What is QoS in Networking? How Packet Prioritization Works (DSCP vs. ToS Field Comparison)
JUN 26, 2025 |
Quality of Service (QoS) is a pivotal concept in networking that ensures the efficient management and prioritization of data packets. As networks handle diverse types of traffic, ranging from video streaming to voice calls, QoS becomes essential in maintaining performance and reliability. By managing bandwidth and prioritizing traffic, QoS ensures that critical applications receive the necessary resources to function optimally, thereby enhancing overall user experience.
Importance of QoS
In today's digital landscape, networks carry a wide variety of data, each with its own requirements. Video conferencing, VoIP calls, and online gaming, for example, are highly sensitive to delays and packet loss. Without QoS, all data packets would be treated equally, potentially leading to congestion and degraded performance for latency-sensitive applications. QoS mechanisms help allocate bandwidth dynamically, minimize latency, and reduce jitter, ensuring that high-priority traffic maintains its integrity during transmission.
Packet Prioritization Mechanisms
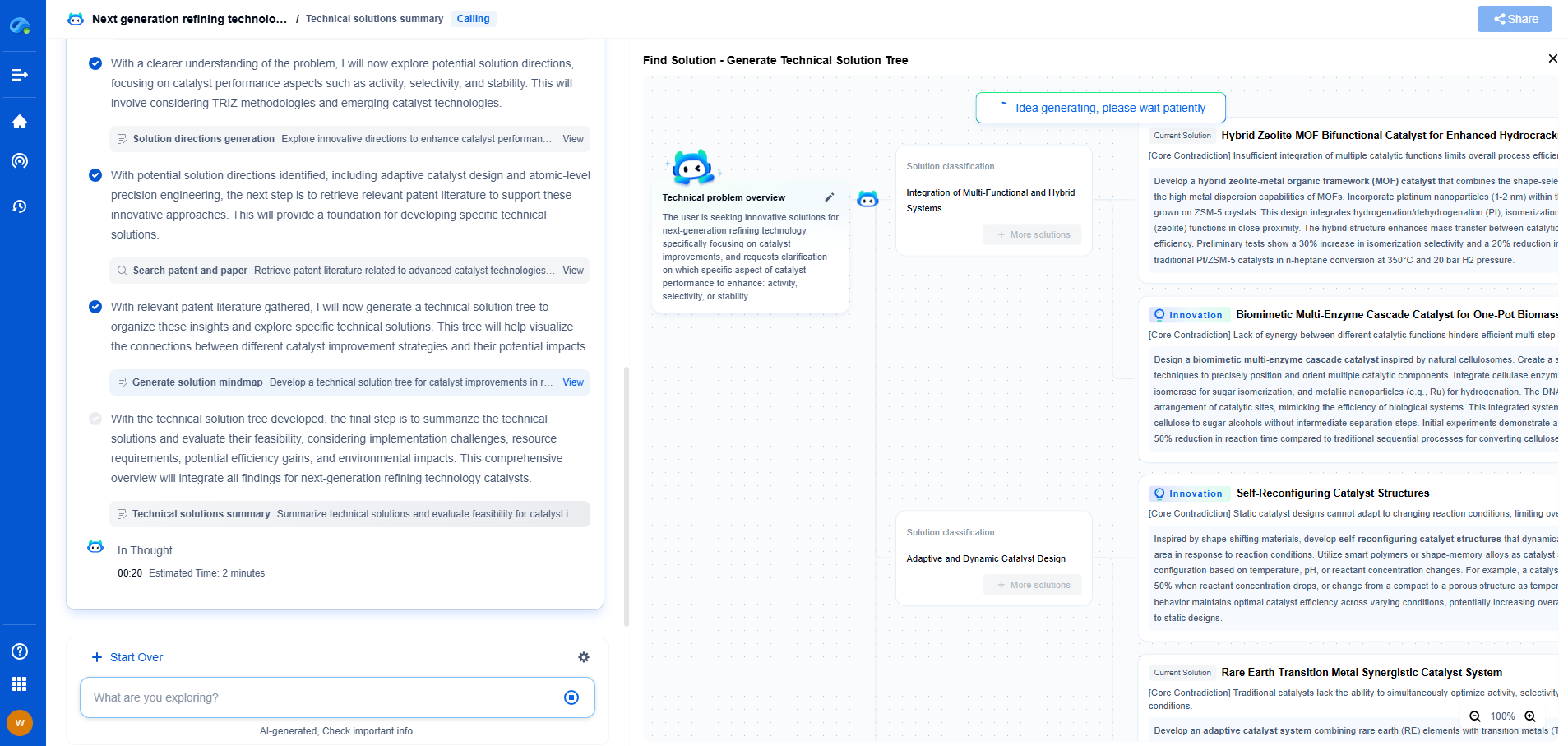
Packet prioritization is at the heart of QoS. It involves categorizing and managing data packets based on predefined policies to ensure that high-priority traffic gets the attention it requires. Two primary methods for packet prioritization in IP networks are the Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) and the Type of Service (ToS) field.
Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP)
DSCP is a part of the IP header used to classify and manage network traffic. It defines a 6-bit field in the IP header, allowing for 64 different classes of traffic. Each class is associated with a specific level of service, which network devices use to determine how packets should be handled. By marking packets with DSCP values, network administrators can ensure that critical traffic receives priority treatment, such as expedited forwarding or assured forwarding, depending on the network's needs.
Type of Service (ToS) Field
The Type of Service field is an older method for managing network traffic and is present in the IP header. Originally, the ToS field was an 8-bit field, but its use has evolved over time. The ToS field allows network administrators to specify the desired priority of packets, influencing how routers and switches handle them. Though it is less granular than DSCP, the ToS field can still impact packet handling by indicating whether a packet requires low latency, high throughput, or high reliability.
DSCP vs. ToS: A Comparative Analysis
While both DSCP and ToS aim to prioritize network traffic, they have distinct characteristics. DSCP offers a more granular approach with its 64 possible classes, enabling finer control over network traffic. This makes it more suitable for modern networks with complex requirements. On the other hand, the ToS field provides a simpler mechanism but with limited flexibility, which can still be effective in less complex network environments.
In practice, DSCP is more widely adopted due to its scalability and compatibility with modern QoS policies. It allows network devices to efficiently manage a diverse range of services and applications, adapting to varying network conditions. However, ToS can still be useful in specific scenarios where its simpler configuration meets network needs.
