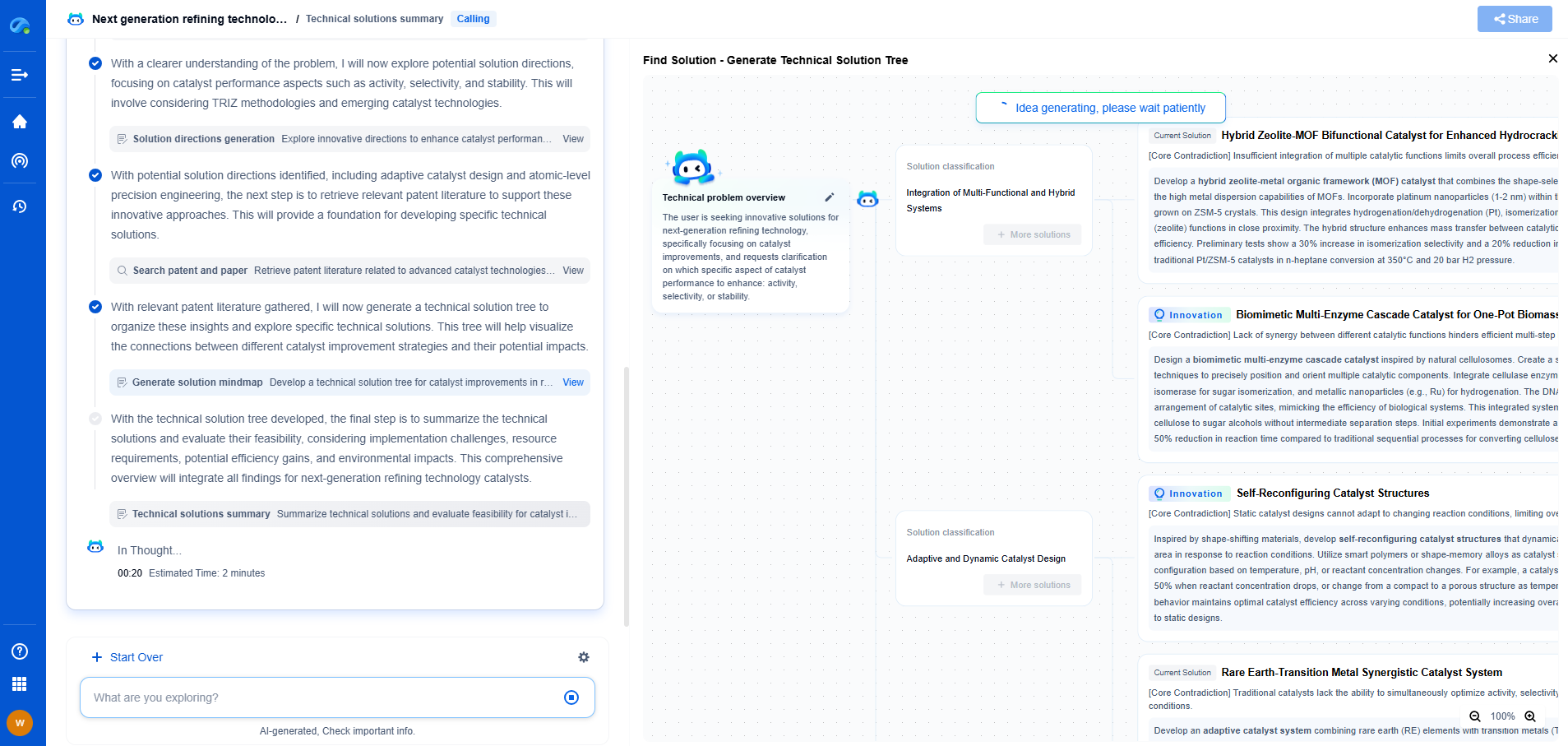
What’s the Difference Between DC Voltage, RMS Voltage, and Peak Voltage?
JUL 9, 2025 |
When discussing electrical systems, voltage is a fundamental concept that comes into play. Simply put, voltage refers to the potential difference between two points in an electric field. It's what drives electric current through a circuit. However, voltage measurements can be expressed in different forms such as DC voltage, RMS voltage, and peak voltage. Understanding the distinctions between these terms is crucial for those working with or learning about electrical systems.
DC Voltage: The Steady Player
Direct Current (DC) voltage is the simplest form to understand. DC voltage remains constant over time, meaning it does not fluctuate or change its direction. It provides a steady and unidirectional flow of electricity. This is the kind of voltage you'd find in batteries, where the positive and negative terminals maintain a constant voltage level.
In a circuit powered by DC voltage, the current flows in one direction, making it ideal for devices requiring a stable voltage supply. Applications include electronic devices like flashlights, remote controls, and any equipment that runs on battery power. Unlike AC voltage, DC voltage does not need complex circuitry to convert the alternating flow into a usable direct current.
RMS Voltage: The Effective Value
Root Mean Square (RMS) voltage is a term often used in the context of Alternating Current (AC) systems. AC voltage periodically reverses direction, and its waveform typically takes the shape of a sine wave. Because the voltage is continuously changing, the RMS value provides a way to express an equivalent DC voltage that would deliver the same power to a load as the AC voltage does over one cycle.
The RMS voltage is particularly useful in power calculations because it reflects the real, effective voltage that can perform work. It is calculated as the square root of the average of the squares of all instantaneous values over a cycle. In practical terms, RMS voltage for a household outlet in the United States is about 120 volts, meaning it provides the same power as 120 volts of DC voltage.
Peak Voltage: The Maximum Threshold
Peak voltage, as the name suggests, refers to the maximum voltage level reached by an AC waveform during a cycle. This measurement is crucial for understanding the highest point an AC voltage can reach, which is particularly important in preventing over-voltage damage to electrical components.
In a sine wave, the peak voltage occurs twice during each cycle—once at the positive peak and once at the negative peak. It's important to note that the peak voltage is not used in power calculations like the RMS voltage; instead, it helps in assessing the voltage tolerance of components and insulation systems.
Comparing the Three
When comparing DC, RMS, and peak voltages, it's important to consider their applications and implications:
- DC Voltage is consistent and ideal for applications needing stable power.
- RMS Voltage is an average measure used for AC systems, reflecting the effective voltage that can perform work.
- Peak Voltage indicates the maximum voltage level of an AC waveform, crucial for assessing the limits of electrical components.
When working with electrical systems, understanding these different voltage metrics helps in making informed decisions regarding component selection, circuit design, and safety measures. Each type of voltage measurement serves a unique purpose and provides valuable information depending on the context of its application.
Conclusion
Voltage is an essential aspect of electrical and electronic systems, and distinguishing between DC, RMS, and peak voltage is crucial for anyone involved in electrical engineering or related fields. These measurements not only help in designing and analyzing circuits but also ensure the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems. Understanding each type's role and application will enable you to better comprehend and work with various electrical systems, ensuring they function effectively and safely.
Navigating the evolving world of electrical measurement—from high-precision signal integrity to advanced test protocols like BERT or TDR—demands more than just expertise; it demands smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka empowers you to keep up—by turning complex patent data, technical parameters, and industry signals into actionable insight. It’s your AI partner for exploring what’s next in test, measurement, and electrical diagnostics.
💡 Try Patsnap Eureka for free and see how it transforms the way you work with electrical measurement technologies.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com