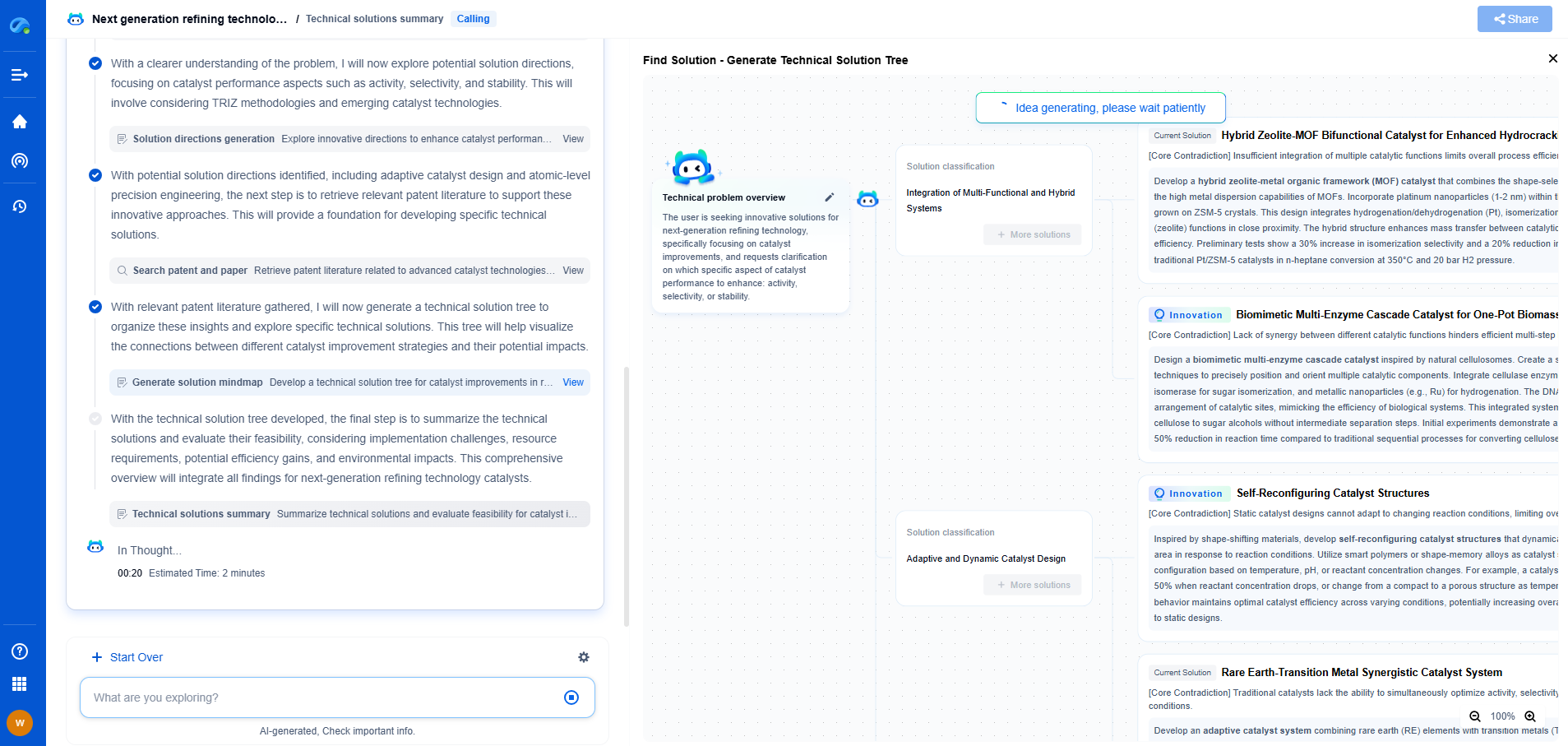
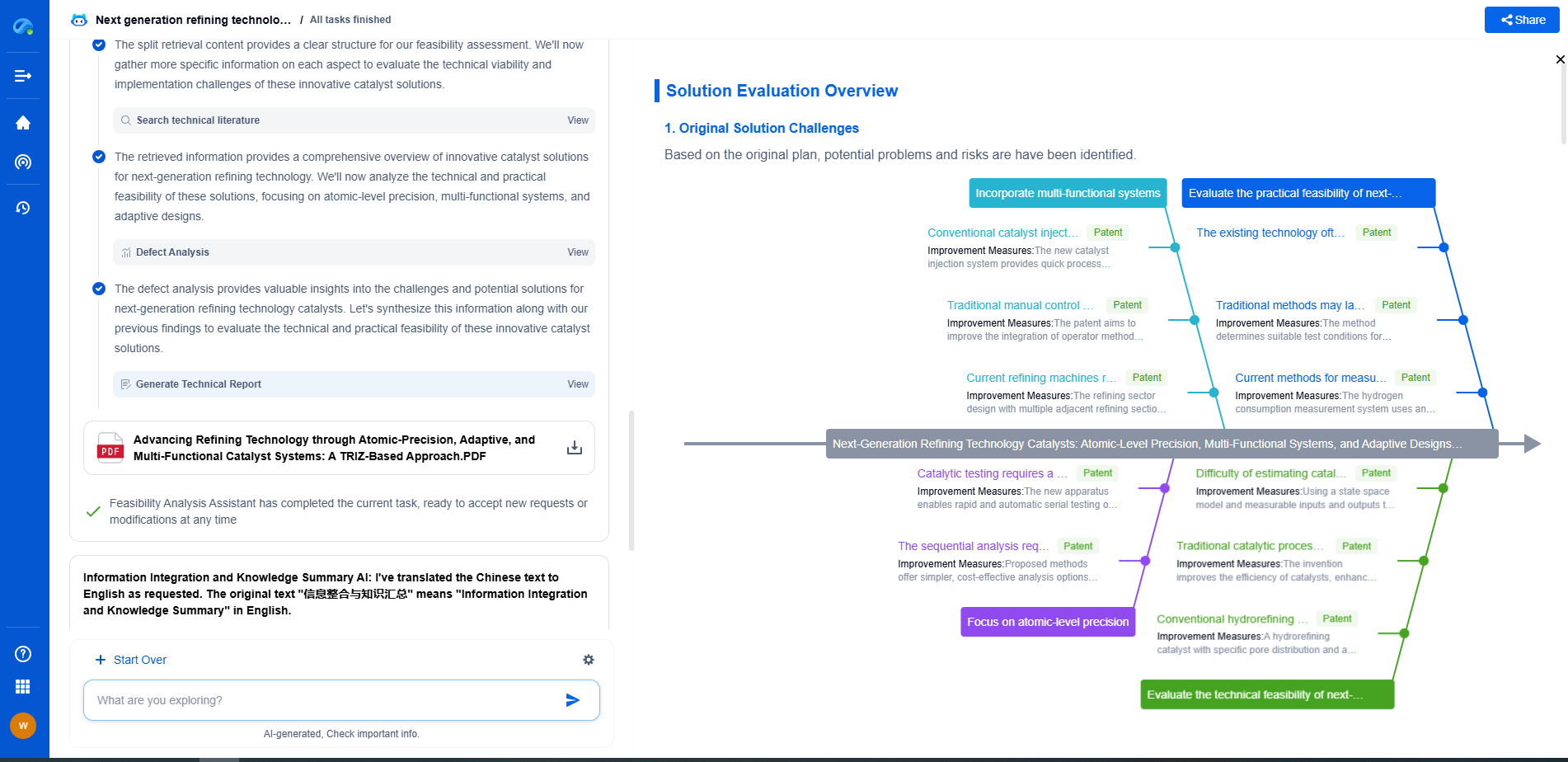
What Is Pipe Wall Thickness and How Does It Affect Performance?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Pipe wall thickness is a crucial parameter in the design and functionality of piping systems. It refers to the distance between the inner and outer surfaces of a pipe, typically measured in millimeters or inches. This seemingly simple characteristic has a significant impact on the performance, durability, and safety of the piping system.
Factors Determining Pipe Wall Thickness
Several factors determine the appropriate wall thickness for a pipe, including the material used, the intended application, and the operating conditions. For instance, pipes designed to transport hazardous materials or fluids at high temperatures and pressures generally have thicker walls to ensure safety and prevent leaks. Material properties such as tensile strength and resistance to corrosion also influence the required wall thickness.
Types of Pipe Wall Thickness
The wall thickness of pipes can vary significantly depending on their classification and intended use. Pipes are often classified by "schedule," which is a standardized system indicating the wall thickness relative to the pipe diameter. Common schedules include Schedule 40, Schedule 80, and Schedule 120, with higher numbers indicating thicker walls. Pipes can also be classified by class, which similarly relates to pressure handling capabilities.
Impact on Performance
The thickness of a pipe’s wall has several implications for its performance. Firstly, thicker walls generally offer better strength and durability, enabling pipes to handle higher pressures and withstand external forces. This is particularly important in industries like oil and gas, where pipes are subject to extreme conditions. Thicker walls also help in reducing the risk of pipe rupture or failure, offering peace of mind in critical applications.