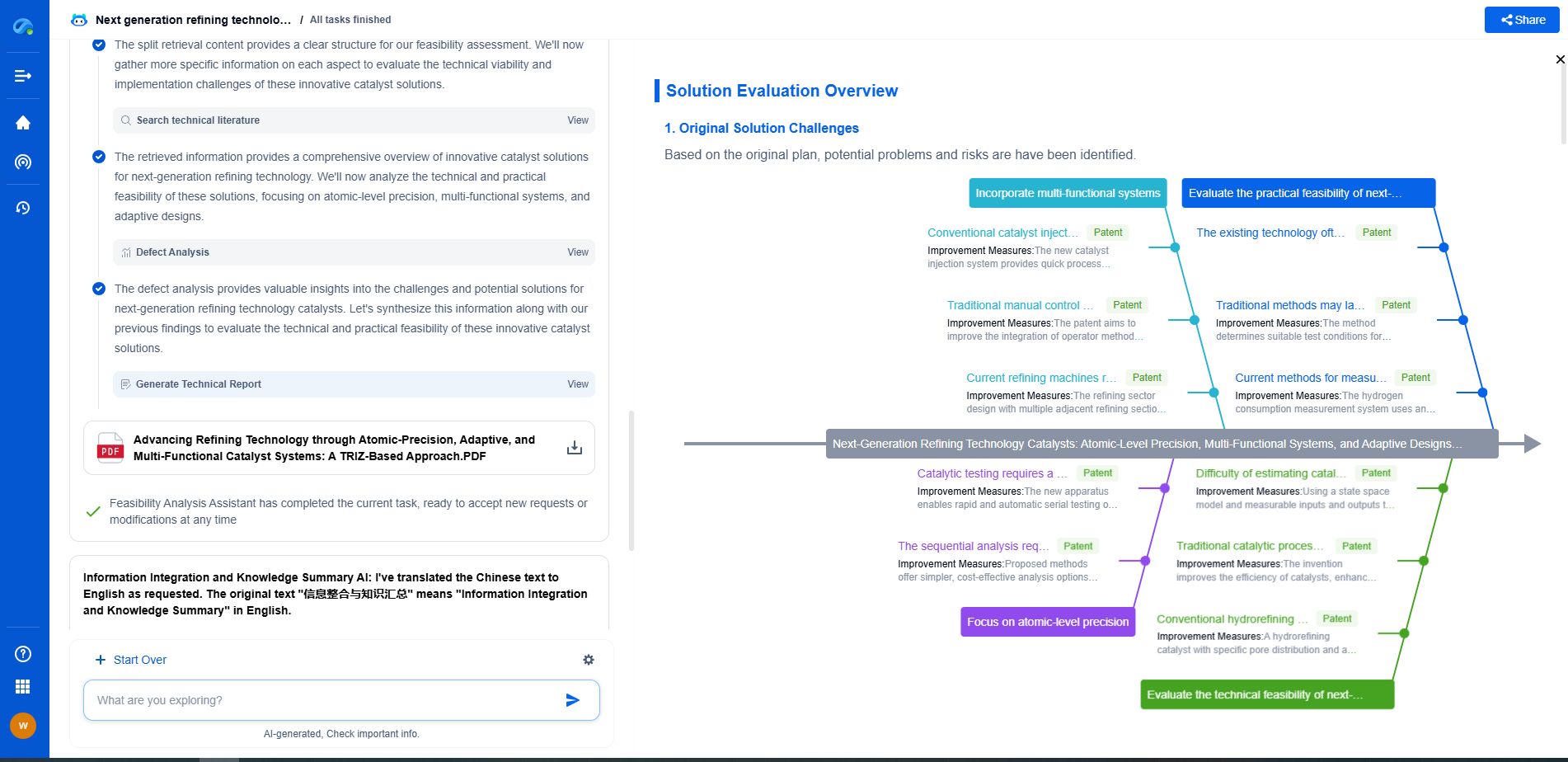
Implementing QoS in Your Network
Successfully implementing QoS involves several steps. First, network administrators must identify the types of traffic that require prioritization and define QoS policies accordingly. This may include prioritizing voice and video traffic while limiting bandwidth for less critical applications.
Next, administrators should configure network devices to recognize and enforce these policies. This often involves setting up DSCP markings on routers and switches to ensure consistent packet handling across the network. Regular monitoring and analysis are also crucial to ensure that QoS policies are effective and adjust them as network conditions change.
Conclusion
Quality of Service is a critical component of modern networking, enabling the effective management and prioritization of diverse traffic types. By utilizing mechanisms like DSCP and the ToS field, network administrators can ensure that essential applications receive the resources they need, enhancing performance and user satisfaction. As networks continue to evolve, understanding and implementing QoS will remain vital in maintaining efficient and reliable communication infrastructures.
Unleash the Full Potential of AI Innovation with Patsnap Eureka
The frontier of machine learning evolves faster than ever—from foundation models and neuromorphic computing to edge AI and self-supervised learning. Whether you're exploring novel architectures, optimizing inference at scale, or tracking patent landscapes in generative AI, staying ahead demands more than human bandwidth.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
👉 Try Patsnap Eureka today to accelerate your journey from ML ideas to IP assets—request a personalized demo or activate your trial now.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com