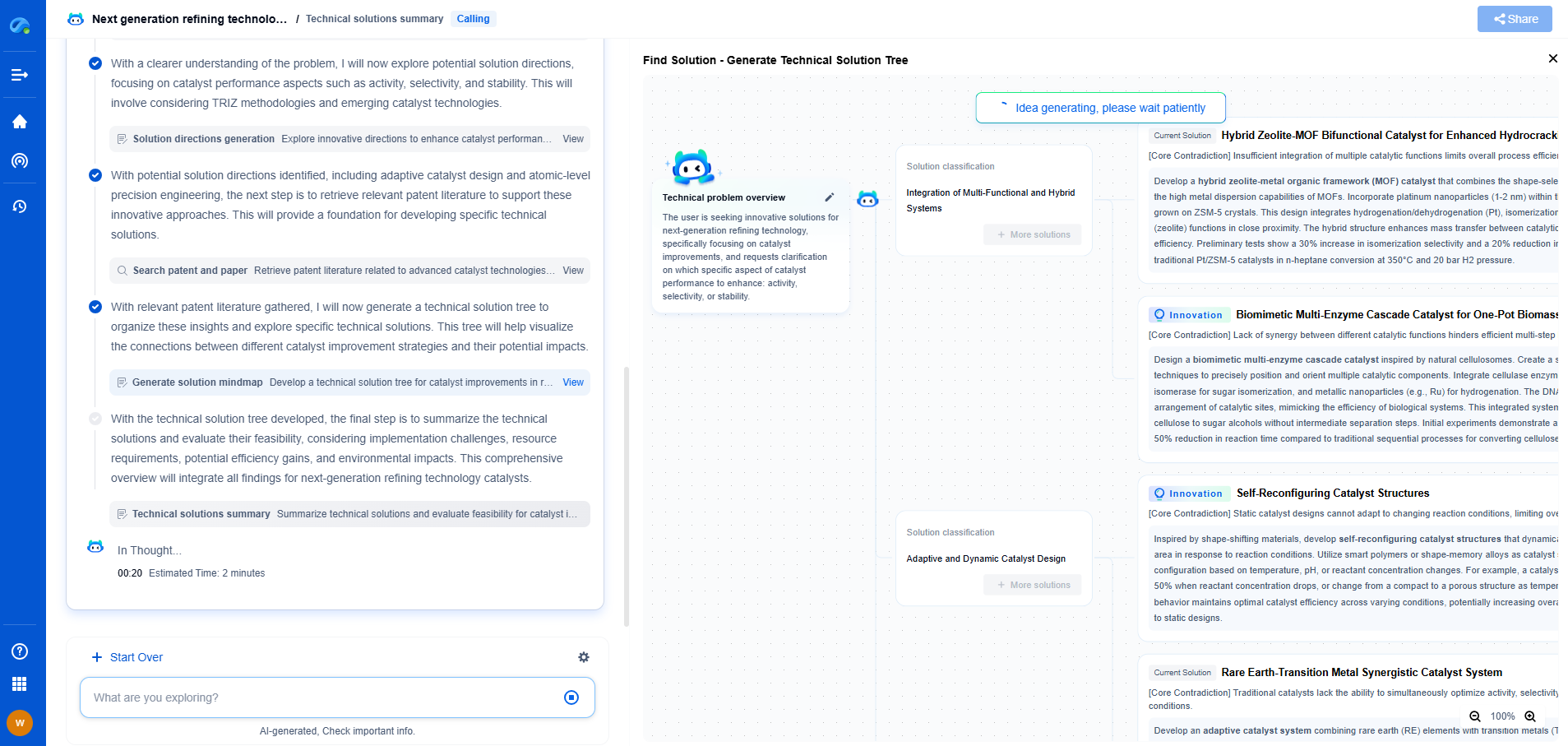
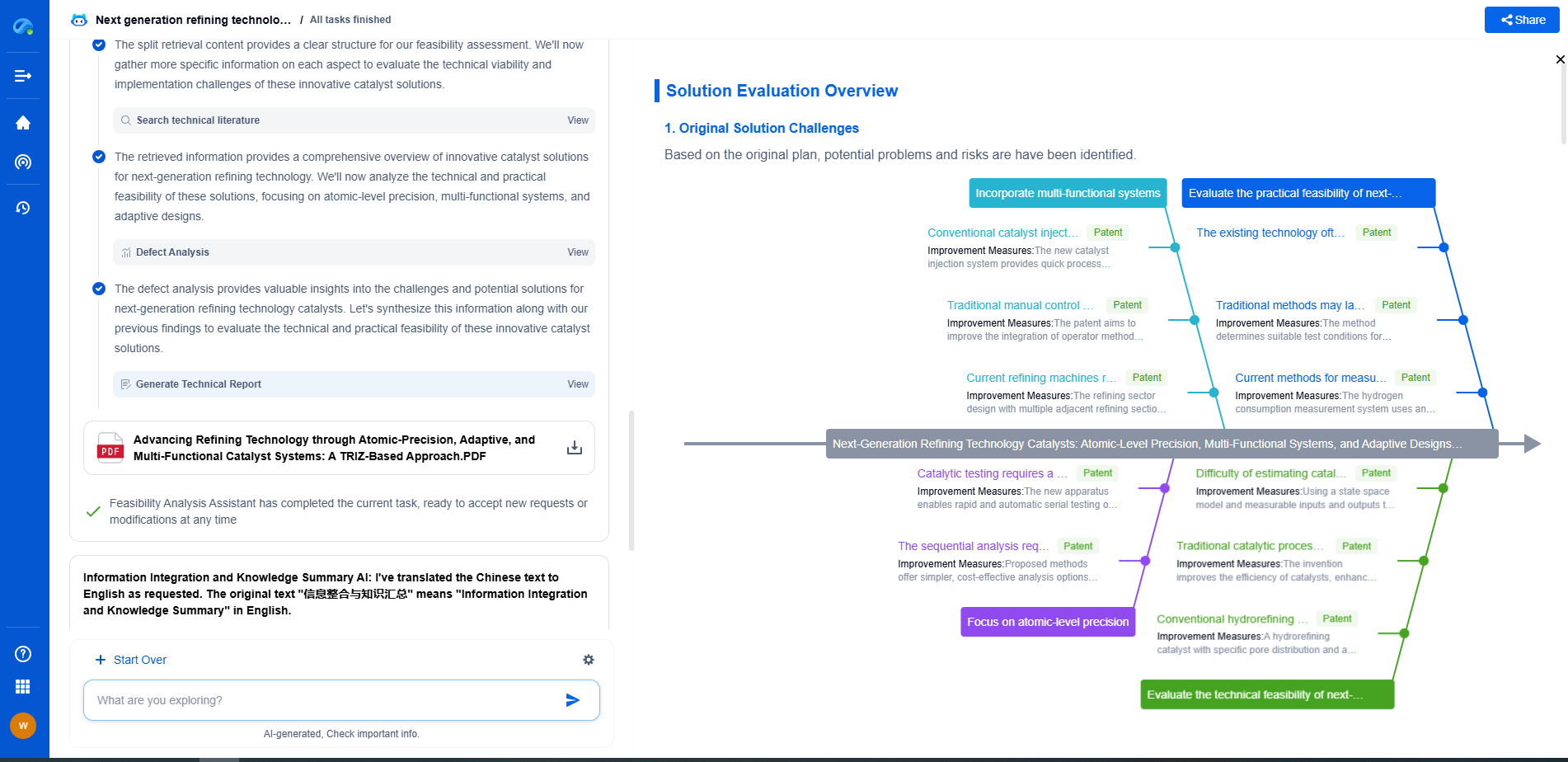
What is a Cathodic Protection System in Pipelines?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Cathodic protection is a critical technique used to control the corrosion of metal surfaces by making them the cathode of an electrochemical cell. In the context of pipelines, which are often made from steel or other metals susceptible to corrosion, cathodic protection systems play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the infrastructure. Corrosion can lead to leaks, environmental hazards, and costly repairs, making cathodic protection an essential component in pipeline management.
How Cathodic Protection Works
The basic principle of cathodic protection involves reducing the oxidation reactions on the metal surface of the pipeline. This is achieved by providing an alternative source of electrons to the metal from a more easily corroded "sacrificial" material or through impressed current. By doing so, the potential difference between the metal and the corrosive environment is minimized, effectively halting the corrosion process.
Types of Cathodic Protection Systems
There are two main types of cathodic protection systems used in pipelines: sacrificial anode cathodic protection (SACP) and impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP).
1. Sacrificial Anode Cathodic Protection (SACP)
In this system, sacrificial anodes made from metals like zinc, magnesium, or aluminum are placed in contact with the pipeline. These anodes are more reactive than the pipeline metal and thus corrode preferentially, protecting the pipeline by acting as a sacrificial source of electrons. The advantages of SACP include its simplicity and the fact that it does not require an external power source. However, it may not be suitable for large or complex pipeline networks due to the limited protection range.
2. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP)
ICCP systems utilize an external power source to drive a current from an inert anode to the metal structure. The external power allows for better control over the protection current, making ICCP suitable for larger pipelines or those with varying environmental conditions. The inert anodes in ICCP systems can be made from materials such as titanium or mixed metal oxides, which ensures longevity and durability. While ICCP systems are generally more complex and costly to install, they offer increased flexibility and effectiveness in a wide range of applications.
