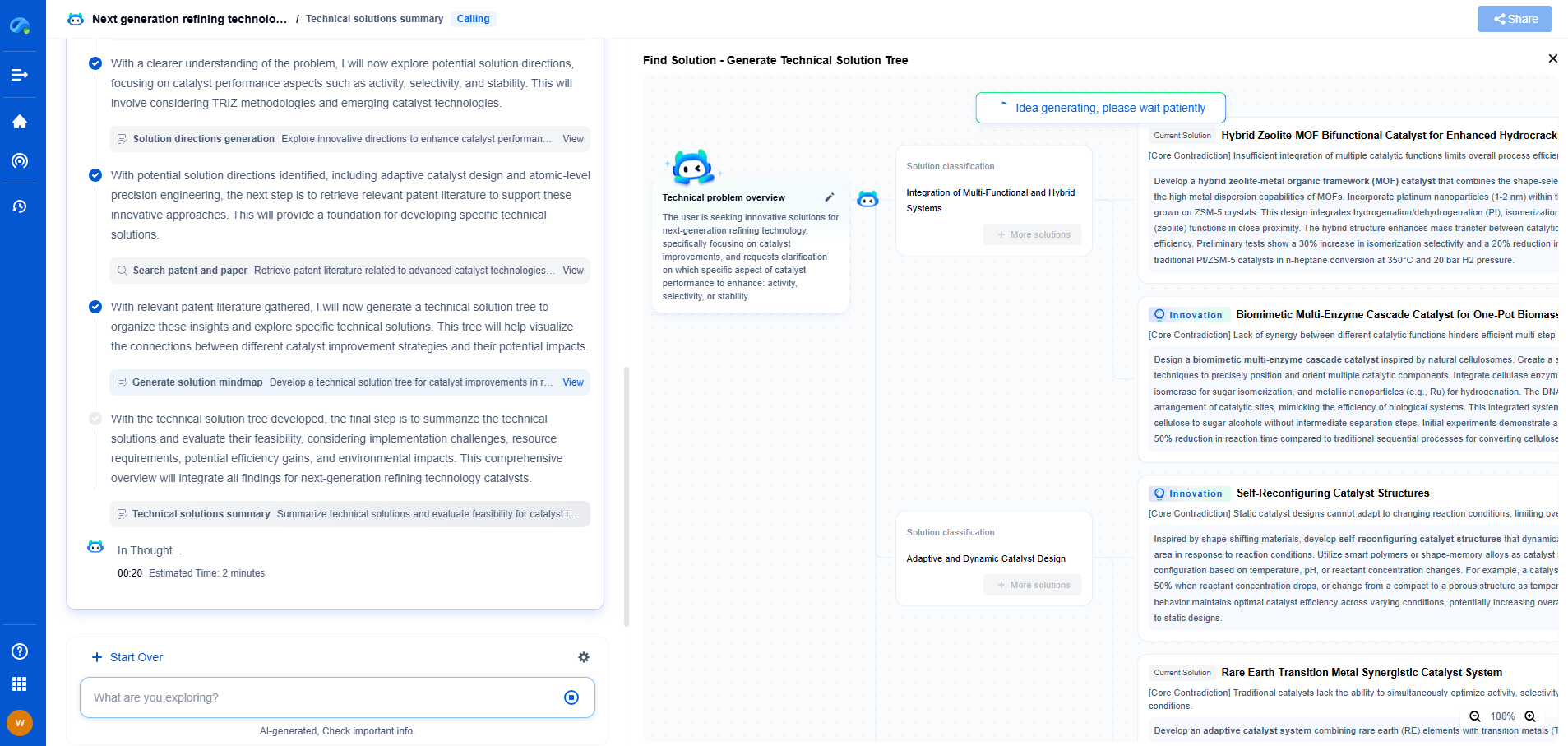
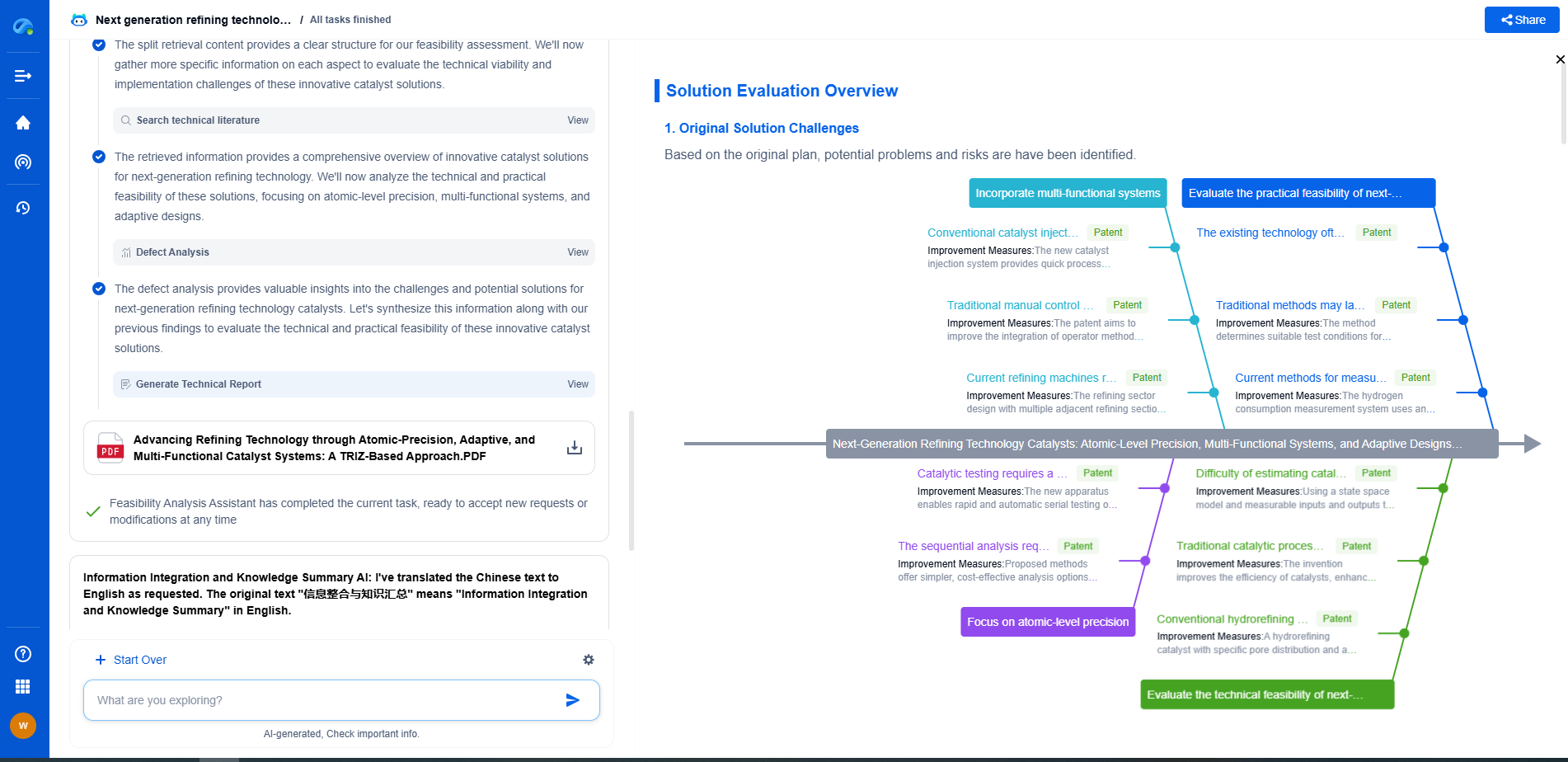
What Is Photogrammetry? Principles, Applications, and Tools
JUL 10, 2025 |
Understanding Photogrammetry
At its core, photogrammetry is the science of making measurements from photographs. It involves the use of overlapping photographs to create maps, drawings, measurements, or 3D models of real-world objects and environments. The fundamental principle of photogrammetry is triangulation, where multiple images taken at different angles are used to determine the exact positions of points in three-dimensional space.
