What is well cementing and how is it done?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Well cementing is a crucial process in the oil and gas industry, essential for the integrity and productivity of a well. It involves the placement of cement in the annular space between the casing and the borehole wall. This process is not only pivotal in preventing fluid migration between the subsurface layers but also in supporting the well's structural integrity. Let's delve deeper into the objectives, types, processes, and challenges associated with well cementing.
Objectives of Well Cementing
The primary goal of well cementing is to stabilize the wellbore and ensure isolation among the different geological formations encountered during drilling. Proper cementing prevents fluid movement and ensures the well can be securely drilled and produced. Additionally, cementing protects the casing from corrosive formation fluids and ensures the well can withstand the high pressures encountered during oil and gas extraction.
Types of Well Cementing
There are two main types of well cementing: primary cementing and remedial cementing.
1. Primary Cementing: This is the initial cementing operation that seals the casing to the wellbore. The main objective is to provide zonal isolation, support the casing, and prevent fluid migration.
2. Remedial Cementing: When issues arise after the primary cementing, such as inadequate zonal isolation or casing leaks, remedial cementing is used to correct these problems. It includes techniques such as squeeze cementing, where cement is forced into specific areas to plug leaks or fill voids.
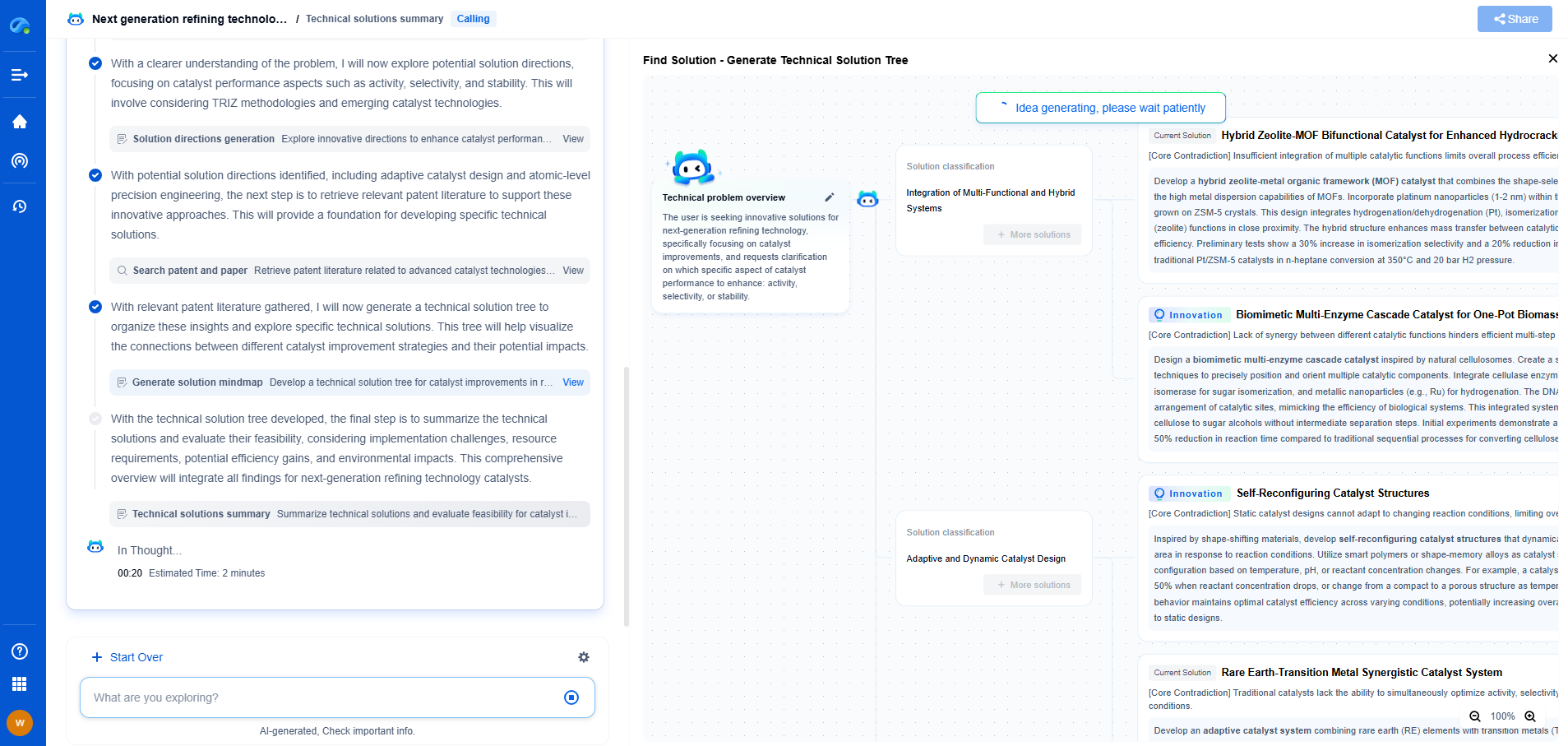
The Well Cementing Process
The well cementing process involves several key steps:
1. Slurry Preparation: Cement slurry is prepared by mixing cement with water and various additives to achieve the desired properties, such as viscosity, setting time, and compressive strength. Additives can include retarders, accelerators, fluid loss agents, and dispersants, depending on the specific requirements of the well conditions.
2. Casing Placement: The well casing, a steel pipe, is placed into the drilled wellbore. It serves as a conduit for the extracted hydrocarbons and provides structural support to the wellbore.
