What is cementing in well construction?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Understanding Cementing
Cementing refers to the process of placing a cement slurry between the casing and the wellbore to isolate the wellbore from the surrounding rock formations. This procedure is vital in ensuring the integrity of the well and preventing the migration of fluids between different geological layers. The cement acts as a seal to stabilize the wellbore, support the casing, and protect it from corrosive formation fluids.
The Cementing Process
The cementing process begins after the well has been drilled to the desired depth and the casing has been installed. The casing is a large-diameter pipe that is inserted into the wellbore to maintain its structural integrity and prevent contamination of aquifers. Once the casing is in place, the cement slurry is pumped down through it and back up into the annular space, the gap between the casing and the wellbore wall. The slurry is then allowed to harden and form a solid sheath around the casing.
Types of Cementing Operations
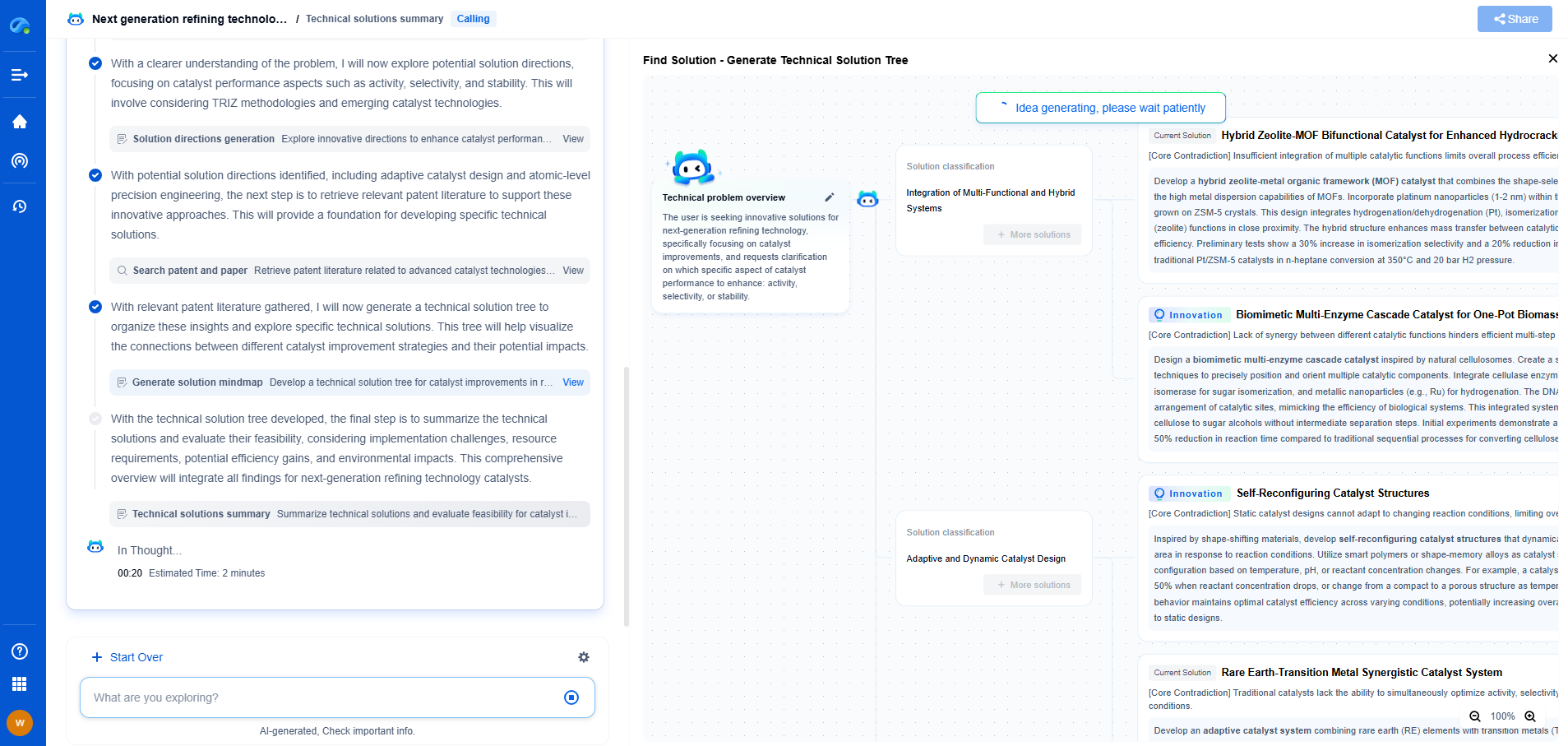
There are various types of cementing operations, each serving a specific purpose in well construction. Primary cementing is the initial placement of cement to achieve zonal isolation. Remedial cementing involves correcting issues in the well, such as leaks or casing failures. It may also include squeeze cementing, where cement is forced into specific sections to seal off unwanted fluid paths.
Materials Used in Cementing
The primary material used in cementing is Portland cement, which is mixed with water and various additives to create a slurry with the desired properties. Additives can enhance the slurry's viscosity, density, and setting time to suit the specific conditions of the well. For instance, retarders may be used to slow the setting time in high-temperature environments, while accelerators can speed up the process in colder conditions.
