences
WBM Performance
WBM offers the advantage of being more readily adaptable to a wide range of drilling conditions. It effectively prevents shale swelling and is generally easier to clean up. However, WBM is less effective in inhibiting the hydration of reactive shale formations, which can lead to wellbore instability and other operational challenges. Its performance can diminish under extreme temperatures and pressures.
OBM Performance
OBM is known for its exceptional lubricating properties, which reduce torque and drag on the drill string, making it ideal for challenging drilling conditions like deep wells and horizontal drilling. It provides excellent wellbore stability and inhibits shale hydration effectively. OBM's robustness under high temperatures and pressures makes it the preferred choice in deep-water and high-angle drilling operations. However, its use is often restricted due to environmental concerns and higher handling costs.
Environmental Impact
WBM Environmental Considerations
WBM is generally considered more environmentally friendly than OBM. Its water-based nature means that it typically requires less complex waste management, and its disposal poses fewer risks to the environment. However, the use of certain additives can still present environmental challenges, necessitating careful selection and management.
OBM Environmental Considerations
The environmental impact of OBM is significantly greater due to its oil-based composition. Spills and discharges pose a high risk to marine and terrestrial ecosystems. The handling, transport, and disposal of OBM require stringent regulatory compliance to minimize environmental risks. The higher cost of treatment and disposal of OBM cuttings and fluids often adds to the overall operational costs.
Cost Implications
WBM Costs
WBM is generally more cost-effective in terms of initial formulation and disposal. Its simpler makeup and easier waste management contribute to lower operational costs. However, in challenging drilling scenarios where its performance may be compromised, additional costs might be incurred due to downtime and increased maintenance.
OBM Costs
The initial cost of OBM is higher, given the expenses associated with oil-based components and specialized additives. The rigorous environmental regulations lead to increased costs for safe handling and disposal. Despite these costs, its superior performance in difficult drilling conditions can lead to overall cost savings by reducing non-productive time and enhancing drilling efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing between Water-Based Mud and Oil-Based Mud involves a careful evaluation of the drilling environment, regulatory landscape, and budget constraints. While WBM offers cost and environmental advantages, OBM's performance under challenging conditions can be unmatched. The decision must weigh these factors to ensure optimal drilling performance and environmental compliance. Understanding the core differences between WBM and OBM helps operators make informed choices that align with both operational goals and environmental stewardship.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com