3. Slurry Pumping: The cement slurry is pumped down the casing and up into the annular space between the casing and the borehole wall. This is typically done using specialized cementing equipment to ensure proper flow rates and pressures.
4. Setting and Curing: Once the slurry is in place, it needs time to set and cure. The setting time can vary depending on the additives used and the temperature and pressure conditions within the well. Proper curing ensures the cement achieves the necessary strength and bonding to maintain zonal isolation and structural support.
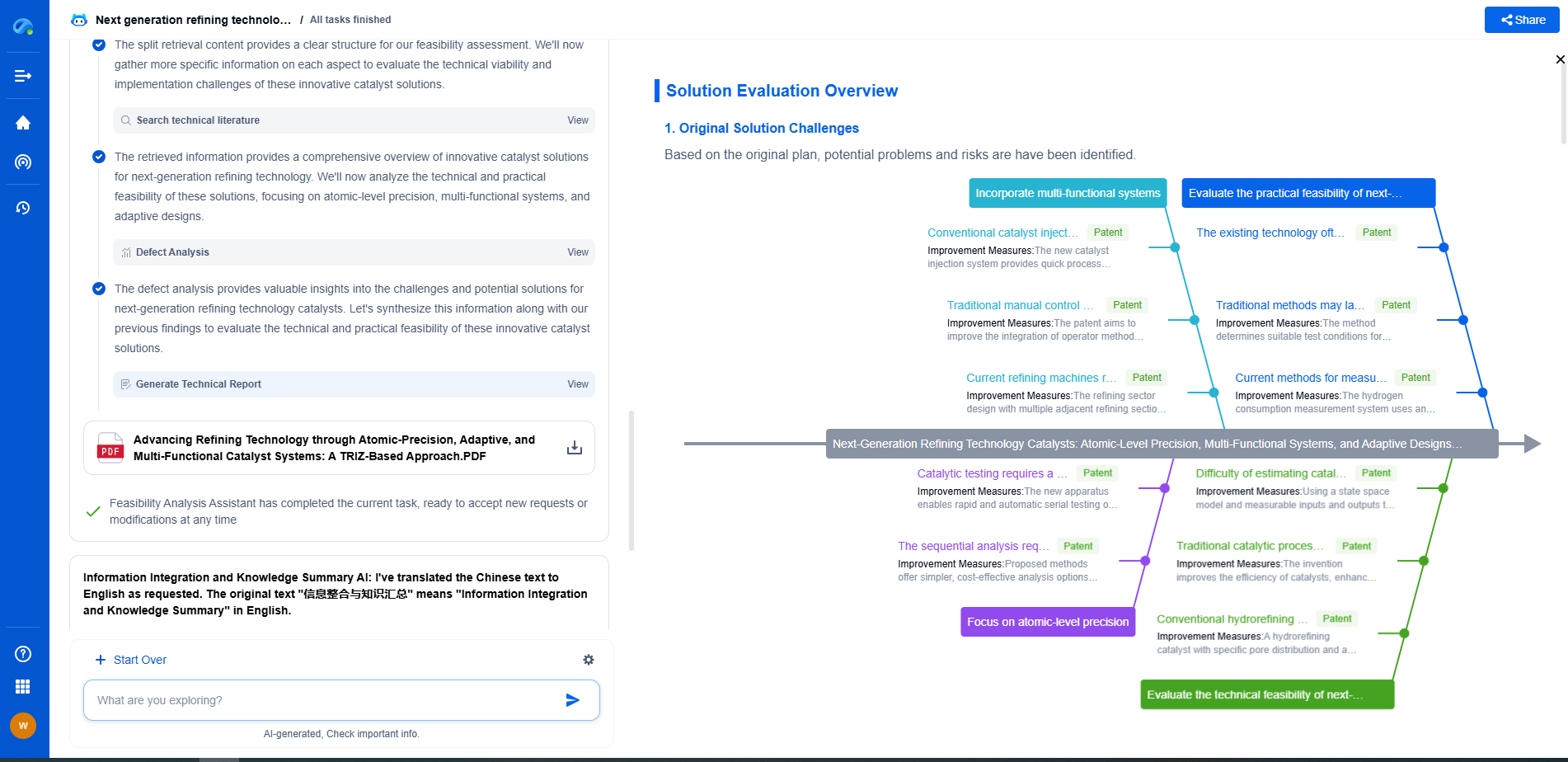
Challenges in Well Cementing
Well cementing is a complex operation that can face several challenges. Achieving a uniform cement sheath around the casing can be difficult, especially in wells with irregular borehole geometries or challenging subsurface conditions. Ensuring complete displacement of drilling fluid from the annulus is essential to avoid contamination of the cement slurry. Additionally, temperature and pressure fluctuations can affect the setting time and performance of the cement.
Innovations and Future Trends
The industry continues to innovate with advanced cement formulations and techniques to address these challenges. Smart cements with self-healing properties and enhanced monitoring technologies are being developed to improve the reliability and longevity of cement jobs. Automation and digital technologies are also playing an increasing role in optimizing cementing operations.
Conclusion
Well cementing is a vital component of the drilling process, providing the necessary integrity and stability for oil and gas wells. While it comes with its set of challenges, ongoing advancements and innovations are enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of cementing operations. Understanding the intricacies of well cementing is essential for ensuring the safe and productive extraction of hydrocarbons, safeguarding both the environment and the valuable resources beneath the Earth's surface.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com