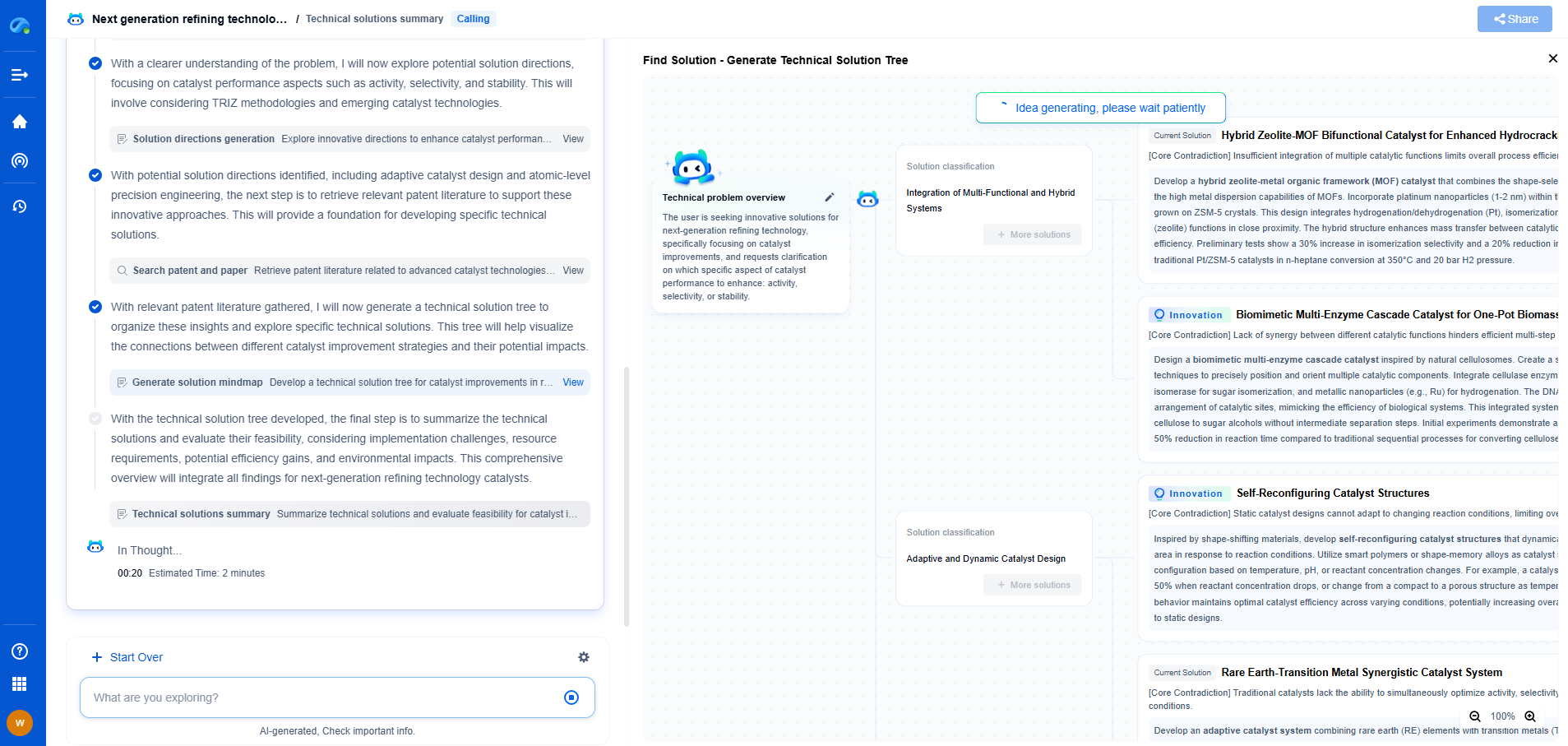
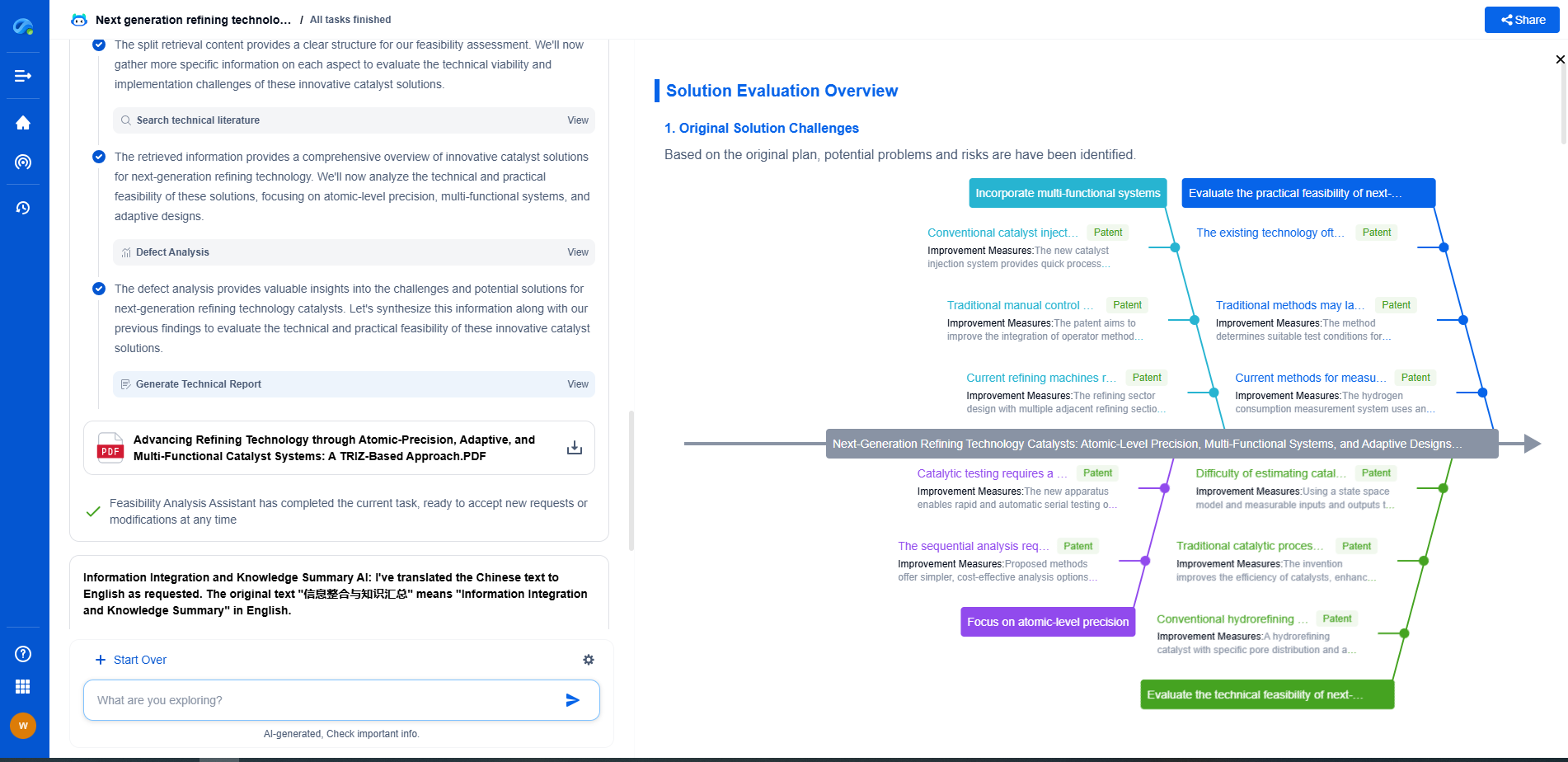
What Is a Load Cell? Types, Working Principle, and Applications
JUL 14, 2025 |
Load cells are transducers that convert force or pressure into an electrical signal, playing a crucial role in a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. They are designed to measure weight, tension, compression, torque, and pressure with high precision. In essence, a load cell transforms a mechanical input into readable data, allowing for accurate monitoring and control of forces in various settings.
Types of Load Cells
1. **Strain Gauge Load Cells**: The most common type, strain gauge load cells, rely on the deformation of a material. When a load is applied, the strain gauge deforms and changes its electrical resistance, which is then measured and converted into a digital signal. Strain gauge load cells are versatile and used in numerous applications, from industrial scales to laboratory testing.
2. **Hydraulic Load Cells**: These load cells use a piston and a cylinder mechanism filled with oil or water. When force is applied, it produces pressure in the fluid, which correlates with the weight or force acting on the cell. Hydraulic load cells are robust and ideal for heavy-duty applications, often found in environments where electrical equipment might pose a risk.
3. **Pneumatic Load Cells**: Operating similarly to hydraulic cells, pneumatic load cells use air pressure instead of liquid. They are known for their safety in hazardous environments and can be used in applications where avoiding contamination is crucial, such as in the food industry.
4. **Capacitive Load Cells**: These cells measure changes in capacitance caused by the movement of a diaphragm or other structure when a load is applied. Capacitive load cells are sensitive and can be used for precise measurements, though they might be more expensive and complex than other types.
Working Principle of Load Cells
Load cells operate based on the underlying physics of force conversion. The working principle involves several key components:
- **Mechanical Structure**: The load cell's structure deforms slightly under load, creating the change necessary for measurement.
