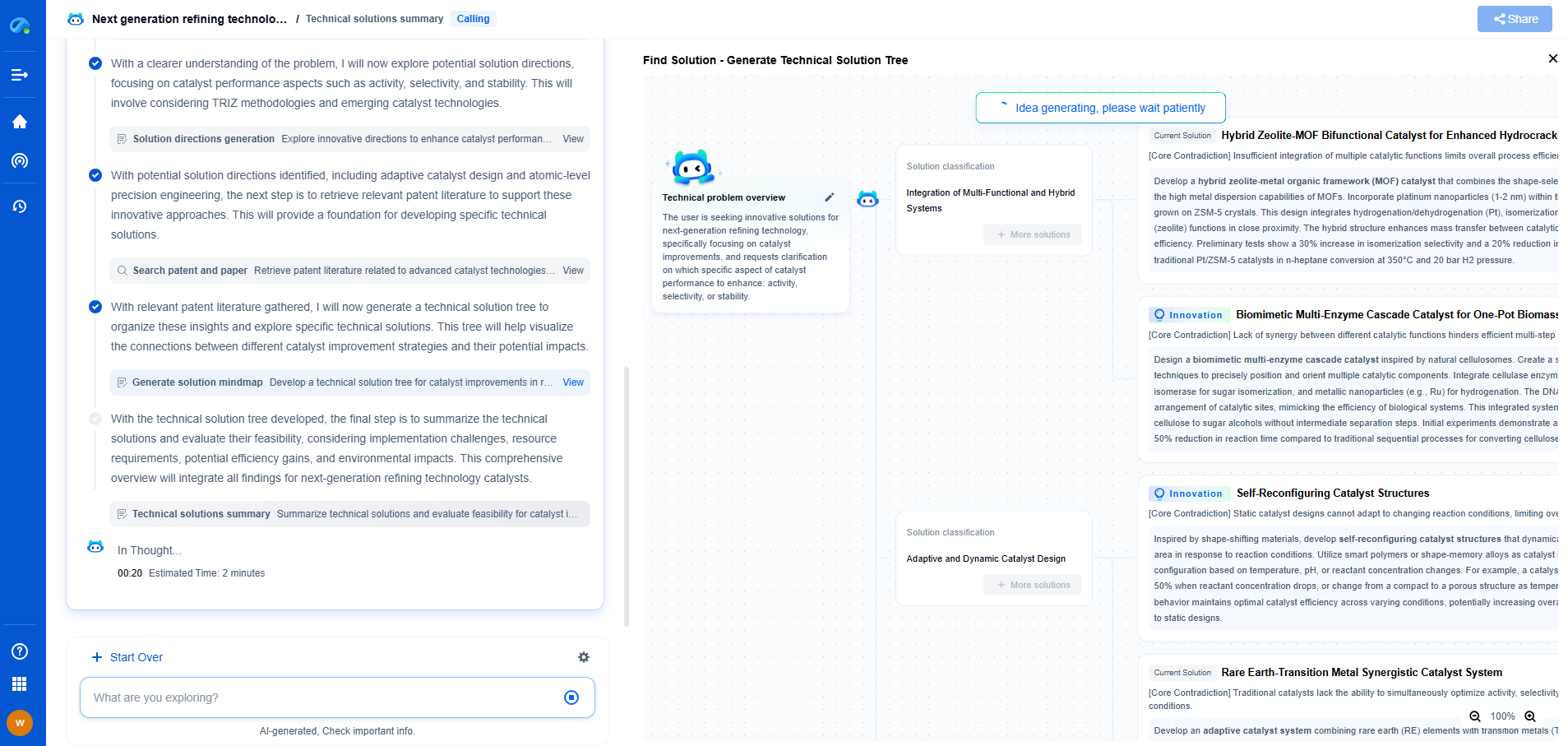
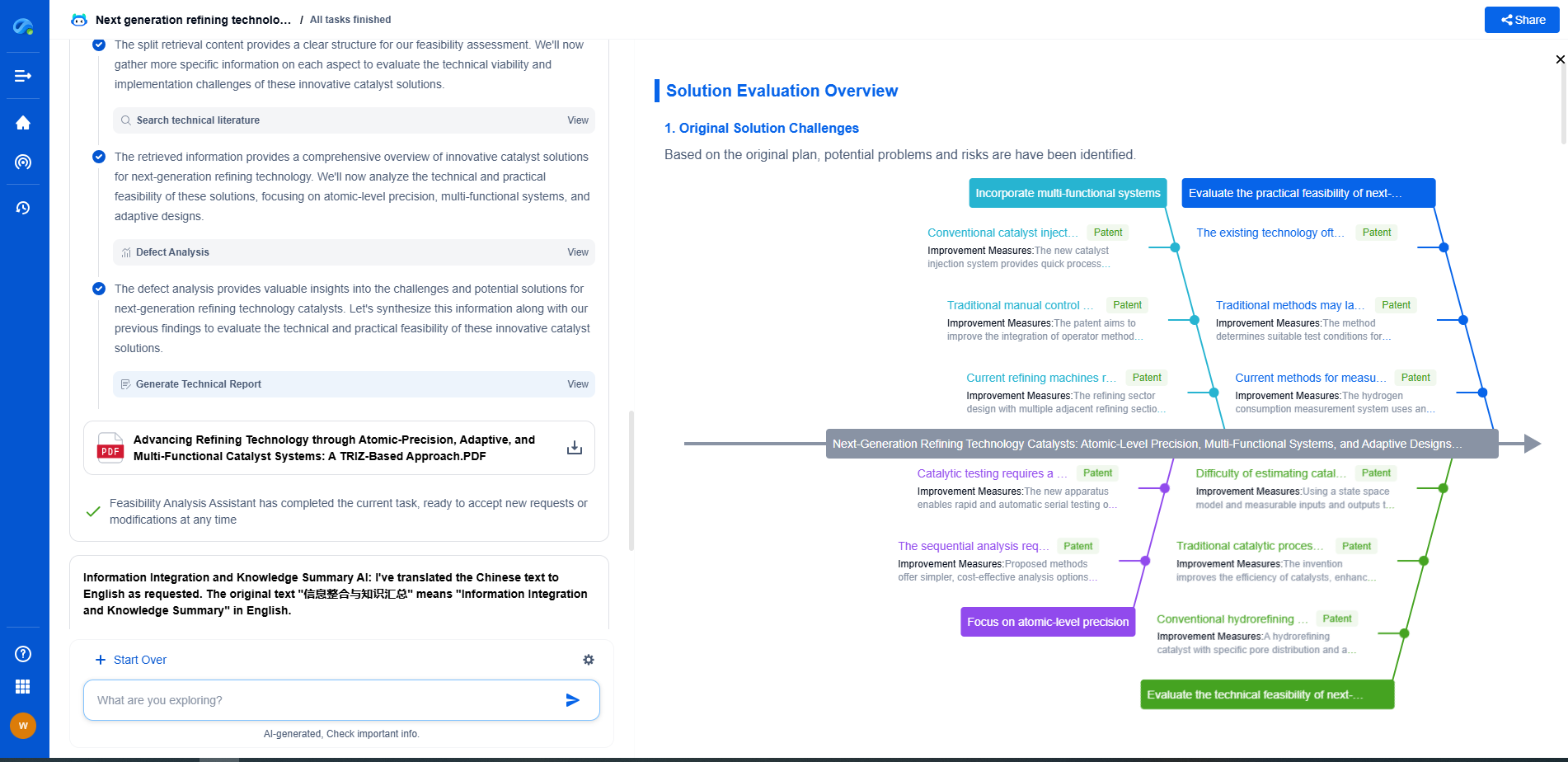
What Is the Difference Between a Pinion and a Gear?
JUL 2, 2025 |
When diving into the world of mechanical engineering, one often encounters the terms "pinion" and "gear". Both are fundamental components in machinery, transmitting power and motion between different parts of a system. However, while they are related, they are not identical. Understanding the differences between a pinion and a gear is crucial for anyone involved in mechanical design or repair.
Defining Gears
A gear is defined as a rotating machine part with cut teeth or cogs, which mesh with another toothed part to transmit torque. Gears are essential in changing the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. They come in various sizes and can be found in numerous shapes such as spur, helical, bevel, and worm gears, among others. The primary purpose of gears is to convert rotational motion and force from one component to another.
Pinion as a Type of Gear
A pinion, on the other hand, is a specific type of gear. It is typically the smallest gear in a gear drive system. In most applications, the pinion is the driving gear, meaning it is attached to the engine or motor and initiates movement in the gear system. Its role is to engage with a larger gear or a rack to generate motion. The pinion's smaller size allows it to provide higher speed but with lower torque, making it ideal for specific applications where rapid motion is needed.
Key Differences Between Pinion and Gear
Size and Role: The most apparent difference between a pinion and a gear lies in their size and role within a gear system. The pinion is usually the smaller of the two engaging gears and often serves as the driver. In comparison, the gear is generally larger and acts as the driven component.
