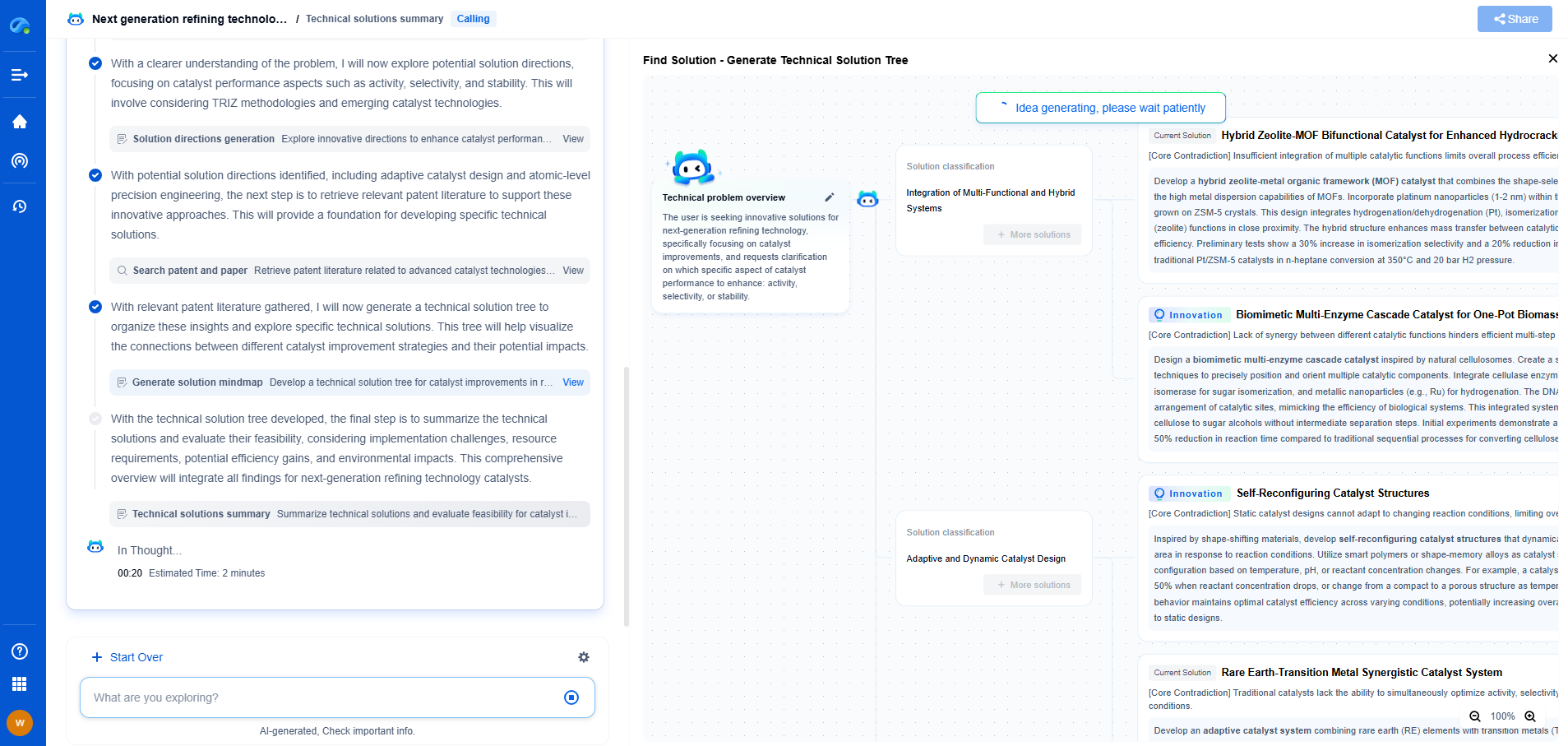
What is a resistivity log and how is it interpreted?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Resistivity logs are a crucial tool in the field of petrophysics and are primarily used in the exploration and evaluation of hydrocarbon reservoirs. They provide valuable information about the subsurface formations that help geoscientists and engineers make informed decisions regarding drilling and production. This blog explores the fundamentals of resistivity logs and their interpretation, offering insights into their significance in the oil and gas industry.
What is a Resistivity Log?
A resistivity log is a type of well log that measures the electrical resistivity of rock formations encountered in a borehole. Resistivity, in this context, refers to the ability of a material to resist the flow of electric current. In the subsurface, this property is influenced by the presence of water, hydrocarbons, and the composition of the rock itself.
The resistivity log is obtained by lowering a tool equipped with electrodes into the wellbore. These electrodes send an electrical current into the surrounding formations, and the tool measures the resulting voltage difference. By analyzing these voltage measurements, the resistivity of the rock can be calculated.
Types of Resistivity Logs
There are several types of resistivity logs, each designed for specific purposes and conditions. Some of the most common types include:
1. **Induction Logs**: These are used primarily in non-conductive mud environments. Induction tools generate an electromagnetic field that induces currents in the surrounding formations. The response is proportional to the formation conductivity, which can be converted to resistivity.
2. **Laterologs**: These are suitable for environments with conductive muds. Laterolog tools inject a focused current into the formation and measure the resulting potential differences, providing a direct resistivity reading.
3. **Microresistivity Logs**: These measure the resistivity of the formations very close to the borehole wall. They are particularly useful for identifying thin beds and determining borehole conditions.
