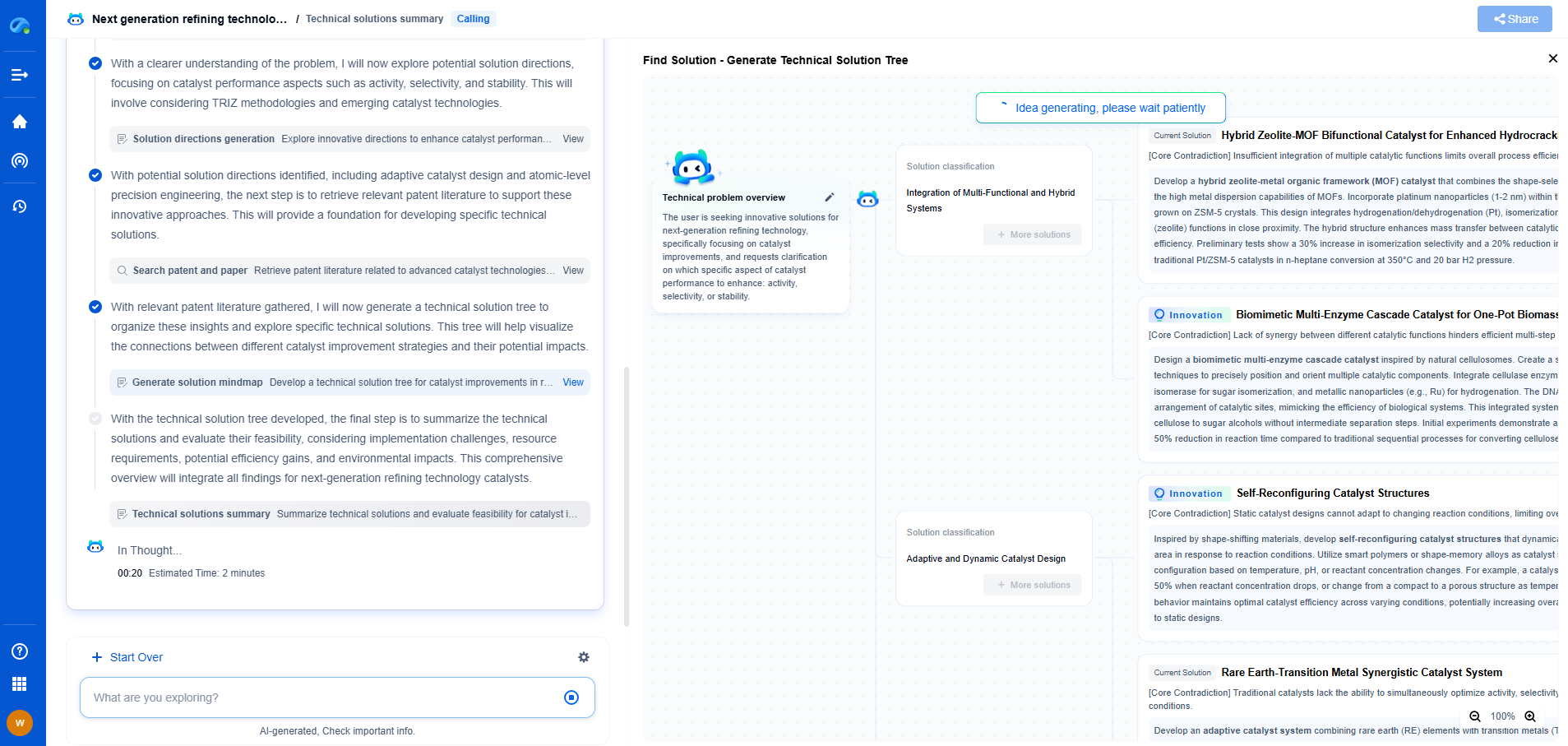
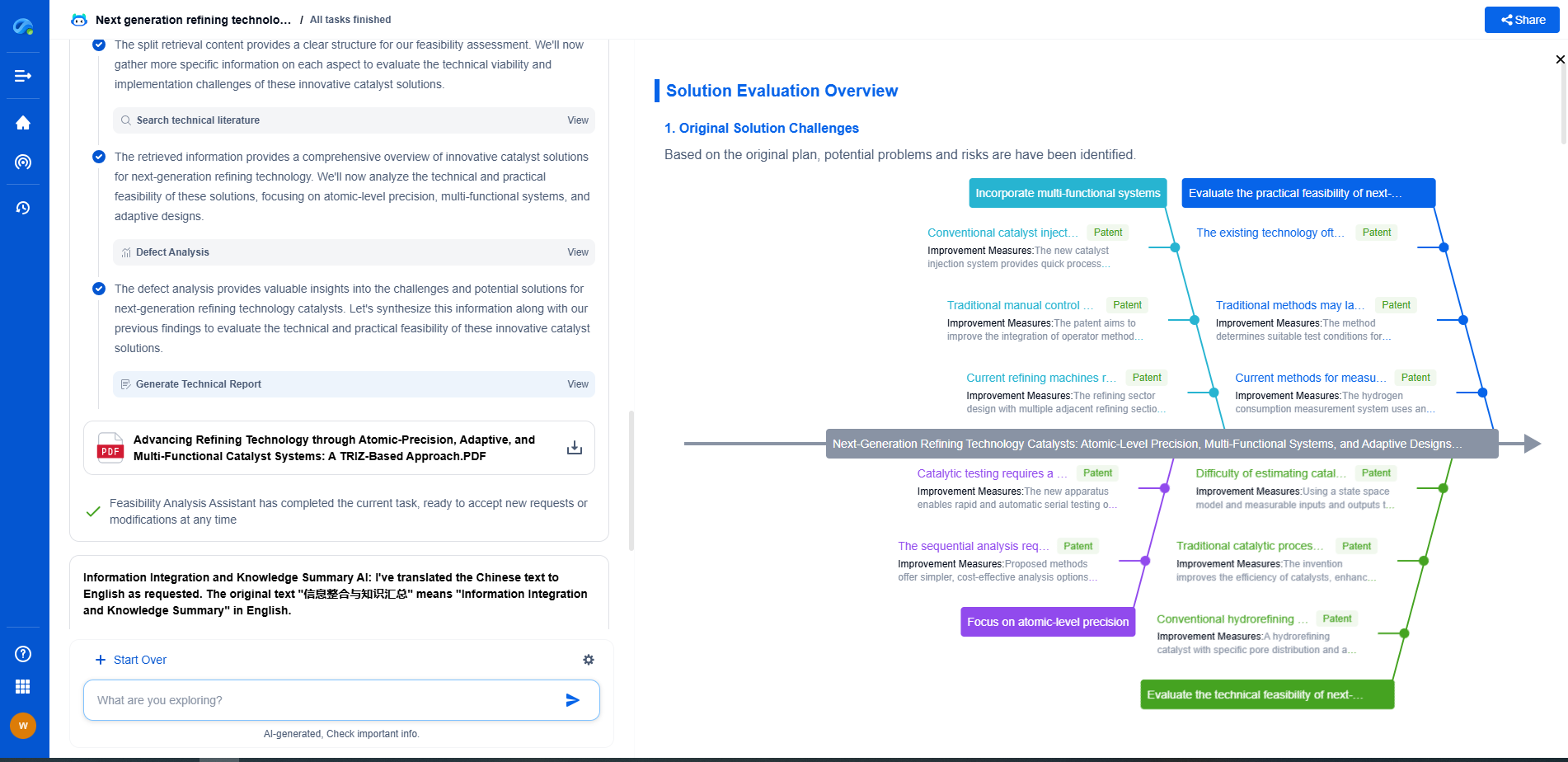
What Is a PZT Material? Basics of Lead Zirconate Titanate in Sensing
JUL 14, 2025 |
Lead Zirconate Titanate, commonly known as PZT, is a standout material in the realm of piezoelectric materials. It has gained immense popularity due to its high piezoelectric coefficients, making it an ideal choice for various sensing applications. Understanding the basics of PZT materials can provide insight into their versatile uses and advantages in the world of sensors.
Piezoelectricity: The Core Concept
Piezoelectricity is the ability of certain materials to generate an electric charge in response to applied mechanical stress. The piezoelectric effect is reversible, meaning that PZT materials can also change shape when subjected to an electric field. This dual function makes them invaluable in sensing technologies where converting mechanical energy into electrical energy and vice versa is essential.
Composition and Structure
PZT materials are solid solutions composed of lead zirconate (PbZrO3) and lead titanate (PbTiO3). The combination of these two compounds results in a perovskite crystal structure, which is crucial for the piezoelectric properties of PZT. The balance between zirconate and titanate in the composition can be adjusted to optimize the material's properties for specific applications, including its dielectric constant, piezoelectric coefficients, and mechanical strength.
Advantages of PZT in Sensing
PZT materials are favored in sensing applications for several reasons. First, they exhibit high piezoelectric coefficients, which translate to higher sensitivity and efficiency in converting mechanical pressure into electrical signals. This makes them suitable for precision applications, such as accelerometers, microphones, and ultrasound transducers.
Additionally, PZT materials have excellent thermal stability, allowing them to function effectively across a wide range of temperatures. This feature is particularly important in industrial and automotive sensors where the environment can be harsh.
Applications in Sensing Technologies
