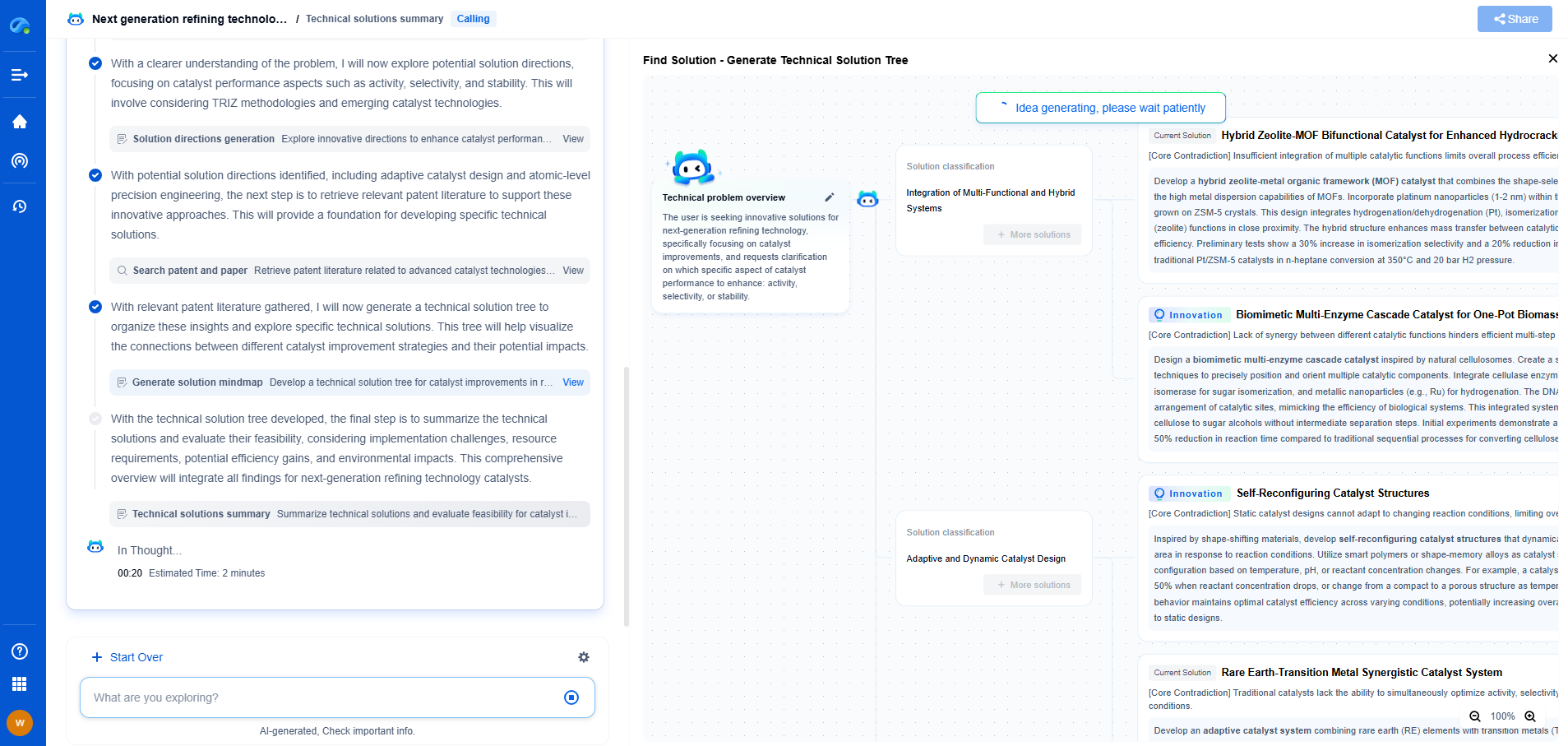
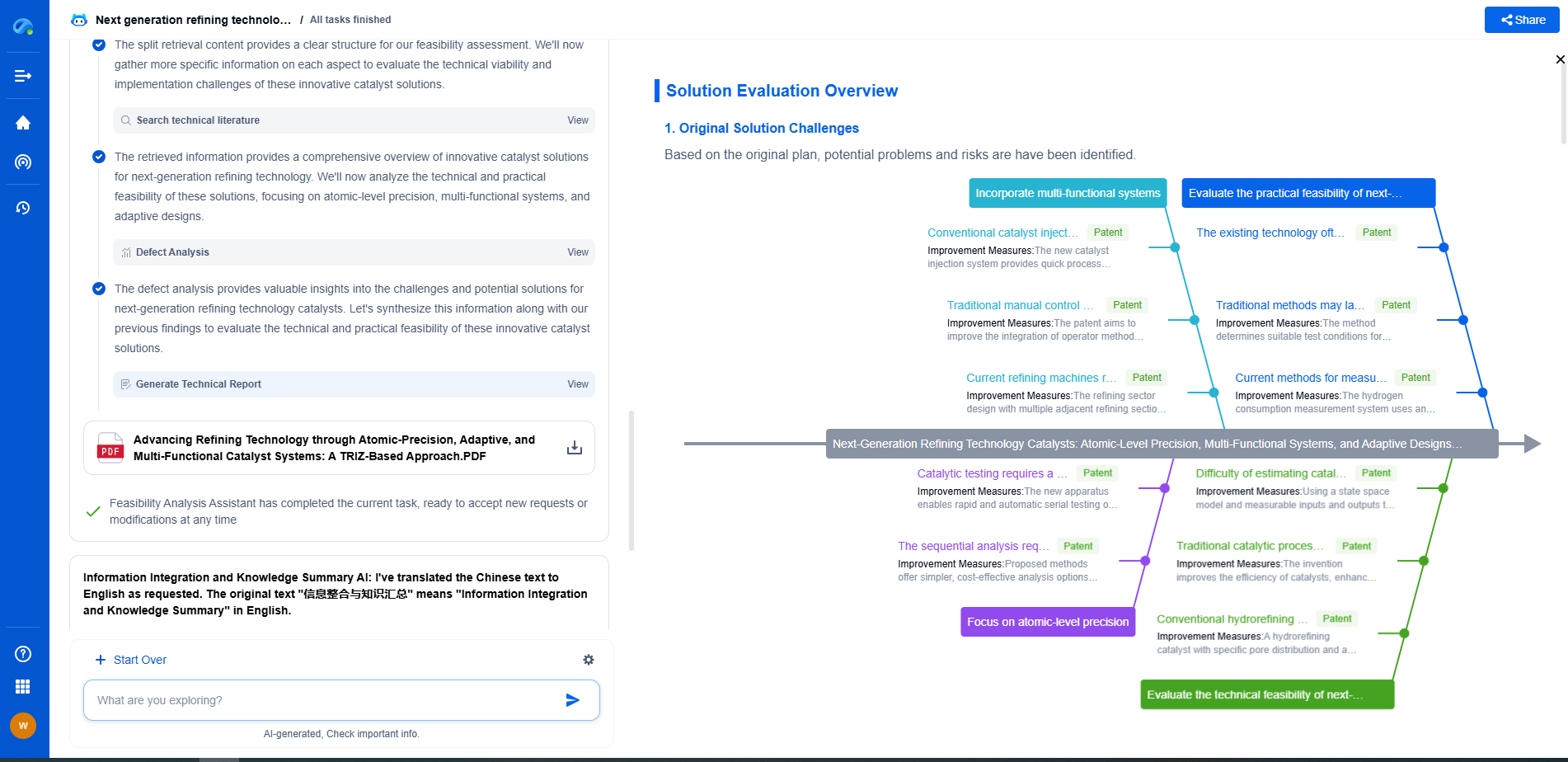
What is tight oil and how is it extracted?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Tight oil, sometimes referred to as shale oil, is a type of crude oil found in dense rock formations known as shale. Unlike traditional oil deposits, where oil flows freely, tight oil is trapped within microscopic pores of the rock, making it more challenging to extract. The term "tight" describes the low permeability of the rock, which restricts the natural movement of oil. As global energy demands increase and conventional oil reserves diminish, tight oil has become a significant focus for energy production.
How is Tight Oil Formed?
The formation of tight oil is a complex process that occurs over millions of years. Organic materials, primarily the remains of ancient marine organisms, are buried under sediment. Over time, heat and pressure transform these materials into hydrocarbons, including oil and natural gas. The key difference between tight oil and conventional oil is the type of rock in which the oil is stored, with tight oil primarily found within shale formations.
Extraction Techniques for Tight Oil
Horizontal Drilling
One of the pivotal techniques in extracting tight oil is horizontal drilling. This method involves drilling down vertically and then turning the drill bit to extend horizontally. By doing so, the drill can access a larger surface area within the oil-rich rock layers, maximizing the extraction. Horizontal drilling is particularly effective in reaching extensive shale formations, allowing for more efficient oil recovery than traditional vertical wells.
Hydraulic Fracturing
Hydraulic fracturing, commonly known as fracking, is another essential technique used to extract tight oil. This process involves injecting a high-pressure mixture of water, sand, and chemicals into the rock layers. The high-pressure fluid creates cracks or fractures in the rock, releasing the oil trapped in the tiny pores. The sand in the mixture keeps these fractures open, facilitating the flow of oil to the wellbore.
Advancements in Technology
