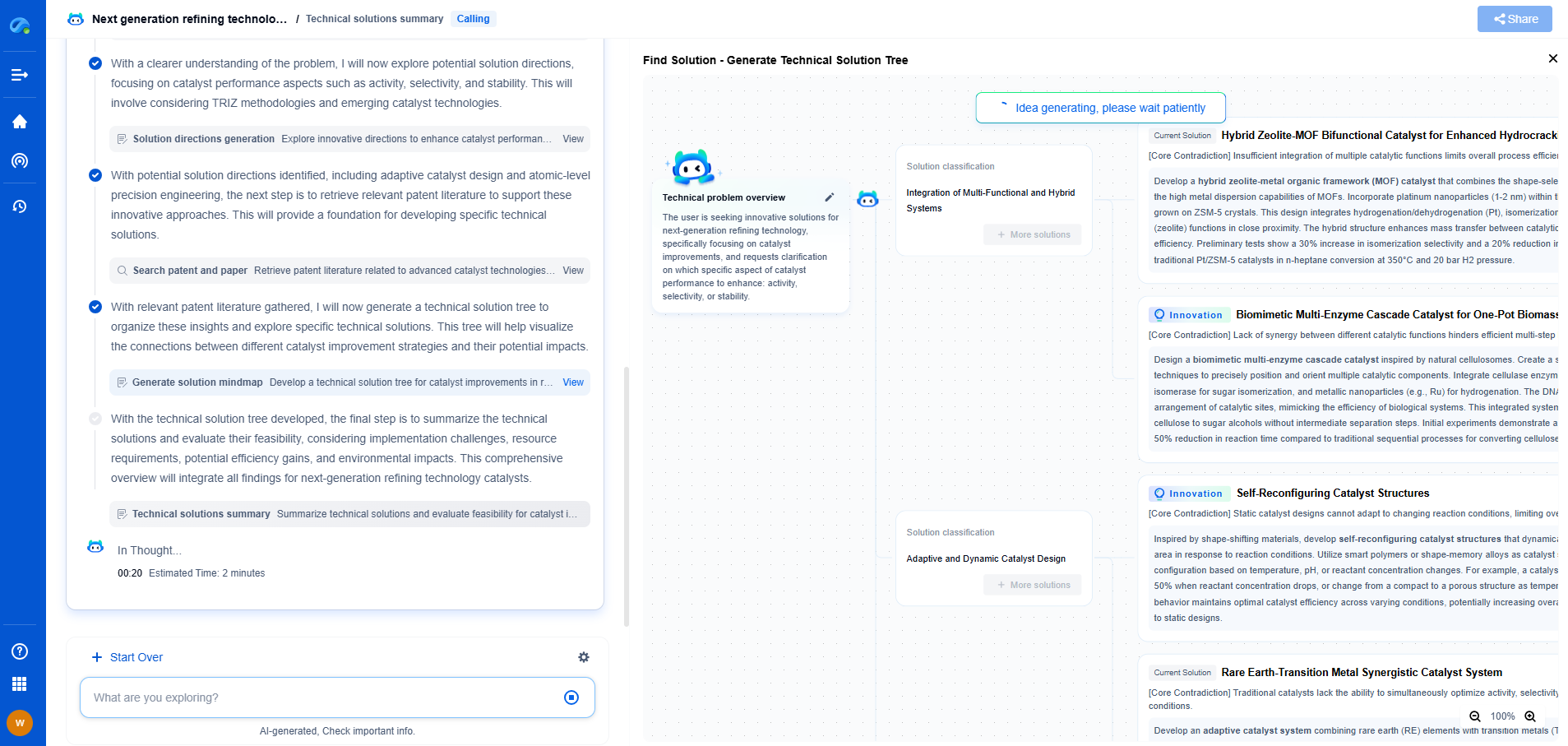
What Is a Floating Solar Power Plant and Where Is It Used?
JUL 22, 2025 |
Floating solar power plants, also known as floating photovoltaic (FPV) systems, are an innovative and increasingly popular method for harnessing solar energy. Unlike traditional solar farms that are installed on land, these systems are designed to float on bodies of water such as reservoirs, lakes, and even near coastlines. As the demand for renewable energy sources grows, floating solar power plants offer an efficient and versatile solution while addressing some of the limitations of land-based solar installations.
How Do Floating Solar Power Plants Work?
Floating solar power plants operate on the same basic principle as terrestrial solar farms. Photovoltaic panels are utilized to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. However, instead of mounting these panels on land, they are placed on floating platforms anchored to the water body. These platforms are engineered to withstand various environmental conditions, ensuring stability and durability.
The electricity generated by the floating solar panels is transmitted to the shore via underwater cables, where it can be integrated into the local power grid. The setup includes components such as inverters, transformers, and monitoring systems to ensure efficient energy conversion and distribution.
Benefits of Floating Solar Power Plants
One of the primary advantages of floating solar power plants is their ability to conserve land. By utilizing water surfaces, these installations reduce the need for large tracts of land that could otherwise be used for agriculture, housing, or natural habitats. This makes them particularly appealing in densely populated areas or regions where land is scarce and expensive.
Additionally, floating solar panels benefit from the cooling effect of water, which can enhance their efficiency. Solar panels tend to lose efficiency as they heat up, but the proximity to water helps maintain a lower temperature, thus optimizing energy output. Furthermore, the shade provided by the panels can reduce water evaporation, which is particularly beneficial in water-scarce regions.
Environmental and Economic Impact
Floating solar power plants can have a positive environmental impact by reducing reliance on fossil fuels, thus lowering carbon emissions. They also offer an opportunity to repurpose underutilized or non-productive water bodies, such as industrial ponds or reservoirs, contributing to sustainable energy goals without significant ecological disruption.
Economically, these systems can potentially lower energy costs by providing a renewable and local source of electricity. They also create new opportunities for jobs in the renewable energy sector, from manufacturing and installation to maintenance and operation.
Global Examples of Floating Solar Power Plants
Floating solar power plants are being adopted worldwide, with notable installations in countries such as China, Japan, India, and the United States. China, for instance, is home to some of the largest floating solar farms, including the Huainan plant in Anhui province, which was built on a former coal mining area that became flooded.
In Japan, where land is limited, floating solar panels are increasingly deployed on reservoirs, offering a solution that aligns with the nation’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions. Similarly, India has embarked on ambitious solar projects, including floating solar plants on dams and water bodies to meet its growing energy demands sustainably.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their advantages, floating solar power plants face several challenges. The initial cost of installation can be higher than land-based systems due to the need for specialized floating platforms and anchoring systems. Additionally, environmental concerns such as the impact on aquatic ecosystems and water quality need careful consideration and management.
Looking ahead, technological advancements and economies of scale are expected to reduce costs and enhance the feasibility of floating solar power plants. As global interest in renewable energy continues to rise, these systems are poised to play a significant role in the transition to sustainable energy sources.
Conclusion
Floating solar power plants represent an exciting frontier in renewable energy. By leveraging water surfaces for solar installations, they offer a sustainable and space-efficient alternative to traditional solar farms. As countries strive to meet their renewable energy targets, floating solar power plants are set to become an integral part of the global energy landscape, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com