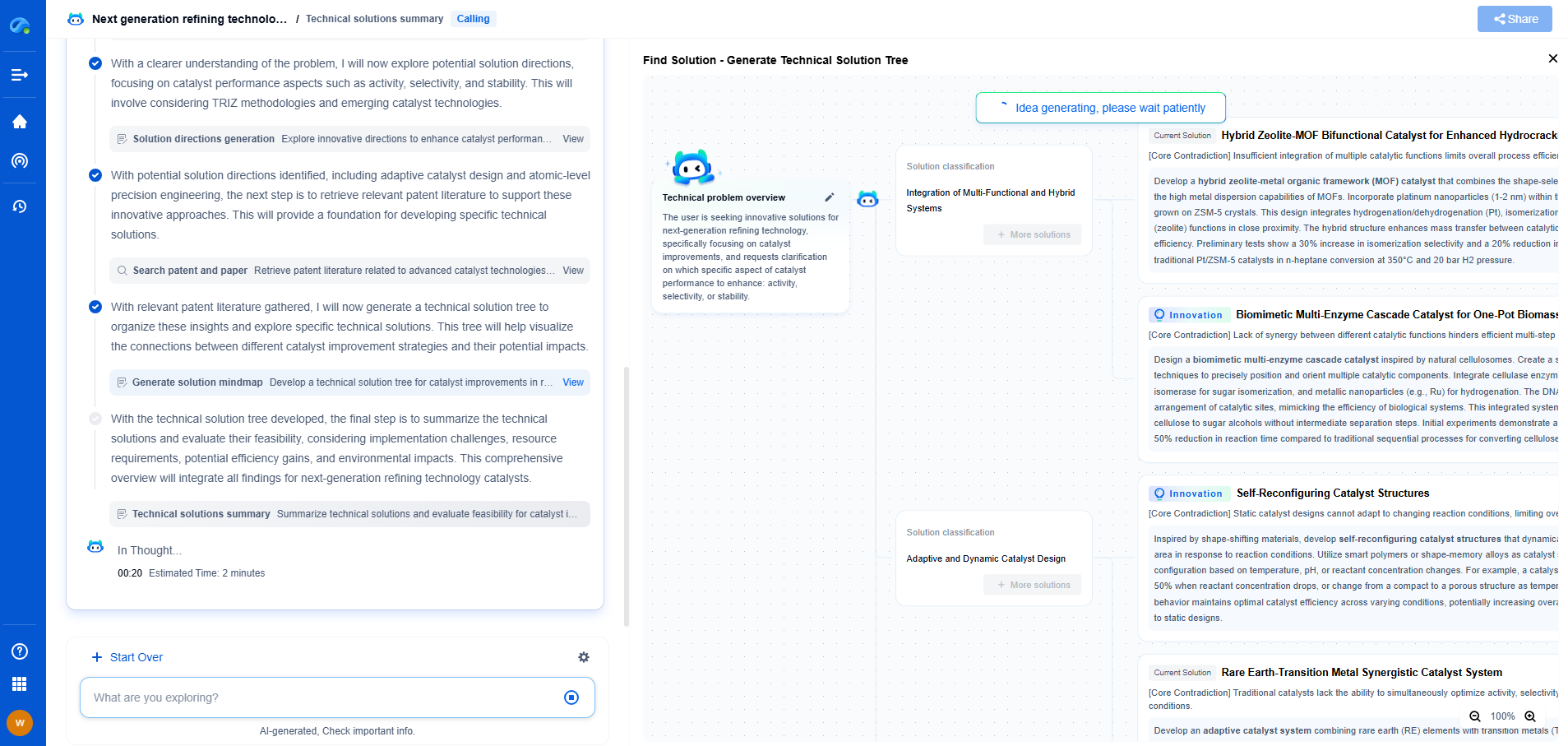
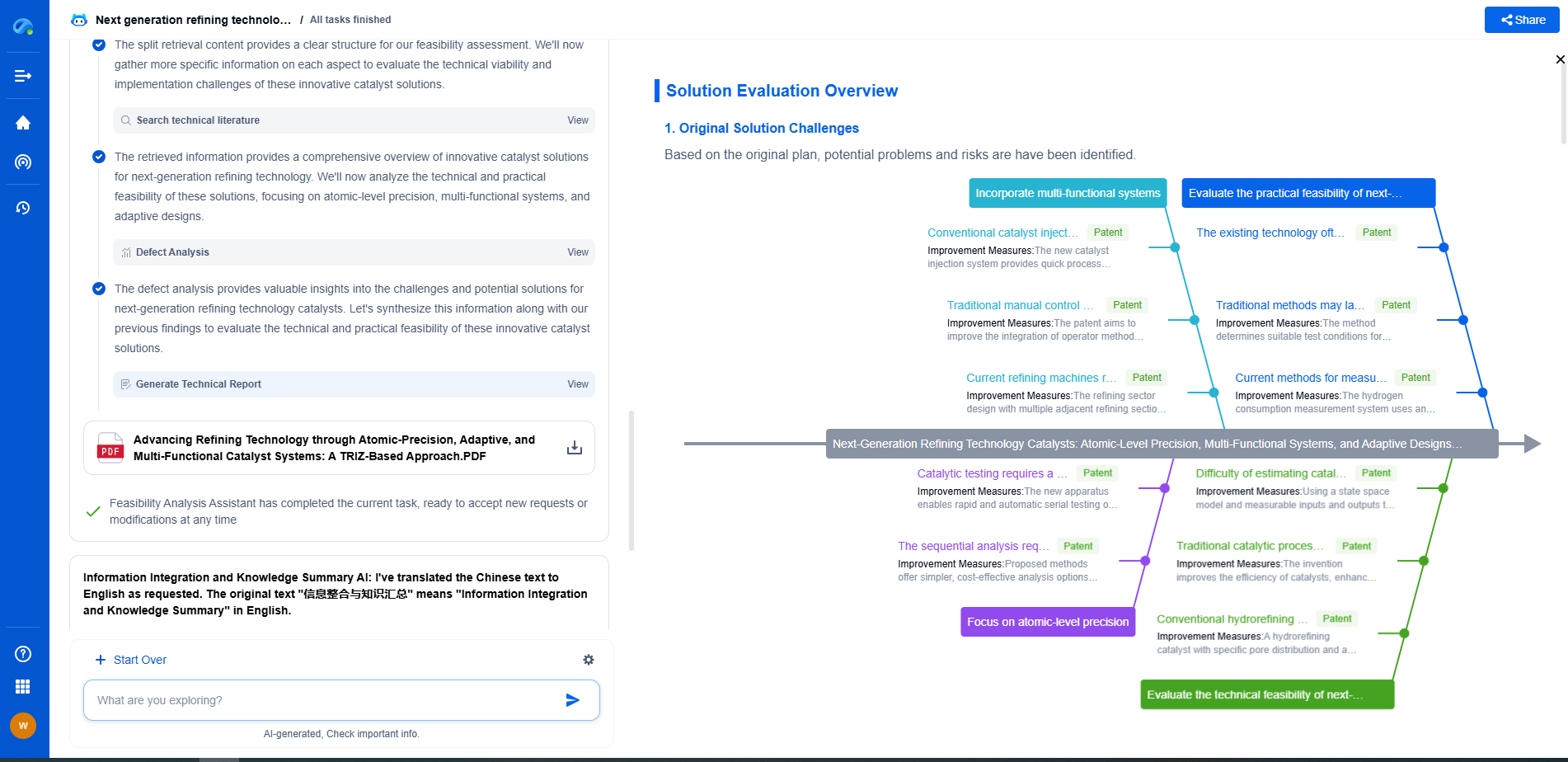
What is shale gas drilling and what technologies are used?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Shale gas drilling has emerged as a key player in the global energy landscape, driven by the continuous demand for cleaner and more efficient energy sources. This process involves extracting natural gas from shale formations deep underground, providing an alternative to conventional gas production. But what exactly does shale gas drilling entail, and what technologies are used to make it possible? Let's delve into the intricacies of this significant industry.
The Basics of Shale Gas
Shale gas is a type of natural gas found trapped within shale formations, which are fine-grained sedimentary rocks. These formations can be located thousands of feet underground and contain natural gas in tiny pore spaces. The extraction of this gas is challenging due to the low permeability of shale, which makes it difficult for the gas to flow freely to the surface. This is where advanced drilling technologies come into play, enabling the efficient extraction of shale gas.
The Process of Hydraulic Fracturing
Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, is a central technology in shale gas drilling. This process involves injecting a high-pressure fluid mixture into the shale rock to create small fractures. The fluid, primarily composed of water, sand, and chemical additives, helps to keep these newly created fractures open, allowing the trapped gas to flow to the surface. Fracking has revolutionized the energy sector by unlocking vast reserves of natural gas that were previously considered inaccessible.
Directional and Horizontal Drilling Techniques
Another critical technology used in shale gas drilling is directional and horizontal drilling. Unlike conventional vertical drilling, directional drilling allows operators to reach gas reserves located beneath areas that are inaccessible or environmentally sensitive. Horizontal drilling, on the other hand, involves drilling a well vertically to a certain depth and then turning it horizontally to extend across the shale formation. This technique significantly increases the surface area in contact with the gas-rich rock, enhancing the efficiency of gas extraction.