Application Scenarios: Gears can be used independently in applications where size and torque are critical. However, pinions are almost always used in conjunction with larger gears or racks, especially in systems requiring a shift in rotational speed or direction through meshing.
Design and Functionality: While all pinions are gears, not all gears are pinions. This distinction is vital in understanding their design and functionality within a system. A pinion’s primary function is often to translate motion from a motor into a larger gear, thereby increasing speed or changing direction.
Importance in Gear Systems
In any gear system, both pinions and gears play significant roles. Their interaction is essential for the effective transmission of power and motion. For instance, in an automobile's steering system, a pinion attached to the steering shaft meshes with the rack, allowing the wheels to turn with minimal effort from the driver. Similarly, in clocks, pinions help in transmitting motion from the mainspring to the gears, ensuring accurate timekeeping.
Common Applications
Pinions and gears are found across numerous industries. In the automotive industry, they are integral to the function of transmissions, differentials, and steering systems. In industrial machinery, they play a critical role in powering conveyors, elevators, and other heavy-duty equipment. The precision and reliability of these components are paramount, making them crucial in any application where movement and power transmission are required.
Conclusion
While pinions and gears are closely related, understanding their differences is essential for effective mechanical design and application. The pinion, as the smaller driving gear, works in tandem with larger gears to achieve desired speed and torque levels. Both components are indispensable in the intricate dance of machinery, transforming energy into motion and power with remarkable precision. Whether in everyday devices or complex industrial machines, their contribution to mechanical engineering is invaluable.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com