What is a Torque Converter and How Does It Function?
JUL 2, 2025 |
A torque converter is an essential component in automatic transmissions, acting as a bridge between the engine and the transmission system. Its primary function is to transfer and multiply the engine's torque to the transmission, allowing the vehicle to move. Unlike a manual transmission, which uses a clutch to engage and disengage the engine from the drivetrain, a torque converter achieves this through fluid dynamics.
Components of a Torque Converter
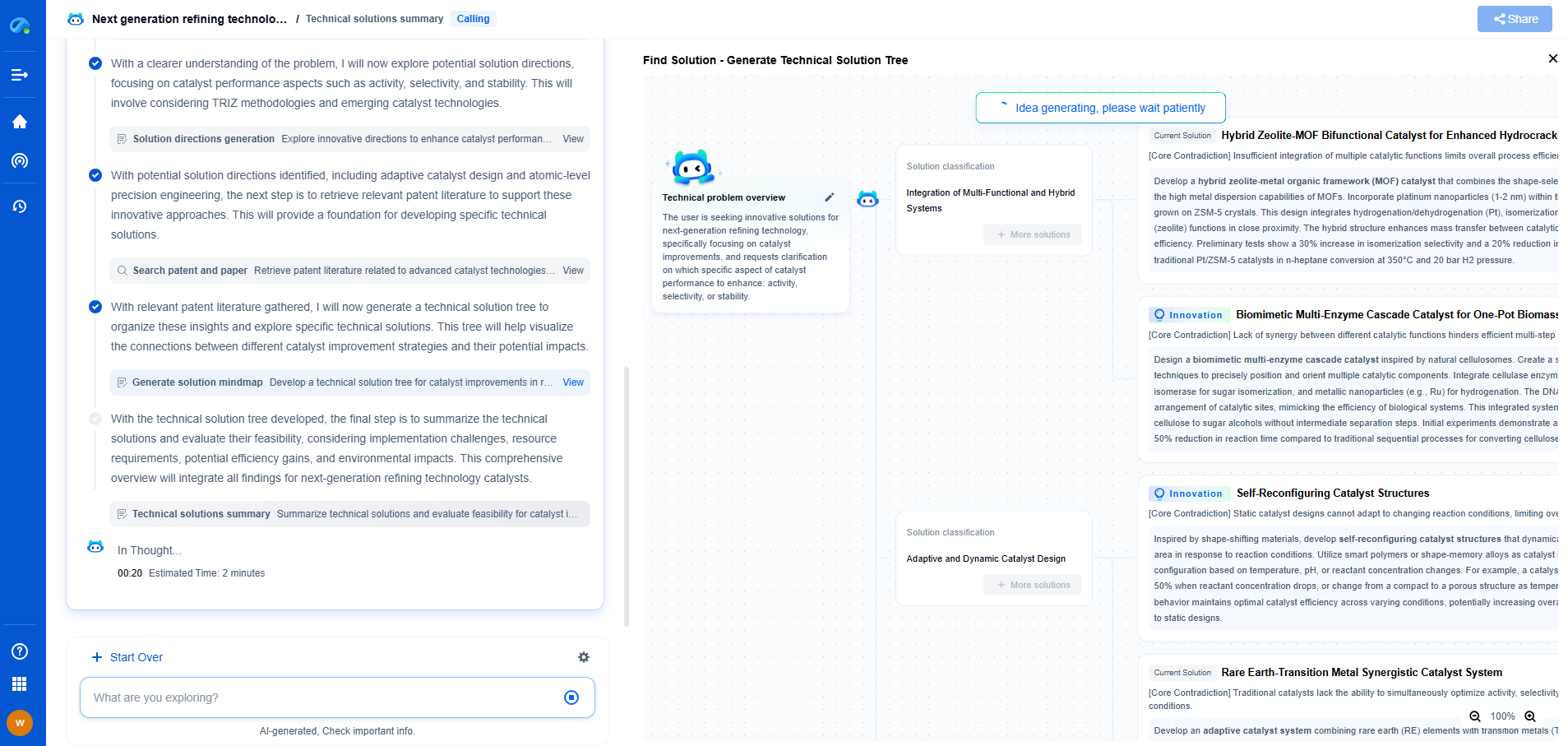
A torque converter consists of four main components: the pump, the turbine, the stator, and the transmission fluid. These elements work together to transmit power and facilitate smooth vehicle operation.
1. Pump: Also known as the impeller, the pump is connected to the engine's flywheel and rotates with the engine. Its main function is to push transmission fluid towards the turbine.
2. Turbine: Located opposite the pump, the turbine is connected to the transmission input shaft. As the fluid from the pump hits the turbine's blades, it causes the turbine to spin, transmitting power to the transmission.
3. Stator: Positioned between the pump and the turbine, the stator redirects fluid from the turbine back to the pump. This component is crucial for torque multiplication, as it increases the efficiency of the fluid flow, allowing for better power transfer.
4. Transmission Fluid: Acting as the medium for power transfer, transmission fluid is circulated between the pump and the turbine. It also serves as a cooling and lubricating agent for the components within the torque converter.
How Does a Torque Converter Function?
The operation of a torque converter relies on the principles of fluid dynamics and centrifugal force. Here’s a step-by-step explanation of how it functions:
1. When the engine starts, the pump rotates with the engine's crankshaft. This rotation causes the transmission fluid inside the torque converter to be thrown outward due to centrifugal force.
2. The outward flow of fluid from the pump hits the turbine blades, causing the turbine to spin. This action transmits power to the transmission, allowing the vehicle to move.
