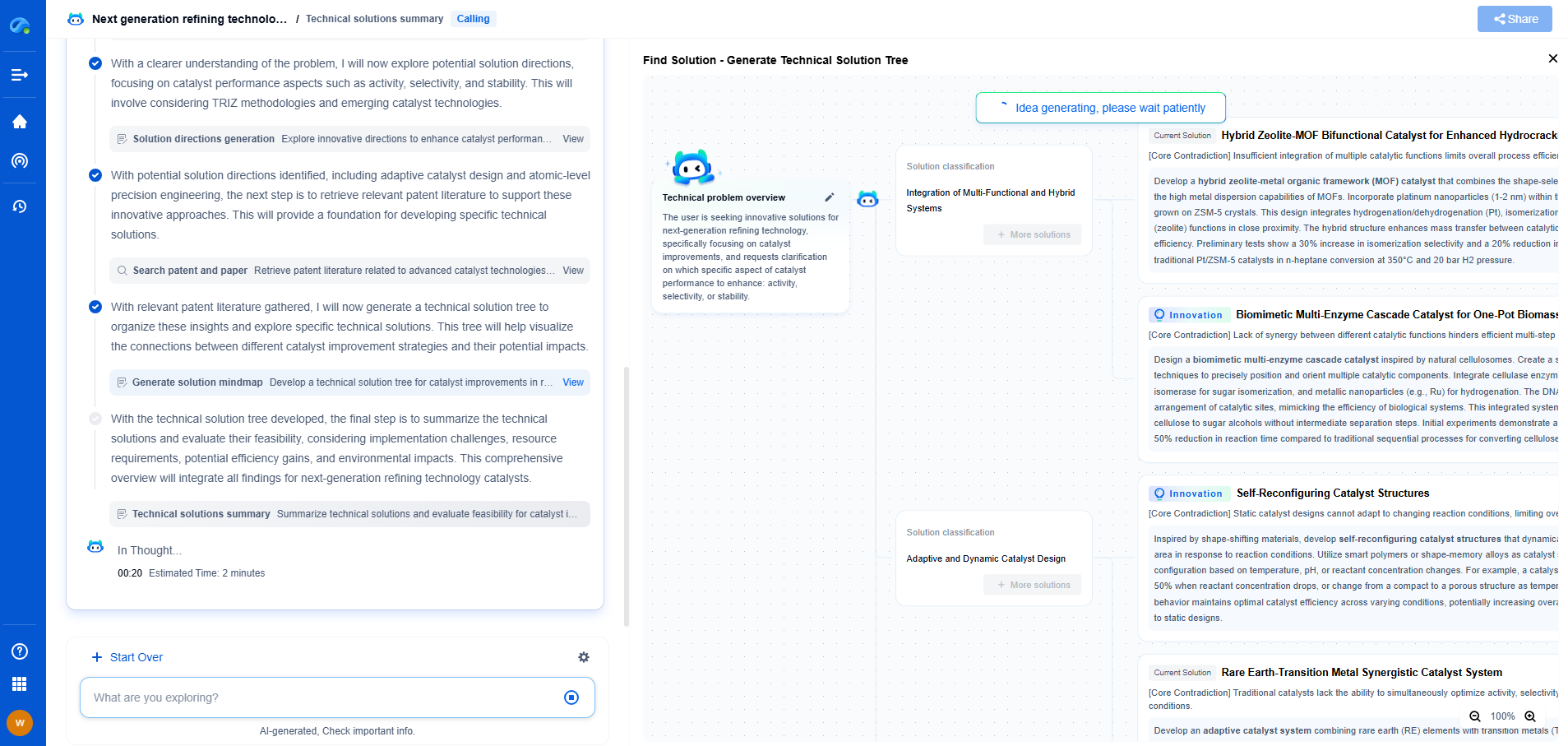
What is hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and how is it used in unconventional drilling?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, is a technique used to extract oil and natural gas from deep underground formations. This method has revolutionized the energy industry, allowing access to previously inaccessible resources. Fracking involves injecting a high-pressure fluid mixture into subterranean rock formations to create small fractures. These fractures release oil and natural gas, which can then be collected and brought to the surface.
The Fracking Process Explained
The process begins with drilling a vertical or horizontal well into the rock formation. Once the desired depth is reached, a perforating gun is used to create small holes in the wellbore, which allows the fracking fluid to be injected. This fluid is composed of water, sand, and a mix of chemicals that help in breaking the rock and keeping the fractures open.
The high-pressure injection of fracking fluid generates fractures in the rock, and the sand in the mixture acts as a proppant, holding the fractures open once the pressure is released. This allows the trapped oil and gas to flow more freely into the well, from where it can be extracted to the surface.
Fracking in Unconventional Drilling
Unconventional drilling refers to methods used to extract oil and natural gas from rock formations where traditional drilling techniques are ineffective. Fracking is a key component of unconventional drilling, particularly in shale formations. Shale rock is typically dense and non-porous, making traditional extraction methods insufficient. Fracking enables the release of hydrocarbons from these tightly packed formations.
Horizontal drilling, often paired with fracking, is a pivotal technique in unconventional drilling. By drilling horizontally along the rock layer, more of the resource-rich formation is exposed to the fracking process, significantly increasing the potential yield from a single well.