Moreover, wall thickness affects the flow characteristics within the pipe. Thicker walls reduce the internal diameter, potentially impacting the flow rate of fluids. Engineers must account for this when designing systems to ensure optimal flow and avoid pressure drop issues. In applications where fluid flow efficiency is critical, such as water distribution systems, the balance between wall thickness and internal diameter becomes a key consideration.
Durability and Maintenance
From a maintenance perspective, pipes with thicker walls tend to have longer lifespans and require less frequent replacements. They are better suited to handle wear and tear caused by abrasive materials, extreme temperatures, or corrosive substances. This longevity translates to reduced maintenance costs and enhanced reliability, which is especially valuable in industrial settings where downtime can be costly.
However, it is important to note that increased wall thickness also means a heavier pipe, which can complicate installation and increase transportation costs. Therefore, choosing the right wall thickness involves a trade-off between durability and logistical considerations.
Safety Considerations
Safety is another critical aspect influenced by pipe wall thickness. Adequate wall thickness ensures that pipes can withstand internal pressures without bursting, protecting both the environment and human health. In the case of transporting hazardous materials, this is vital to prevent leaks and spills. Engineers must carefully calculate the appropriate wall thickness to meet safety standards and regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
In summary, pipe wall thickness is a fundamental aspect of piping system design that affects performance, durability, flow characteristics, maintenance needs, and safety. Understanding the factors that influence wall thickness and its impact on various applications is essential for making informed decisions in engineering and design processes. By considering these elements, industries can optimize their piping systems to meet specific operational requirements while ensuring safety and efficiency.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com