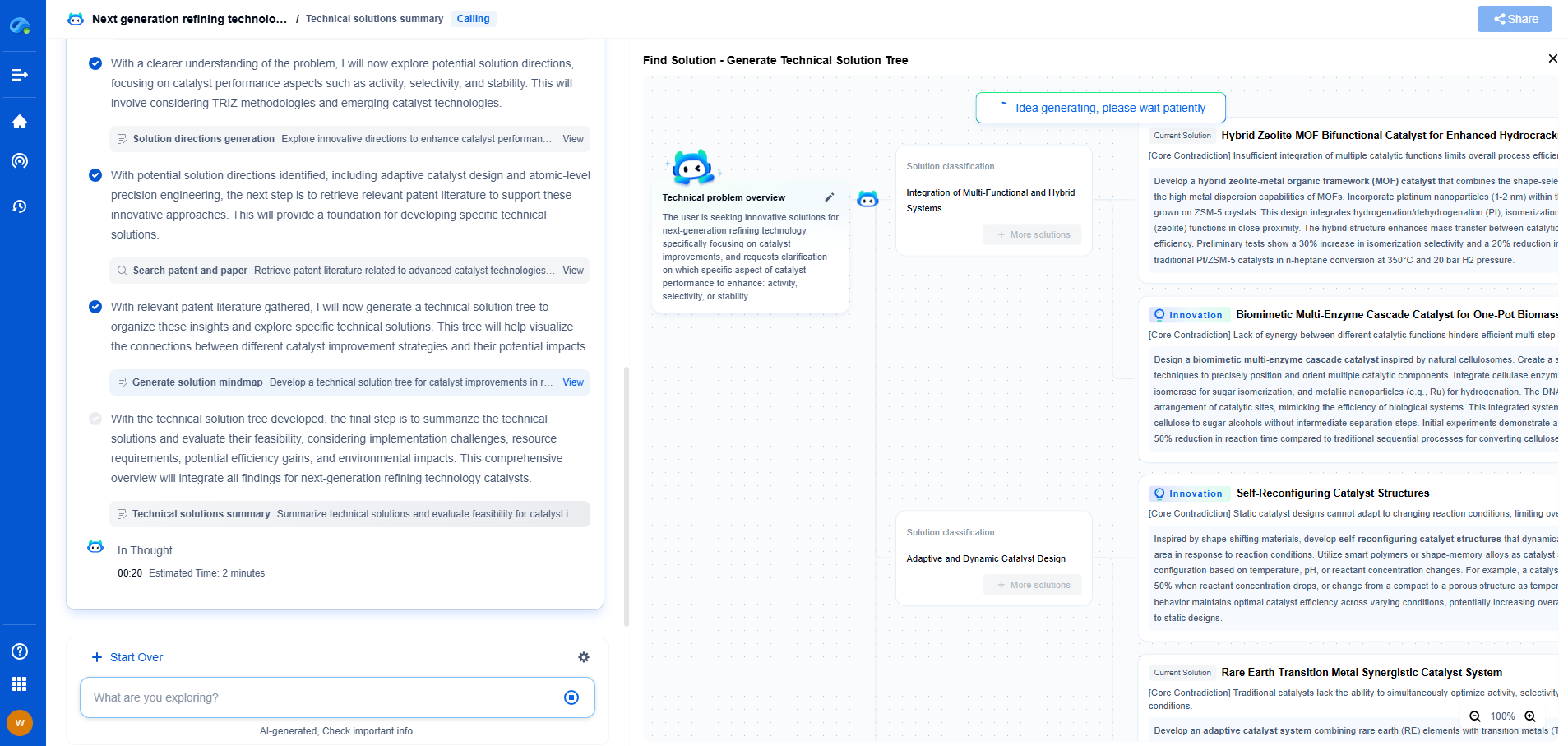
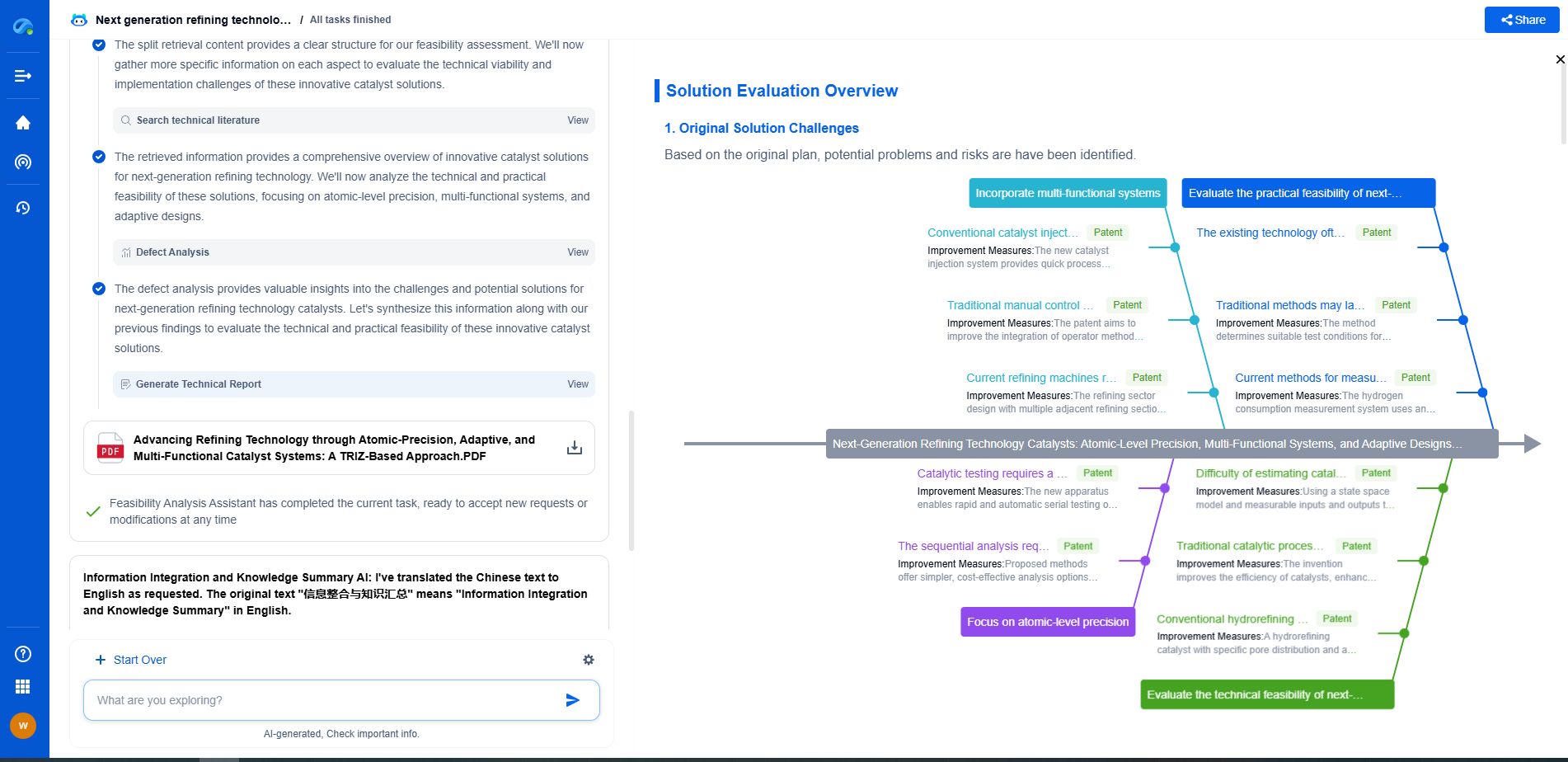
What is BFD Protocol? Achieving Sub-50ms Fault Detection in Carrier Networks
JUN 26, 2025 |
Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) protocol is a network protocol that plays a crucial role in detecting faults in communication paths between two forwarding engines, such as routers or switches. Devised to provide quick and efficient detection of faults in the path between two forwarding engines, BFD serves as a rapid failure detection mechanism for network devices. Its primary function is to ensure uninterrupted network communication by identifying faults that could potentially disrupt data flow in networks, specifically in carrier or service provider networks.