Challenges in Cementing
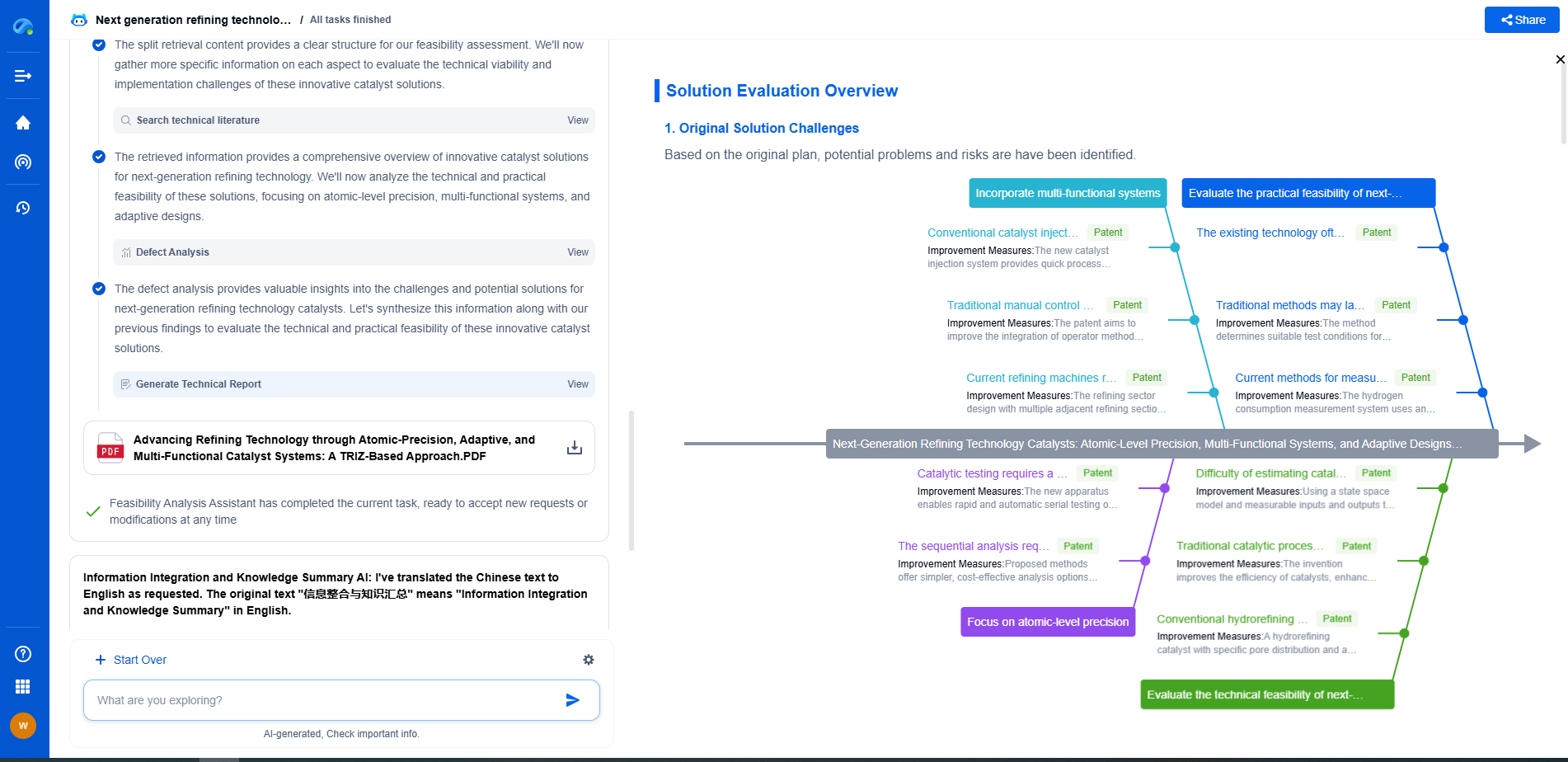
Cementing operations can be fraught with challenges, including the risk of poor bonding between the cement and the casing or formation. Such issues can lead to gas migration, where gas escapes from the reservoir and migrates to the surface, posing safety and environmental hazards. Achieving a successful cement job requires careful planning, precise execution, and thorough evaluation of subsurface conditions.
Technological Advances
Recent technological advances have significantly improved the cementing process. Innovations such as advanced cement formulations, real-time monitoring systems, and enhanced placement techniques have increased the reliability and effectiveness of cementing operations. These advancements help ensure that wells are constructed safely and sustainably, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource recovery.
Conclusion
Cementing in well construction is an indispensable process that safeguards the structural integrity and productivity of wells. By creating a reliable barrier between the wellbore and the surrounding formations, cementing prevents fluid migration, protects groundwater resources, and ensures efficient resource extraction. As technology continues to evolve, the cementing process will become even more robust, supporting the energy industry's ongoing efforts to meet global energy demands safely and efficiently.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com