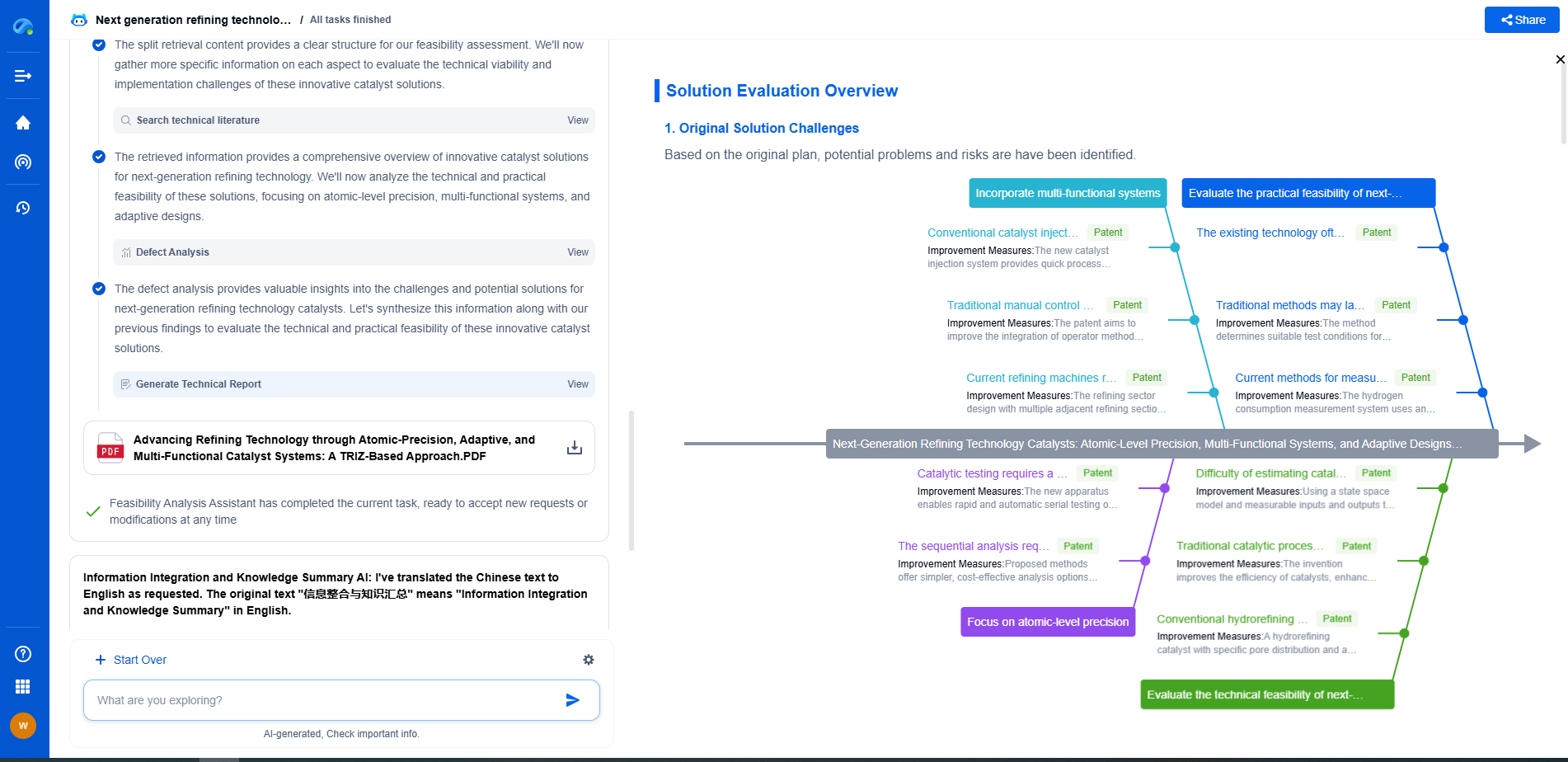
Environmental and Economic Impact
The use of fracking has generated both economic benefits and environmental concerns. On the economic front, fracking has contributed to the increase in domestic oil and gas production, reducing reliance on foreign energy sources and lowering energy costs. The technique has also spurred job creation in many regions, particularly in areas rich in shale formations.
However, environmental considerations cannot be overlooked. Fracking has been associated with potential risks such as groundwater contamination, increased seismic activity, and significant water usage. The chemicals used in the fracking fluid, if not managed properly, could pose a threat to water supplies. Moreover, the disposal of wastewater from fracking operations presents further environmental challenges.
Regulation and Technological Advancements
To address environmental concerns, regulations governing fracking operations have been put in place in various jurisdictions. These regulations aim to ensure that fracking is conducted safely and responsibly, minimizing risks to the environment and public health. Operators are required to disclose the composition of their fracking fluids, and measures are enforced to protect water sources and manage waste disposal.
Technological advancements continue to improve the efficiency and safety of fracking. Researchers are exploring the use of more environmentally friendly additives and methods to recycle water used in the fracking process. Additionally, innovations in seismic monitoring help mitigate the risk of induced earthquakes.
Conclusion
Hydraulic fracturing has undeniably transformed the landscape of energy production, unlocking vast reserves of oil and natural gas. As the demand for energy continues to grow, fracking remains a critical tool in meeting global energy needs. However, balancing the economic benefits with environmental stewardship is essential. Continued innovation and stringent regulations will play a crucial role in ensuring that fracking is conducted safely and sustainably, allowing us to harness its potential while protecting our planet.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com