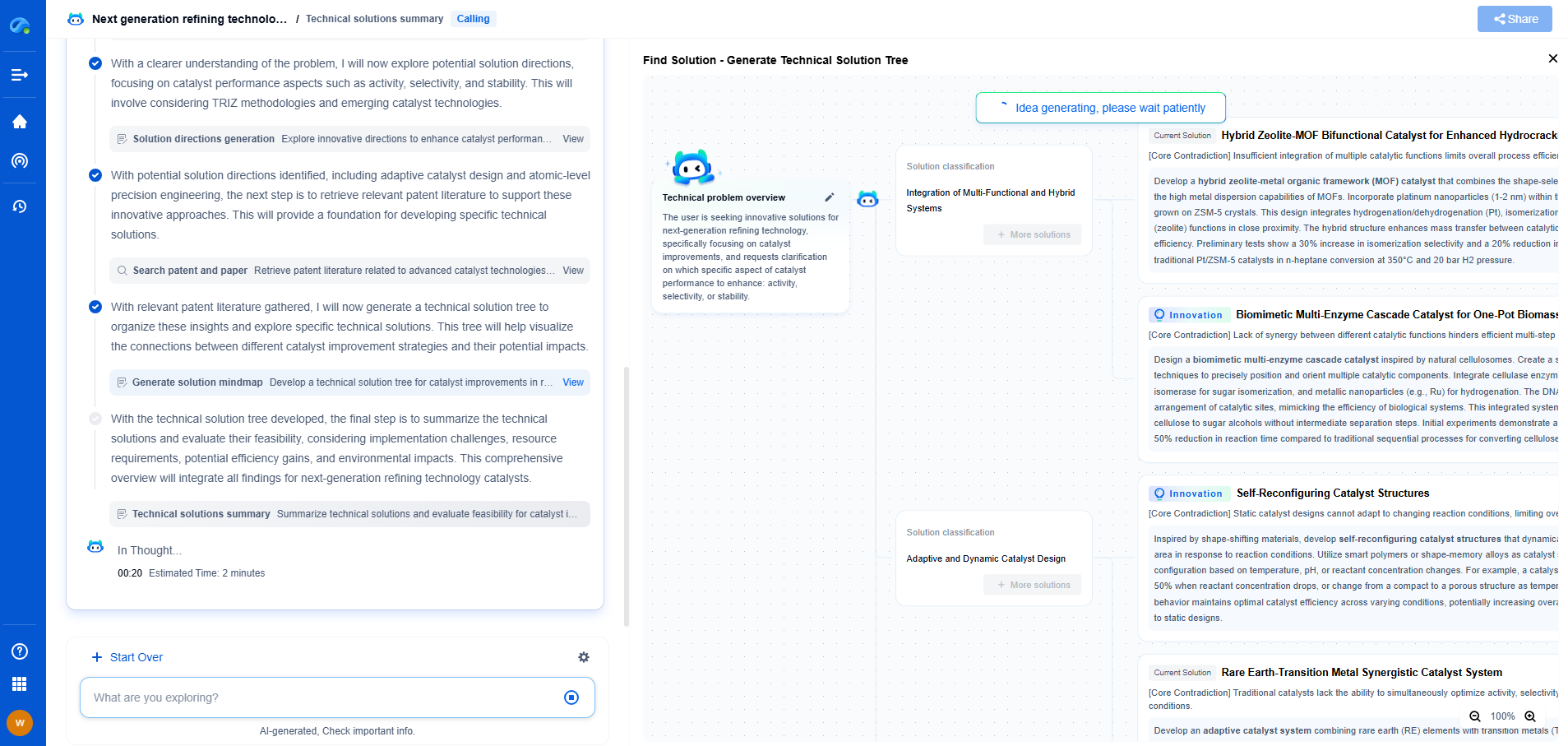
What are enhanced geothermal systems (EGS)?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) represent a cutting-edge approach within the realm of renewable energy, holding immense potential to dramatically expand our capacity to harness geothermal power. Unlike conventional geothermal systems, which rely on naturally occurring hydrothermal resources, EGS technology is designed to tap into the vast heat stored within the Earth's crust, making it accessible even in areas devoid of natural geothermal reservoirs. By artificially enhancing the permeability of underground rocks, EGS can unlock new geothermal resources, contributing significantly to sustainable energy production.
How EGS Works
The fundamental principle of EGS lies in its ability to create an artificial geothermal reservoir by engineering the subsurface environment. The process typically begins with drilling deep boreholes into hot, dry rock formations. Once the target depth is reached, a high-pressure fluid is injected into the well to fracture the rocks, effectively increasing their permeability. This process, known as hydraulic stimulation, creates a network of interconnected fractures through which fluid can circulate.
Once the fracture network is established, water is injected into the hot rock, where it absorbs heat as it flows through the fractures. The heated water is then brought back to the surface, where it can be used to generate electricity through a conventional geothermal power plant, or for direct heating applications. The cooled water is then re-injected into the reservoir to be reheated, creating a closed-loop system that can continuously produce energy.
Advantages of EGS
One of the primary advantages of EGS is its ability to access geothermal resources in regions lacking natural hydrothermal activity. This technology vastly expands the geographical availability of geothermal energy, offering potential deployment in areas traditionally considered unsuitable for geothermal development. By leveraging EGS, regions with minimal geothermal resources can still capitalize on the benefits of renewable energy, increasing their energy independence and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Another significant advantage is the sustainability of EGS. Unlike fossil fuels, geothermal energy is virtually inexhaustible on a human timescale, with the Earth continuously producing heat. EGS provides a stable and reliable source of energy that can operate independently of weather conditions, making it an attractive option for baseload power generation. Additionally, EGS systems have a smaller environmental footprint compared to other energy sources, as they emit minimal greenhouse gases and require less land.
