Why Some Operators Still Preventively Replace Parts Despite Predictive Algos
JUN 20, 2025 |
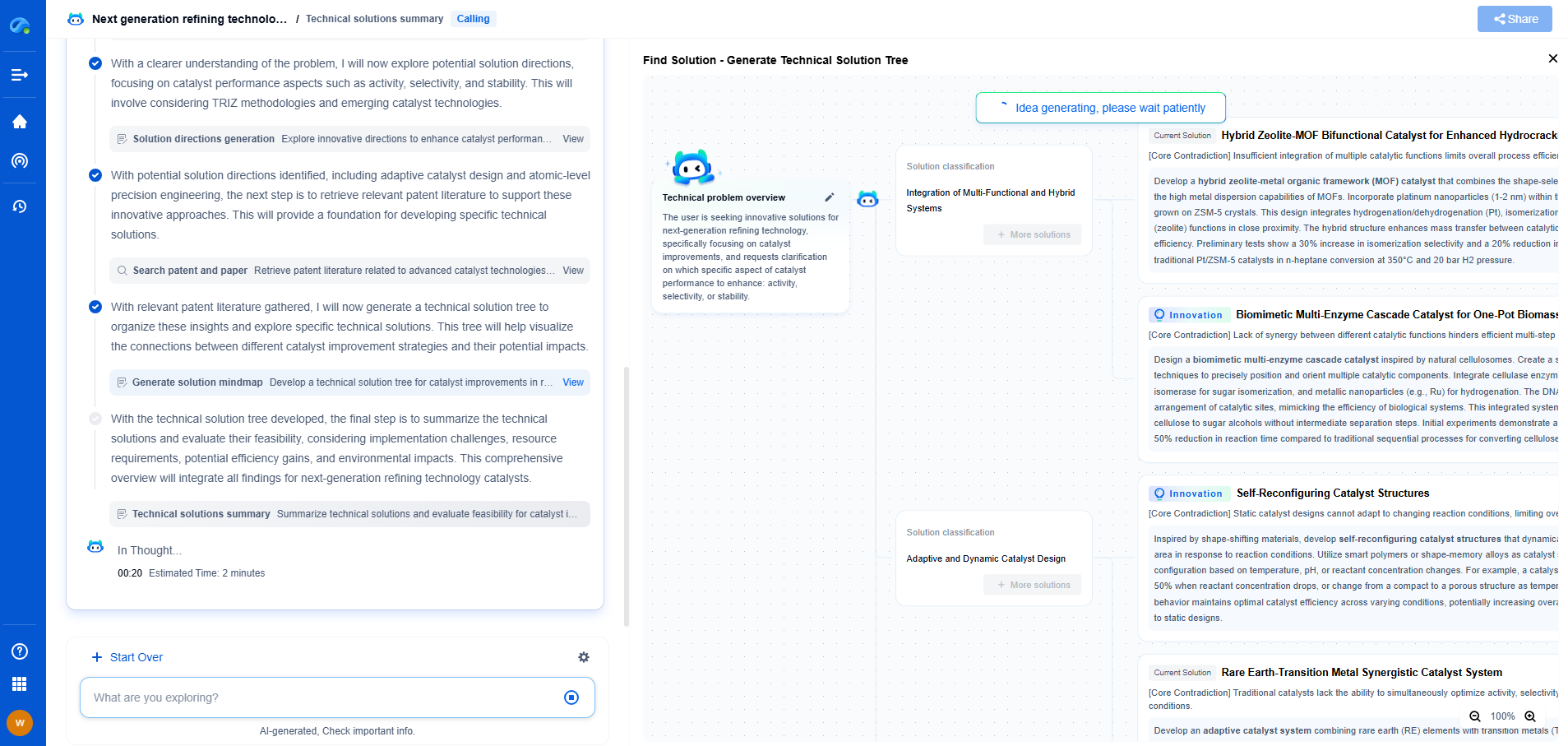
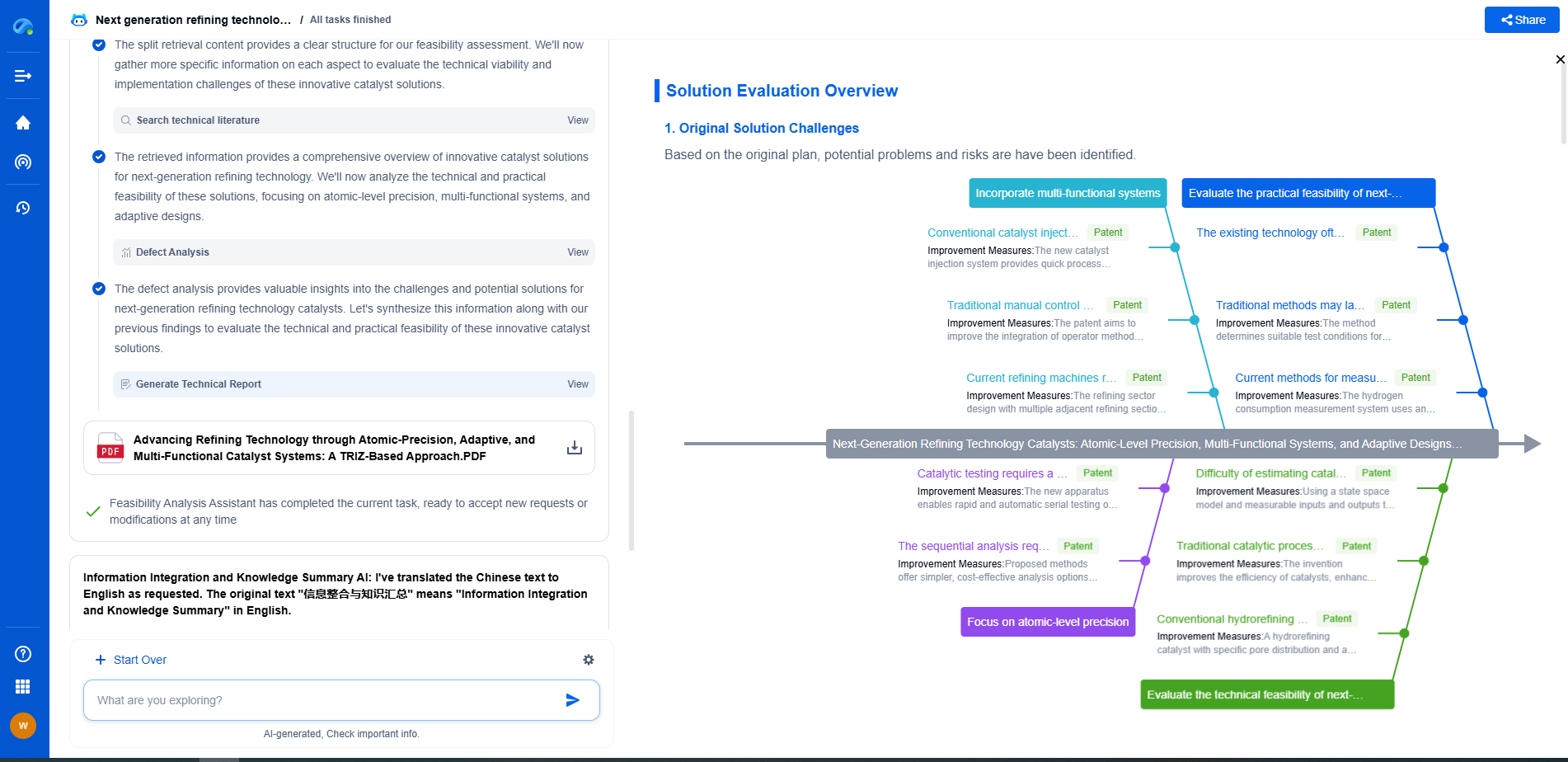
Over the past few years, predictive algorithms have revolutionized the maintenance landscape across various industries. These algorithms use data analytics and machine learning to predict when parts are likely to fail, allowing operators to plan maintenance more efficiently and cost-effectively. However, despite the apparent advantages, some operators still favor preventive replacement strategies. This blog explores the reasons behind this preference and the factors influencing the decision-making process.
The Comfort of Certainty
One of the primary reasons operators opt for preventive replacement is the comfort of certainty it provides. Predictive algorithms, though powerful, are not infallible. They rely heavily on data quality and the assumptions made during model development. In situations where the stakes are high, operators may prefer the certainty of replacing a part before it has a chance to fail. This approach minimizes the risk of unexpected downtime, which can be costly and disruptive.
Moreover, preventive replacement is a straightforward strategy with clear guidelines and timelines. Operators are familiar with scheduled replacements and understand the risks and costs associated with them. Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, may require more complex decision-making processes and a deeper understanding of data analytics. For some operators, the simplicity and reliability of preventive replacement outweigh the uncertainty and potential benefits of predictive algorithms.
The Human Factor
Human factors also play a significant role in choosing preventive replacement over predictive algorithms. Maintenance teams often rely on their experience and intuition when assessing the condition of equipment. This expertise, built over years of hands-on work, provides a level of confidence that data-driven insights may not fully replicate. In environments where seasoned professionals can identify issues that algorithms might miss, their judgment becomes invaluable.
Additionally, the transition to predictive maintenance requires a cultural shift within organizations. Employees need to trust and embrace data-driven decision-making processes, which can be challenging to achieve. Skepticism can arise from past failures or the perception that algorithms lack the nuanced understanding that humans possess. Therefore, some operators continue preventive replacement practices, valuing the experience of their workforce above algorithmic predictions.
The Challenge of Integration