The Role of Advanced Imaging and Monitoring
To optimize drilling operations and ensure safety, advanced imaging and monitoring technologies are utilized. Seismic imaging, for example, provides detailed subsurface maps that help identify the most promising drilling sites. Real-time monitoring systems track key parameters such as pressure and temperature, allowing operators to make informed decisions and minimize risks associated with drilling.
Environmental Considerations and Innovations
While shale gas drilling has brought substantial economic benefits, it also raises environmental concerns. The use of large volumes of water in fracking, potential groundwater contamination, and induced seismicity are some of the issues associated with the process. To address these challenges, the industry is continually innovating. Water recycling technologies, for instance, are being developed to reduce the water footprint of drilling operations. Additionally, efforts are underway to formulate more environmentally friendly fracking fluids.
Future Prospects of Shale Gas Drilling
The future of shale gas drilling looks promising, with ongoing technological advancements poised to enhance its efficiency and environmental sustainability. As countries seek to diversify their energy portfolios and reduce carbon emissions, shale gas is likely to play a pivotal role in the transition to cleaner energy sources. The continued evolution of drilling technologies, coupled with stringent regulatory frameworks, will be crucial in ensuring that shale gas remains a viable and responsible component of the global energy mix.
In conclusion, shale gas drilling is a complex process that relies on a combination of innovative technologies to extract natural gas from deep underground formations. As the industry evolves, it is imperative to balance the economic benefits with environmental stewardship to ensure a sustainable energy future.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com