3. As the fluid exits the turbine, it loses some energy but is redirected by the stator towards the pump. The stator plays a crucial role here, as it changes the direction of the returning fluid, increasing its speed before it re-enters the pump.
4. This circulation of fluid creates a continuous cycle of energy transfer from the engine to the transmission, enabling the vehicle to accelerate smoothly.
Torque Multiplication
One of the significant advantages of a torque converter is its ability to multiply torque. During acceleration, when there is a difference in speed between the pump and the turbine, the stator redirects the fluid more efficiently, resulting in increased torque. This multiplication effect provides the necessary power for the vehicle to accelerate from a standstill, making driving smoother and more responsive.
Lockup Clutch Mechanism
Modern torque converters are equipped with a lockup clutch mechanism, which improves efficiency by mechanically locking the turbine to the pump. This eliminates slippage between the components, ensuring that nearly all of the engine's power is transferred to the transmission. The lockup clutch engages at higher speeds, providing better fuel economy and reducing heat buildup within the torque converter.
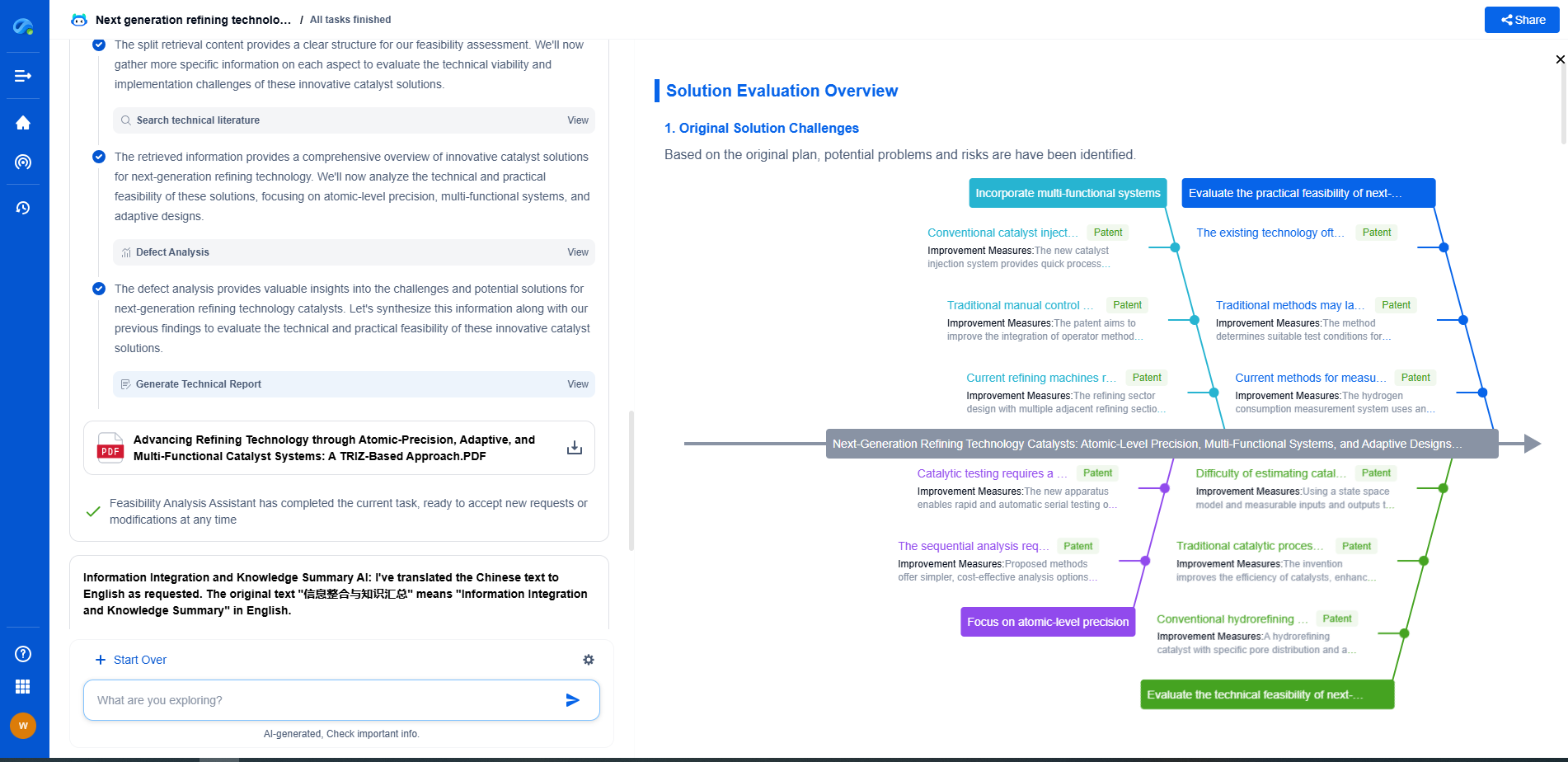
Common Issues and Maintenance
While torque converters are generally robust, they can experience issues such as excessive slipping, shuddering, or overheating. These problems often stem from low transmission fluid levels, worn-out components, or clogged fluid passages. Regular maintenance, including checking and replacing transmission fluid, can help prevent these issues and ensure the longevity of the torque converter.
Conclusion
In summary, a torque converter plays a vital role in the functioning of an automatic transmission by transferring and multiplying engine torque through fluid dynamics. Understanding its components and operation can help drivers appreciate the complexity of their vehicles and maintain their performance over time. By keeping an eye on potential issues and performing regular maintenance, drivers can ensure their torque converters remain in optimal condition, providing smooth and efficient driving experiences.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com