PZT materials are integral to various sensing technologies. In medical imaging, they are used in ultrasound transducers to generate sound waves and receive the returning echoes, producing detailed images of internal organs. Their ability to function at high frequencies enhances image resolution and precision.
In the automotive industry, PZT sensors are employed for knock detection in engines and tire pressure monitoring systems. Their reliability and sensitivity contribute to vehicle safety and performance.
Moreover, PZT is used in industrial applications such as vibration monitoring and flow measurement. Its robustness and adaptability make it suitable for measuring mechanical changes in diverse environments.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, PZT materials come with challenges that need consideration. The incorporation of lead in PZT raises environmental concerns due to its toxicity. Efforts are underway to develop lead-free piezoelectric materials, but PZT remains the standard due to its superior properties.
Another challenge is the brittleness of PZT ceramics, which requires careful handling and packaging to prevent fractures during usage. Innovations in material processing and design are continually being pursued to enhance the durability and lifespan of PZT sensors.
Future Potential and Innovations
The ongoing research into enhancing PZT materials continues to expand their potential applications. Advances in nanotechnology and material science are paving the way for more efficient and miniaturized sensors. The development of smart sensing systems that integrate PZT with other technologies is an exciting frontier, promising improvements in accuracy, responsiveness, and functionality.
Conclusion
Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT) materials remain at the forefront of sensing technology due to their exceptional piezoelectric properties. While challenges such as environmental impact and material brittleness exist, the advantages they offer in sensitivity, precision, and versatility make them indispensable. As research progresses, the potential for PZT materials in innovative sensing applications is vast, promising a future where sensing technologies are more integrated and efficient than ever before.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com