Photogrammetry is divided into two main categories: aerial photogrammetry and terrestrial photogrammetry. Aerial photogrammetry involves taking photographs from an elevated position, typically using drones or airplanes, to map large areas like landscapes, cities, or archaeological sites. Terrestrial photogrammetry, on the other hand, involves taking images from the ground level, often used for smaller-scale projects like building documentation or forensic analysis.
Principles of Photogrammetry
The primary principles that govern photogrammetry are:
1. **Overlapping Images**: To extract 3D information from 2D images, sufficient overlap between images is required. This allows for accurate triangulation and the creation of a coherent 3D model.
2. **Camera Calibration**: To ensure precision, the camera's internal parameters such as focal length, lens distortion, and sensor size must be known and accounted for in the analysis.
3. **Control Points**: These are known points in the area being photographed, used to orient and scale the photogrammetry output accurately.
4. **Data Processing Algorithms**: Advanced algorithms and software are used to process the data, match key points across images, and reconstruct the 3D model or map.
Applications of Photogrammetry
Photogrammetry finds its application across a wide array of fields, owing to its versatility and precision.
1. **Cartography and Geography**: Photogrammetry is extensively used in creating topographic maps. By analyzing aerial photographs, cartographers can produce accurate maps that reflect the terrain's elevation and features.
2. **Architecture and Construction**: In architecture, photogrammetry is employed to document existing structures, allowing architects to create accurate blueprints and plans. It is also used in construction to monitor site progress and ensure that projects adhere to the original designs.
3. **Archaeology**: Archaeologists use photogrammetry to document and analyze excavation sites, preserving a digital record of artifacts and site layouts which aids in research and public dissemination.
4. **Forensics**: In forensic investigations, photogrammetry assists in reconstructing accident scenes or crime sites, providing accurate and detailed models that can be analyzed for evidence.
5. **Film and Gaming Industries**: In these industries, photogrammetry is used to create realistic 3D models and environments, enhancing the visual experience with highly detailed textures and surfaces.
Tools and Software for Photogrammetry
Several tools and software are available that facilitate the process of photogrammetry, ranging from basic to highly advanced systems.
1. **Agisoft Metashape**: A popular choice for professionals, Metashape offers advanced photogrammetric processing of digital images and 3D spatial data generation.
2. **Pix4D**: Known for its user-friendly interface, Pix4D provides solutions for capturing, processing, and analyzing drone data.
3. **RealityCapture**: This software is recognized for its speed and efficiency in producing highly detailed models and maps, making it a favorite among professionals in various industries.
4. **DroneDeploy**: Primarily used for aerial photogrammetry, DroneDeploy offers a comprehensive suite of tools for mapping, modeling, and analysis.
Conclusion
Photogrammetry stands as a vital tool in the modern data-driven world, offering precise and detailed insights across a wide range of applications. Whether for creating maps, reconstructing historical sites, or enhancing digital media, the principles and tools of photogrammetry continue to evolve, unlocking new possibilities and expanding its impact on various industries. As technology advances, the integration of photogrammetry with other technologies like AI and machine learning promises to further revolutionize how we capture and interpret the world around us.
Image processing technologies—from semantic segmentation to photorealistic rendering—are driving the next generation of intelligent systems. For IP analysts and innovation scouts, identifying novel ideas before they go mainstream is essential.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
🎯 Try Patsnap Eureka now to explore the next wave of breakthroughs in image processing, before anyone else does.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com