Integrating predictive algorithms into existing maintenance systems presents its own set of challenges. For predictive maintenance to be effective, it requires seamless integration with other systems, such as inventory management and scheduling. This integration can be complex and time-consuming, demanding significant investment in both technology and training. For smaller organizations or those with limited resources, this transition may be impractical or too costly, making preventive replacement a more feasible option.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of predictive algorithms relies on the accuracy and availability of data. In industries where data collection is inconsistent or where equipment lacks the necessary sensors, predictive maintenance might not be viable. Preventive replacement, being a more traditional approach, does not demand the same level of technological infrastructure, making it a safe choice for operators with limited data capabilities.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
In certain industries, regulatory and compliance requirements dictate maintenance practices. Safety standards, environmental regulations, and industry-specific guidelines may mandate preventive replacement schedules. In such cases, operators have little choice but to adhere to these regulations, regardless of predictive algorithm insights. Compliance ensures that equipment remains safe and operational within legal parameters, and any deviation could result in penalties or safety hazards.
Moreover, some industries have critical equipment whose failure could lead to catastrophic outcomes. In these situations, the cost of failure far outweighs the benefits of predictive maintenance. Adopting a cautious approach by replacing parts preventively is seen as the best way to mitigate risks and ensure operational continuity.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Balance
Ultimately, the decision between preventive replacement and predictive algorithms is influenced by a combination of factors, including certainty, human expertise, integration challenges, and regulatory requirements. Operators must weigh the benefits and drawbacks of each approach to find a balance that aligns with their organizational goals and operational realities.
While predictive algorithms offer exciting potential for optimizing maintenance practices, preventive replacement remains a reliable and trusted strategy. As technology continues to advance, operators may increasingly adopt predictive solutions, but the human element, familiarity, and regulatory constraints will ensure that preventive replacement remains an essential part of the maintenance toolkit.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com