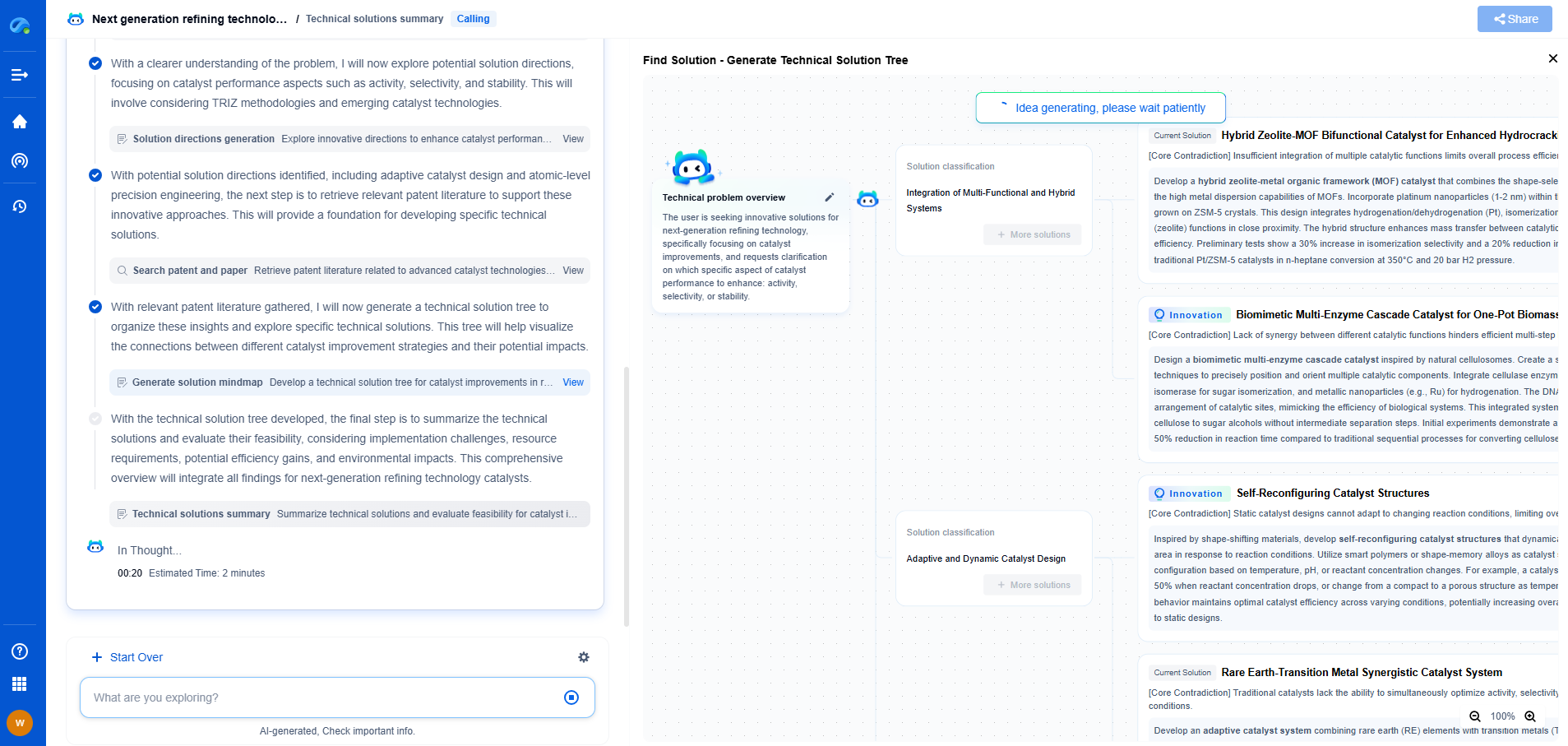
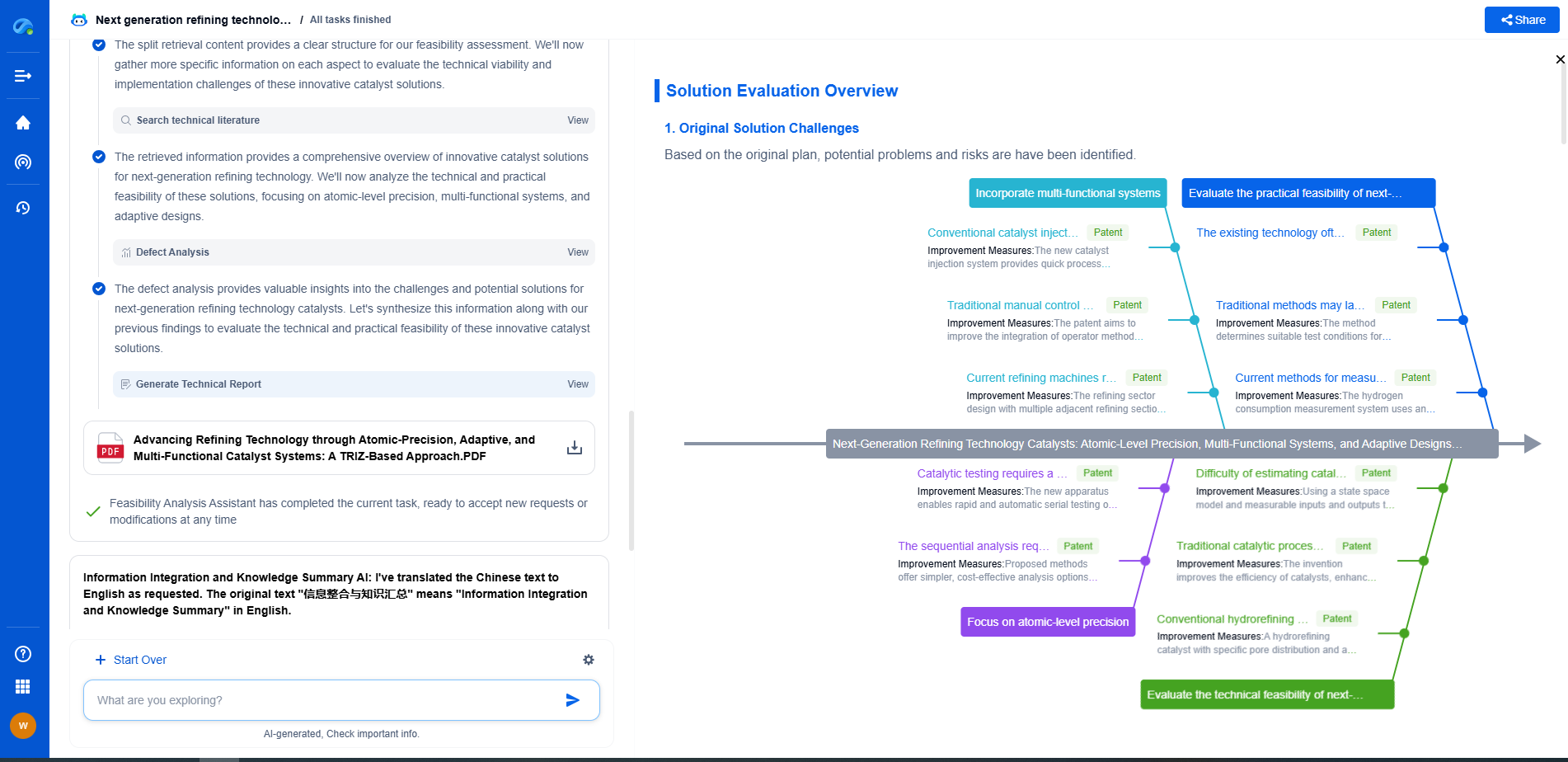
What Are Printable Solar Cells and Their Advantages?
JUL 22, 2025 |
Printable solar cells, also known as organic photovoltaics (OPVs) or plastic solar cells, are an innovative advancement in solar technology. These solar cells are made from organic materials that can be printed onto flexible sheets using techniques similar to inkjet printing. The potential to produce lightweight, flexible, and cost-effective solar panels has garnered significant interest from researchers, manufacturers, and environmentalists.
How Printable Solar Cells Work
At the core of printable solar cells are organic semiconductors, which are composed of carbon-based molecules or polymers. These materials have properties that allow them to absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. When light photons strike these semiconductors, they excite electrons, creating electron-hole pairs. These excited electrons are then directed towards electrodes, generating an electric current.
Printable solar cells are often produced using roll-to-roll printing processes, which are both efficient and scalable. This printing method involves layering the organic materials onto a substrate, creating a thin, flexible solar panel that can be applied to a variety of surfaces.
Advantages of Printable Solar Cells
1. Cost-Effectiveness
One of the most significant advantages of printable solar cells is their potential to reduce the cost of solar energy. Traditional silicon-based solar panels are expensive to produce due to the complexity and energy-intensive nature of their manufacturing process. In contrast, printable solar cells can be manufactured at a lower cost using roll-to-roll printing, reducing the overall expense of solar power installation.
2. Flexibility and Versatility
Printable solar cells are lightweight and flexible, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. Unlike rigid silicon panels, these cells can be integrated into clothing, windows, and even curved surfaces, allowing for creative and innovative uses. This versatility opens the door to embedding solar technology in places previously deemed impractical, such as on vehicles, mobile devices, and other portable electronics.
3. Environmental Benefits