The Need for Rapid Fault Detection
In today's fast-paced digital world, network uptime is critical. Businesses rely heavily on their networks to deliver services, communicate, and operate efficiently. Any downtime can result in significant financial losses and damage to reputation. Traditional methods of failure detection, such as those used by routing protocols, often take several seconds to detect a fault. This is unacceptable in environments that require high availability and minimal disruption. Therefore, the industry demanded a method that could detect failures in mere milliseconds, which is where BFD comes into play.
How BFD Works
BFD operates by establishing a session between two network devices. Once a session is established, the devices exchange control packets at regular intervals. These packets are small in size and provide minimal overhead, ensuring that BFD does not consume significant network resources. The devices involved in the BFD session continuously monitor these packets. If a device does not receive a packet within a specified interval, it concludes that there is a failure in the path and takes necessary actions, such as rerouting the traffic or alerting higher-level protocols to handle the fault.
Sub-50ms Fault Detection
One of the standout features of BFD is its ability to achieve sub-50ms fault detection. This capability is crucial for maintaining the high availability required in carrier networks, where any delay in detecting a fault could lead to data loss or service interruptions. BFD can achieve this rapid detection by allowing devices to send control packets at very high frequencies. For instance, a device might send a packet every 10ms, thus enabling it to detect a fault in less than 50ms if packets are not received as expected.
Implementation in Carrier Networks
In carrier networks, where reliability and uptime are paramount, BFD is implemented to enhance the stability and efficiency of data transmission. These networks often have complex infrastructures with multiple paths and protocols. BFD integrates seamlessly with existing protocols, such as OSPF, BGP, and IS-IS, to provide an additional layer of reliability. By implementing BFD, carriers can ensure that their networks maintain high performance and are resilient to failures, thus delivering uninterrupted service to their customers.
Benefits of Using BFD
The primary advantage of using BFD is its speed in fault detection, which drastically reduces the time it takes to identify and respond to network issues. Additionally, BFD is highly scalable and can be implemented across a wide range of devices and network configurations. It is also protocol-agnostic, meaning it can work alongside various routing protocols without requiring significant changes to the existing network setup. This flexibility makes it an attractive option for service providers looking to enhance their network reliability without overhauling their infrastructure.
Challenges and Considerations
While BFD offers significant benefits, there are challenges and considerations to keep in mind. The rapid detection intervals demand that network devices and infrastructure are capable of handling the increased processing load. Furthermore, improper configuration of BFD can lead to false positives, where the protocol mistakenly identifies a fault, causing unnecessary rerouting and potential network congestion. Therefore, careful planning and configuration are essential to ensure that BFD performs as intended.
Conclusion
BFD protocol is an invaluable tool in modern carrier networks, providing rapid fault detection to ensure high availability and reliability. Its ability to detect faults in under 50ms makes it an essential component for service providers that require seamless and efficient network operations. As networks continue to grow in complexity and demand for uninterrupted service increases, the role of BFD in maintaining network integrity will only become more significant. By understanding and properly implementing BFD, network operators can enhance their service offerings and provide their customers with the reliability they demand.
Unleash the Full Potential of AI Innovation with Patsnap Eureka
The frontier of machine learning evolves faster than ever—from foundation models and neuromorphic computing to edge AI and self-supervised learning. Whether you're exploring novel architectures, optimizing inference at scale, or tracking patent landscapes in generative AI, staying ahead demands more than human bandwidth.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
👉 Try Patsnap Eureka today to accelerate your journey from ML ideas to IP assets—request a personalized demo or activate your trial now.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com