What Is Cathodic Protection in Pipelines?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Cathodic protection is a crucial technique employed to safeguard pipelines from corrosion, which is a major concern in industries relying on metal infrastructure for transporting fluids. Corrosion weakens pipelines, leading to leaks, failures, and significant economic and environmental consequences. Cathodic protection helps extend the lifespan of pipelines by reducing the rate of corrosion, making it an indispensable method for maintaining the integrity of these critical systems.
The Basics of Corrosion
To grasp the concept of cathodic protection, it is essential to understand the basics of corrosion. Corrosion is an electrochemical process that occurs when metal is exposed to a corrosive environment, such as soil or water. In pipelines, this typically involves the metal reacting with oxygen, moisture, and other chemicals, leading to the formation of rust and a gradual deterioration of the metal.
Corrosion occurs in an electrochemical cell, where the metal acts as an anode (where oxidation occurs) and another material acts as a cathode (where reduction occurs). This process creates an electric current that facilitates the gradual breakdown of the metal. The goal of cathodic protection is to manipulate this electrochemical cell to prevent corrosion.
Types of Cathodic Protection
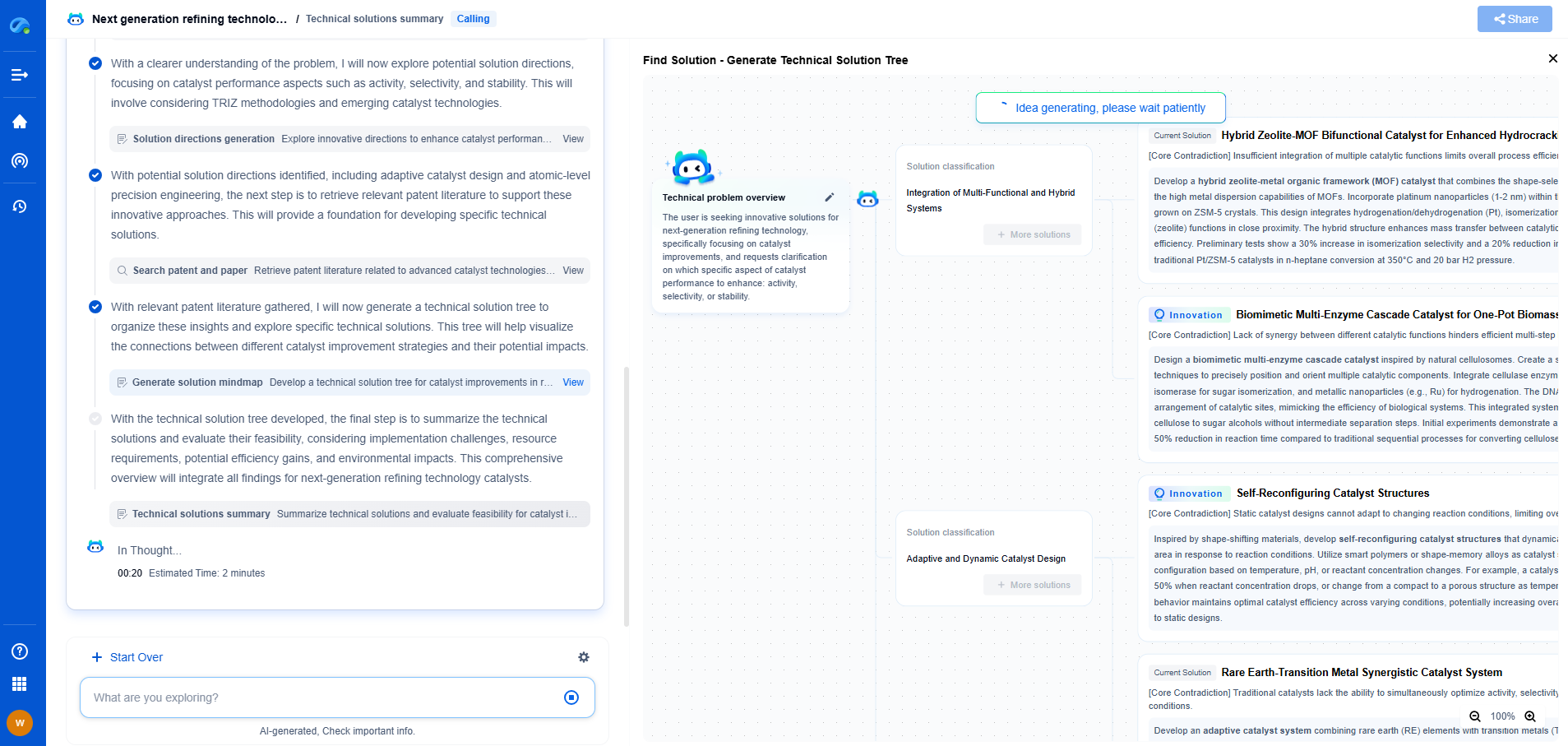
There are two primary types of cathodic protection used in pipelines: sacrificial anode cathodic protection and impressed current cathodic protection.
1. Sacrificial Anode Cathodic Protection:
In this method, more reactive metals, known as sacrificial anodes, are attached to the pipeline. These anodes, typically made from materials like zinc, magnesium, or aluminum, are more prone to corrosion than the pipeline itself. As a result, the sacrificial anodes corrode instead of the pipeline, effectively “sacrificing” themselves to protect the primary metal structure. This method is relatively simple and cost-effective, making it suitable for small-scale or less critical pipeline applications.
2. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection:
This method involves the use of an external power source to provide a constant flow of direct current (DC) to the pipeline. Anodes made of materials like graphite, mixed metal oxide, or high-silicon cast iron are installed in the soil or water around the pipeline, and the DC current is applied to make the pipeline act as a cathode. This approach is used for larger and more complex pipeline systems, offering greater control and protection against corrosion over long distances.
Applications and Benefits
Cathodic protection is widely used in various industries, including oil and gas, water supply, and chemical processing. It is especially crucial in pipelines that traverse areas with high moisture content, saline environments, or aggressive soil conditions. The benefits of cathodic protection are numerous:
1. Longevity: By significantly reducing the rate of corrosion, cathodic protection extends the operational lifespan of pipelines, delaying the need for costly replacements.
2. Safety: Minimizing corrosion helps prevent leaks and failures, ensuring the safe transport of hazardous materials and reducing the risk of environmental contamination and accidents.
3. Cost-Effectiveness: Although there is an initial investment, cathodic protection systems are cost-effective over time, reducing maintenance costs and preventing expensive repairs.
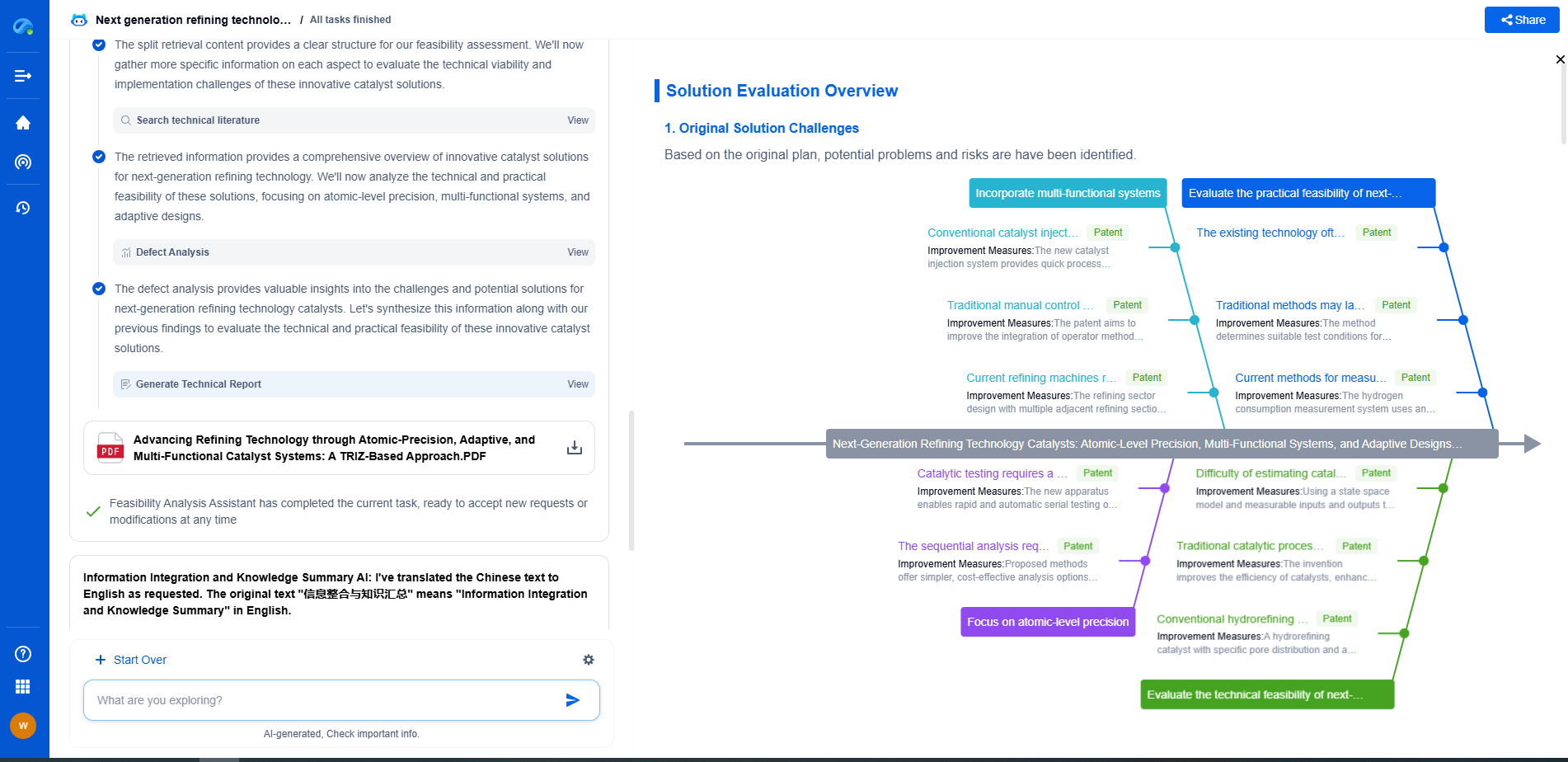
Challenges and Considerations
While cathodic protection is highly effective, it is not without its challenges. The design and implementation require careful consideration of various factors, including soil resistivity, pipeline material, and environmental conditions. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the system are essential to ensure its continued effectiveness. Furthermore, impressed current systems require a reliable power source and can be more complex to install and operate compared to sacrificial anode systems.
Conclusion
Cathodic protection plays a vital role in the preservation and maintenance of pipelines, a backbone of numerous industries worldwide. By understanding the principles of corrosion and employing effective cathodic protection strategies, pipeline operators can ensure the safety, reliability, and longevity of their infrastructure. As technology advances, improvements in cathodic protection systems will continue to enhance their efficiency, further securing the pipelines that underpin modern society.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com