The production of printable solar cells is more environmentally friendly compared to traditional solar panels. The manufacturing process consumes less energy and generates fewer emissions, contributing to a reduced carbon footprint. Additionally, the organic materials used are often more sustainable and less toxic than the materials used in conventional solar cells.
4. Ease of Installation
The lightweight and flexible nature of printable solar cells make them easier to transport and install. Unlike traditional solar panels, which require careful handling and mounting, printable solar panels can be rolled out and adhered to surfaces with minimal effort. This ease of installation can lead to faster deployment and reduced labor costs.
Current Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their promising advantages, printable solar cells face several challenges. The efficiency of these cells is typically lower than that of traditional silicon-based solar panels. Researchers are actively working to improve the efficiency and lifespan of printable solar cells to make them a more viable commercial option.
Additionally, the durability of these cells under prolonged exposure to the elements is a concern. Advances in encapsulation techniques and material science aim to address these issues, making printable solar cells more robust and reliable over time.
The future of printable solar cells is bright, with ongoing research and development paving the way for enhanced performance and broader adoption. As technology continues to evolve, printable solar cells hold the potential to revolutionize the solar energy industry by providing an affordable and flexible energy solution that can be seamlessly integrated into everyday life.
Conclusion
Printable solar cells represent a significant step forward in the pursuit of sustainable and accessible solar energy. Their cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and environmental benefits make them an attractive option for diversifying the applications of solar technology. While challenges remain, the continuous advancements in this field signal a promising future for printable solar cells, potentially transforming the way we harness and utilize solar energy.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com