Interpreting Resistivity Logs
Interpreting resistivity logs requires an understanding of the relationship between resistivity values and formation properties. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. **Hydrocarbon Detection**: One of the primary uses of resistivity logs is to identify hydrocarbon-bearing zones. Hydrocarbons are poor conductors of electricity, so formations containing oil or gas will typically show higher resistivity values compared to water-bearing formations.
2. **Porosity and Saturation**: Resistivity logs can help estimate the porosity and fluid saturation of the formation. By combining resistivity data with other logs, such as density or neutron logs, petrophysicists can calculate important reservoir parameters.
3. **Formation Characteristics**: Different rock types have characteristic resistivity ranges. For instance, shales generally exhibit lower resistivity due to their clay content, while clean sandstones and carbonates have higher resistivity.
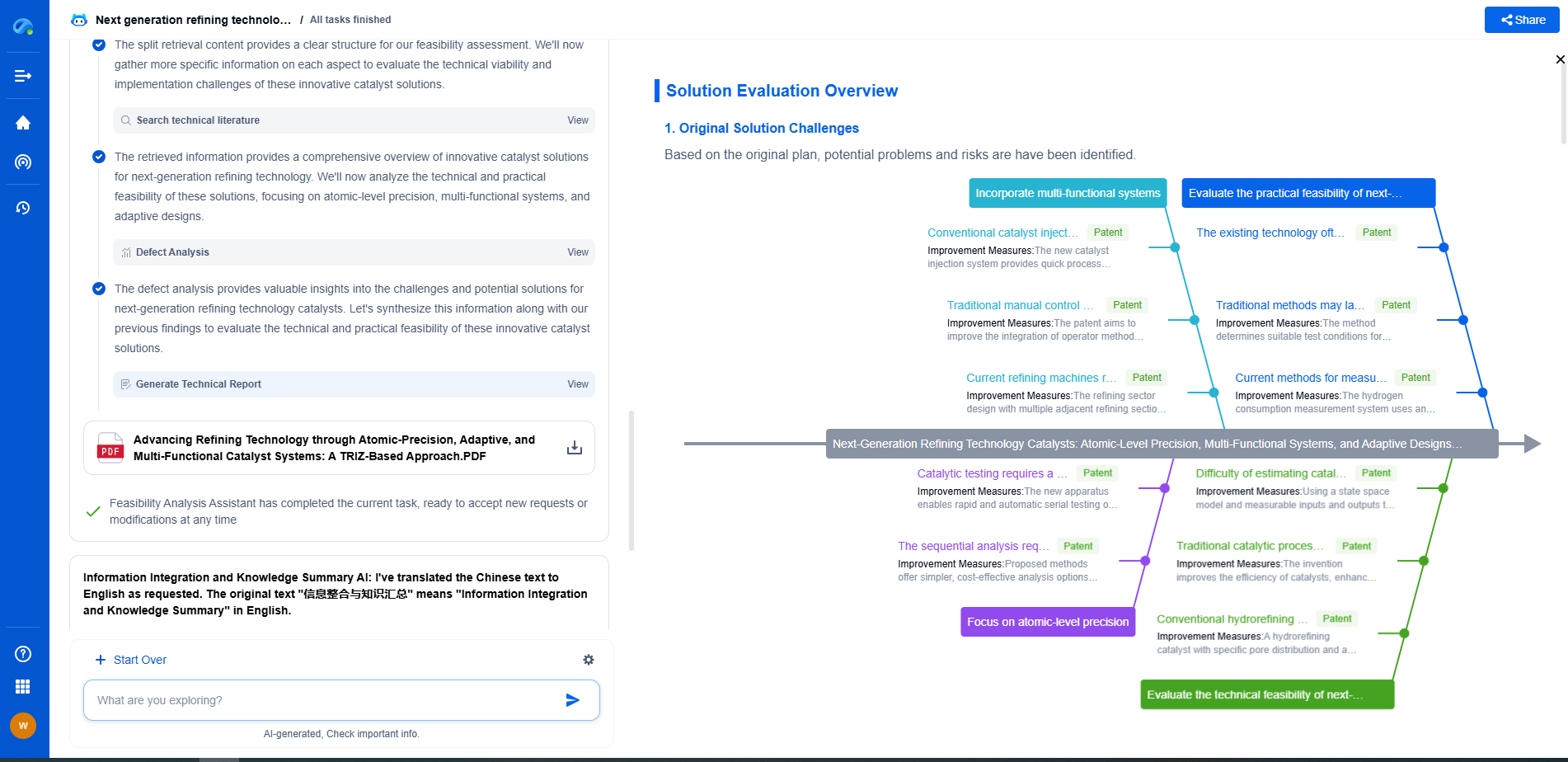
Challenges in Interpretation
While resistivity logs provide valuable information, interpreting them can be challenging due to several factors:
1. **Environmental Effects**: Mud type, borehole size, and temperature can affect resistivity measurements. Proper calibration and corrections are necessary to account for these variables.
2. **Anisotropy**: Some formations might have directional resistivity variations, complicating interpretation. Advanced tools and models are often needed to address anisotropic conditions.
3. **Complex Formations**: In heterogeneous formations with mixed lithologies, interpreting resistivity can be complex. Integration with other logs and geological data is crucial for accurate analysis.
Conclusion
Resistivity logs are indispensable tools in the exploration and development of oil and gas resources, providing critical insights into the subsurface formations. By understanding the principles of resistivity measurement and interpretation, geoscientists can effectively evaluate reservoir potential, aiding in the efficient extraction of hydrocarbons. Despite the complexities involved, advancements in technology and data integration continue to enhance the accuracy and reliability of resistivity log interpretations, enabling more informed decision-making in the energy industry.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com