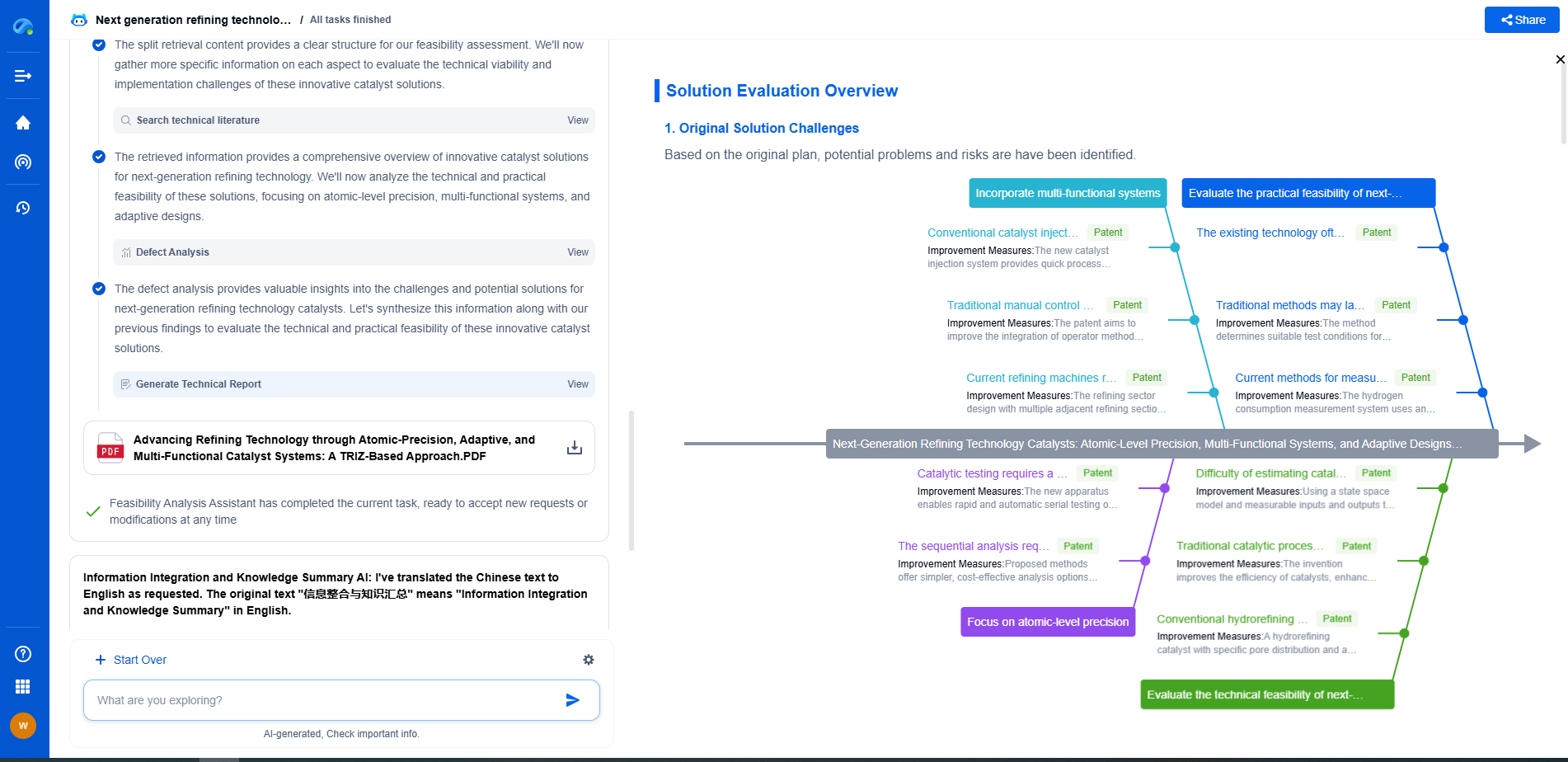
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, the development of EGS is not without challenges. One of the primary concerns is the risk of induced seismicity, which refers to small-scale earthquakes caused by the injection of fluids into the ground. While most induced seismic events are minor and unlikely to cause damage, they can still raise concerns and opposition from local communities. Careful site selection, monitoring, and regulation are essential to minimizing these risks.
Furthermore, the economic viability of EGS projects remains a significant hurdle. The initial costs of drilling and reservoir development can be substantial, and economic returns are highly dependent on the successful creation and maintenance of a productive reservoir. Advances in drilling technology and reservoir management are crucial to reducing costs and improving the commercial viability of EGS.
The Future of EGS
As the world continues to transition towards sustainable energy, EGS holds the promise of contributing significantly to the global energy mix. Ongoing research and development are focused on overcoming the technical and economic challenges associated with EGS, with the goal of making it a commercially viable and widely adopted energy source.
In the future, EGS could play a pivotal role in reducing carbon emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change. By unlocking the Earth's vast geothermal potential, EGS technology offers the possibility of a cleaner, more sustainable energy future, helping to meet global energy demands while preserving the environment for future generations.
Conclusion
Enhanced Geothermal Systems represent an innovative and promising solution in the quest for sustainable energy. With their ability to harness heat from the Earth's crust, EGS has the potential to revolutionize the geothermal industry and expand the availability of renewable energy worldwide. While challenges remain, continued advancements and investment in EGS technology could unlock new energy horizons, providing a powerful tool in the fight against climate change.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com