- **Sensors**: These are often strain gauges that detect mechanical deformation and alter their electrical resistance accordingly.
- **Signal Processing**: The change in resistance is converted into an electrical signal, which is then amplified and processed. This signal is proportional to the force applied and is displayed or recorded for further analysis.
The entire process is designed to ensure minimal error and high precision, often involving temperature compensation and calibration to maintain accuracy across different conditions.
Applications of Load Cells
Load cells are ubiquitous in their applications across various industries due to their precision and reliability:
- **Weighing Systems**: Load cells are central to weighing scales in industries such as agriculture, retail, and logistics. They ensure accurate weight measurements, which are essential for trade and compliance.
- **Safety Monitoring**: In construction and manufacturing, load cells are used to monitor structural load and prevent overloads, ensuring safe operation of cranes, elevators, and other heavy machinery.
- **Automotive Testing**: Load cells play a role in testing vehicle components, including engines and suspensions, by measuring the forces they endure during operation.
- **Aerospace**: In this high-stakes industry, load cells are used for testing aircraft components and ensuring they can withstand the forces encountered during flights.
- **Medical Devices**: From weighing patients to ensuring precision in prosthetics, load cells contribute to a variety of medical applications.
Conclusion
Load cells are indispensable tools in modern industry, capable of accurate force measurement in a variety of challenging environments. Understanding the different types of load cells, their working principles, and their diverse applications can help industries choose the right solution for their specific needs. Whether it's for simple weight measurement or complex force analysis, load cells provide the precision and reliability required to maintain quality and safety standards across numerous sectors.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com