Choosing the Right System for Your Pipeline
Selecting the appropriate cathodic protection system depends on several factors, including the size and complexity of the pipeline, the environment in which it operates, and the specific characteristics of the metal used in the pipeline. A thorough evaluation of these factors, often conducted by corrosion engineers, will determine the most efficient and cost-effective solution.
Maintenance and Monitoring
Once a cathodic protection system is in place, regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure its effectiveness. This includes checking for voltage and current output, inspecting anodes for wear, and conducting surveys to detect any potential failures or areas of inadequate protection. Advances in technology have introduced remote monitoring systems, enabling real-time data collection and analysis, which significantly improves the ability to maintain optimal protection levels.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Implementing cathodic protection systems not only extends the lifespan of pipelines but also offers substantial environmental and economic benefits. By preventing leaks and spills, these systems help protect the surrounding environment and reduce the risk of costly clean-ups and legal liabilities. Additionally, maintaining pipeline integrity through cathodic protection minimizes the need for frequent replacements and repairs, leading to long-term savings and more efficient resource use.
Conclusion
Cathodic protection systems are indispensable for safeguarding pipelines against corrosion-related damage. By understanding the principles, types, and maintenance of these systems, stakeholders can make informed decisions to ensure the longevity and safety of their pipeline infrastructures. Whether opting for sacrificial anodes or impressed current systems, the investment in cathodic protection pays off in improved reliability, environmental conservation, and reduced operational costs.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com