Recent technological advancements have significantly improved the efficiency and environmental impact of tight oil extraction. Enhanced imaging techniques, such as 3D seismic imaging, allow geologists to identify optimal drilling sites more accurately. Additionally, improvements in fracking fluid formulations and water recycling have reduced the environmental footprint of the extraction process. These advancements have made tight oil extraction more viable and economically feasible.
Economic Impact of Tight Oil
The development of tight oil resources has had a profound impact on the global oil market. It has contributed to greater energy independence in countries like the United States, reducing reliance on foreign oil imports. Furthermore, the increased supply of oil has helped stabilize global oil prices, benefiting consumers and industries worldwide. The economic benefits extend to job creation in regions where tight oil extraction is prominent, supporting local economies and infrastructure development.
Environmental Considerations
While tight oil extraction has economic benefits, it also poses environmental challenges. The fracking process requires significant water use, and improperly managed wastewater can contaminate local water supplies. There is also concern about potential seismic activity triggered by fracking. Addressing these issues requires stringent regulations and ongoing research to minimize environmental risks and ensure sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Tight oil represents a significant resource in the modern energy landscape. Through innovative techniques like horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing, it is possible to tap into these challenging reserves and meet growing energy demands. While the economic benefits are substantial, it is crucial to balance them with environmental considerations to ensure the responsible development of tight oil resources. As technology and regulations evolve, tight oil will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of energy production.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com