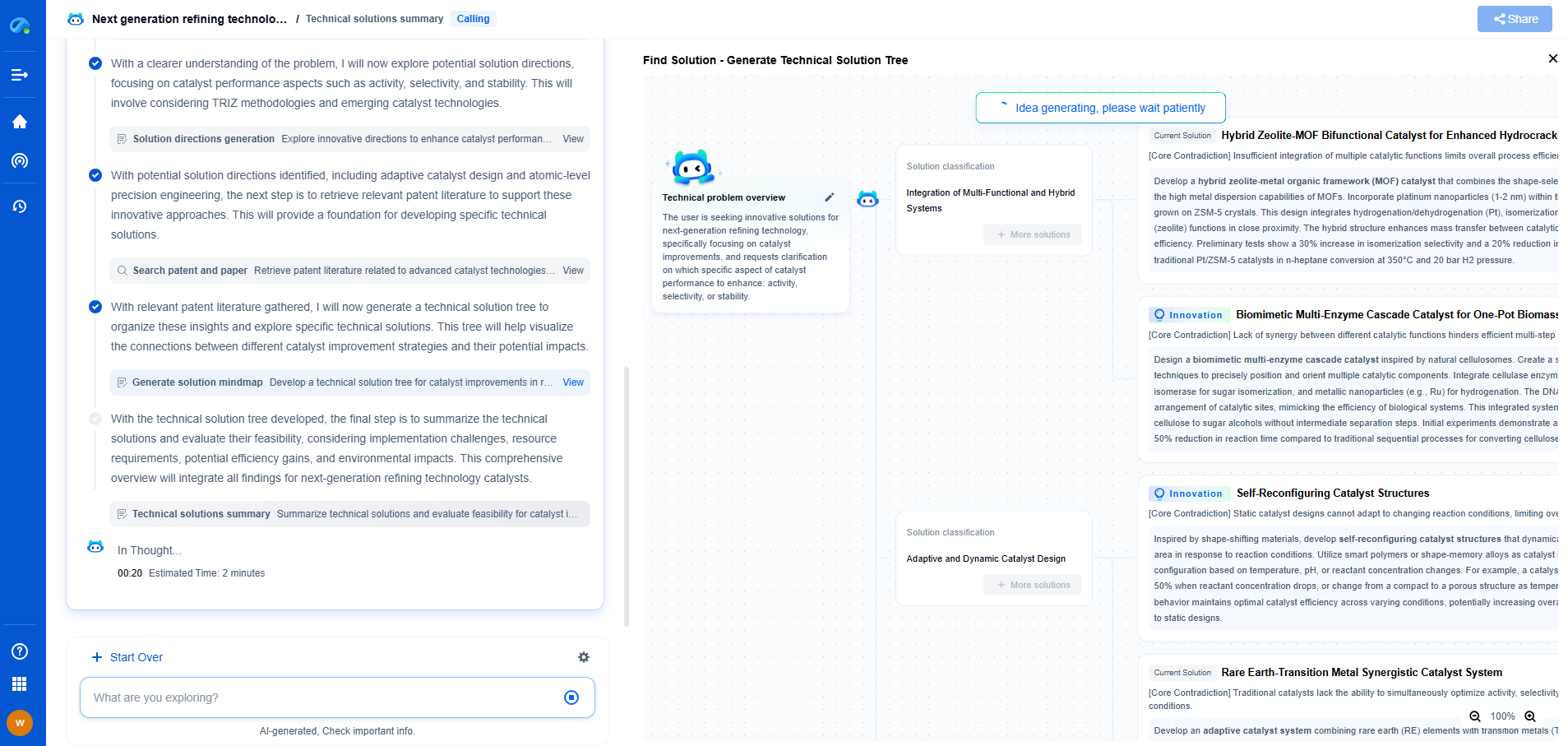
Why Do Gears Overheat? Thermal Behavior Analysis
JUL 2, 2025 |
Gears are fundamental components in many mechanical systems, ranging from simple clocks to complex industrial machinery. They play a crucial role in transmitting power and motion, but like any mechanical component, they are subject to wear and tear. One of the most common issues faced in gear operation is overheating. Understanding why gears overheat and how thermal behavior affects their performance is essential for improving their longevity and efficiency.
## Causes of Gear Overheating
### Friction and Lubrication Issues
The primary cause of gear overheating is friction. When gears are in motion, their surfaces interact, creating friction that generates heat. If the lubrication is inadequate or inappropriate, friction increases, causing excessive heat buildup. Lubricants reduce friction by forming a film between the gear surfaces, but if they break down due to high temperatures, contamination, or incorrect viscosity, the gears can overheat.
### Misalignment and Load Stress
Gears must be properly aligned to ensure smooth operation. Misalignment can cause uneven load distribution, leading to excessive stress on certain gear areas. This uneven stress increases friction and, consequently, the temperature. Similarly, overloading gears beyond their capacity can lead to increased friction and overheating. It's crucial to adhere to the recommended load ratings and ensure proper alignment during installation and maintenance.
### Surface Finish and Material Properties
The surface finish and material properties of gears significantly impact their thermal behavior. A rough surface finish can increase friction, whereas a smoother finish reduces it. Additionally, the materials from which gears are made affect their heat dissipation capabilities. Metals with high thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper alloys, dissipate heat more effectively than those with lower thermal conductivity. Selecting the right material and ensuring an appropriate surface finish can mitigate overheating risks.
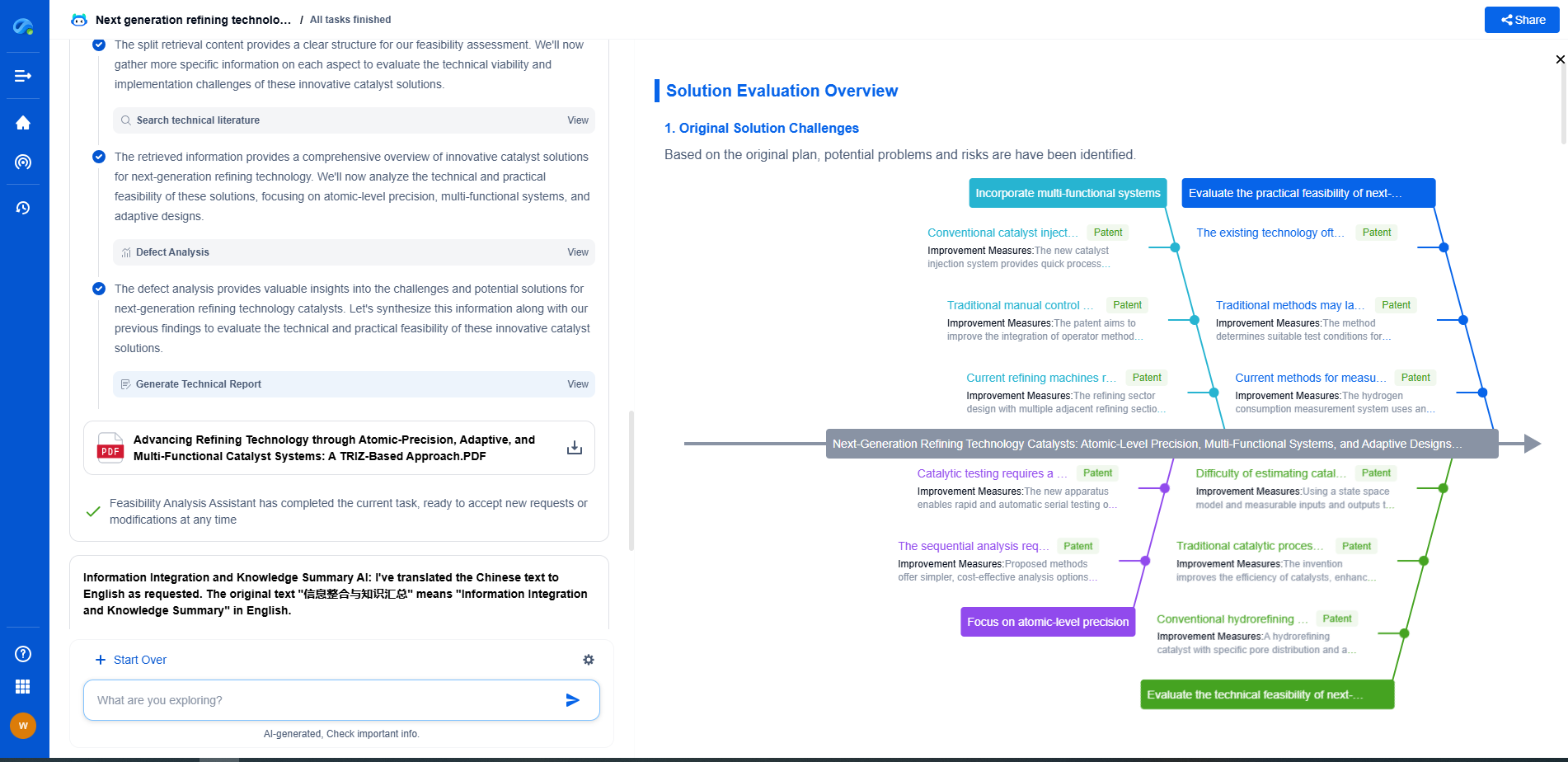
## Thermal Behavior and Its Impact
### Heat Generation and Dissipation
Understanding the balance between heat generation and dissipation is crucial in analyzing gear thermal behavior. While some heat generation is inevitable due to friction, it must be effectively dissipated to avoid damaging temperature levels. Heat dissipation occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. The gear design, including its shape, material, and surrounding environment, plays a vital role in these processes.
### Effects of Overheating on Gear Performance
Overheating can have several detrimental effects on gear performance. It can cause thermal expansion, leading to misalignment and increased wear. High temperatures can also degrade lubricants, further increasing friction and accelerating wear. In severe cases, overheating can cause the gear material to soften or deform, leading to catastrophic failure. Regular monitoring and maintenance can help identify early signs of overheating and prevent these adverse effects.
## Preventive Measures and Solutions
### Proper Lubrication Practices
One of the most effective ways to prevent gear overheating is by ensuring proper lubrication. Regularly check and maintain adequate lubricant levels, and select the right type of lubricant based on the operating conditions and gear material. Implementing a routine lubrication schedule can significantly reduce friction and heat generation.
### Regular Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular inspection and maintenance of gears can help detect early signs of wear and overheating. Implementing temperature monitoring systems can provide real-time data on gear temperatures, allowing for prompt corrective action. Ensuring that gears are properly aligned and not overloaded is also crucial for preventing overheating.
### Design Considerations
Design improvements can play a significant role in reducing gear overheating. Using materials with higher thermal conductivity and optimizing gear geometry can enhance heat dissipation. Incorporating cooling systems or heat sinks may also help manage temperature levels in high-performance applications.
## Conclusion
Understanding the causes and effects of gear overheating is essential for maintaining efficient and reliable mechanical systems. By focusing on factors such as lubrication, alignment, material selection, and design, engineers can mitigate the risks associated with overheating. Regular maintenance and monitoring are key to preventing gear failures and ensuring the longevity and efficiency of mechanical systems. Implementing these preventive measures will not only enhance gear performance but also contribute to the overall success of the machinery in which they operate.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com