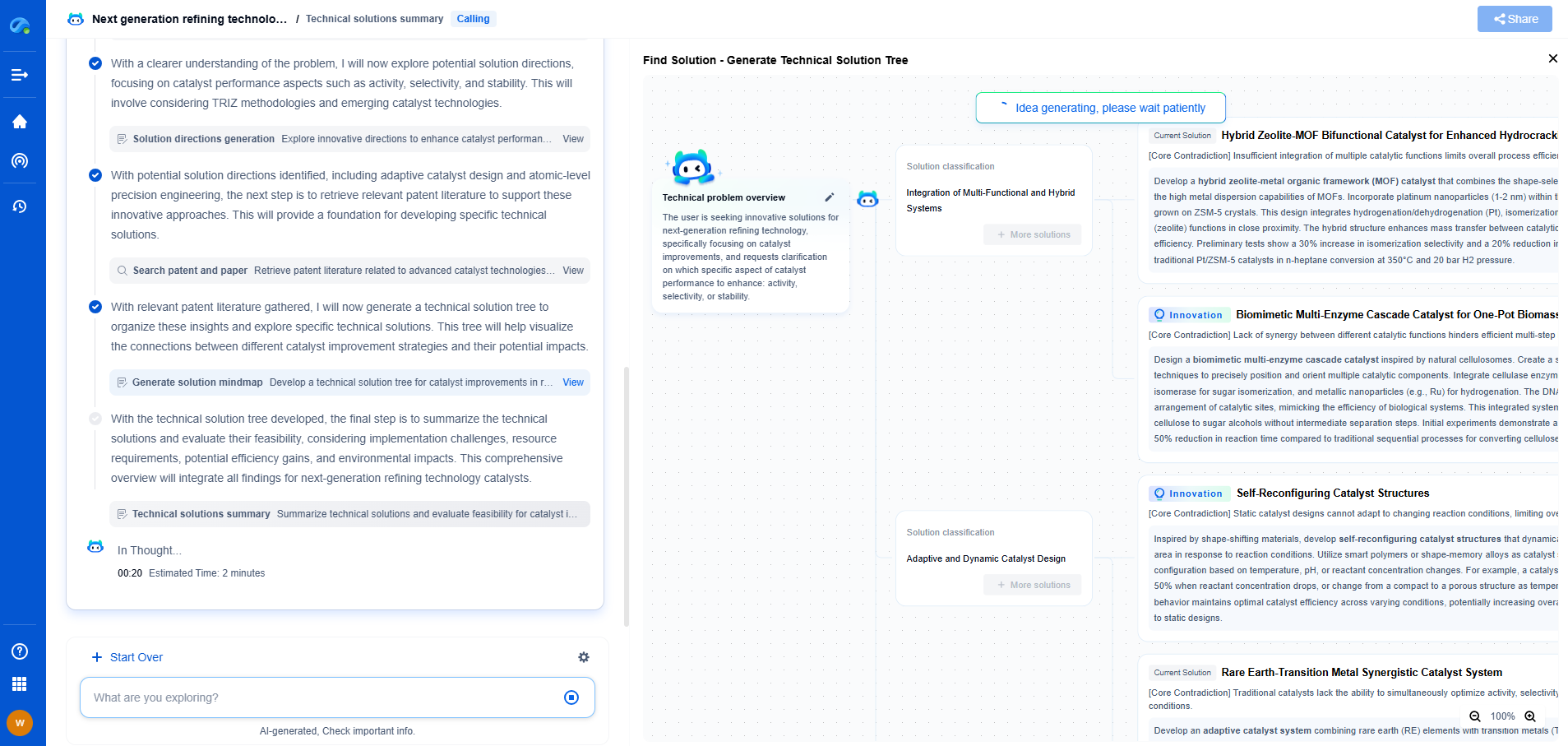
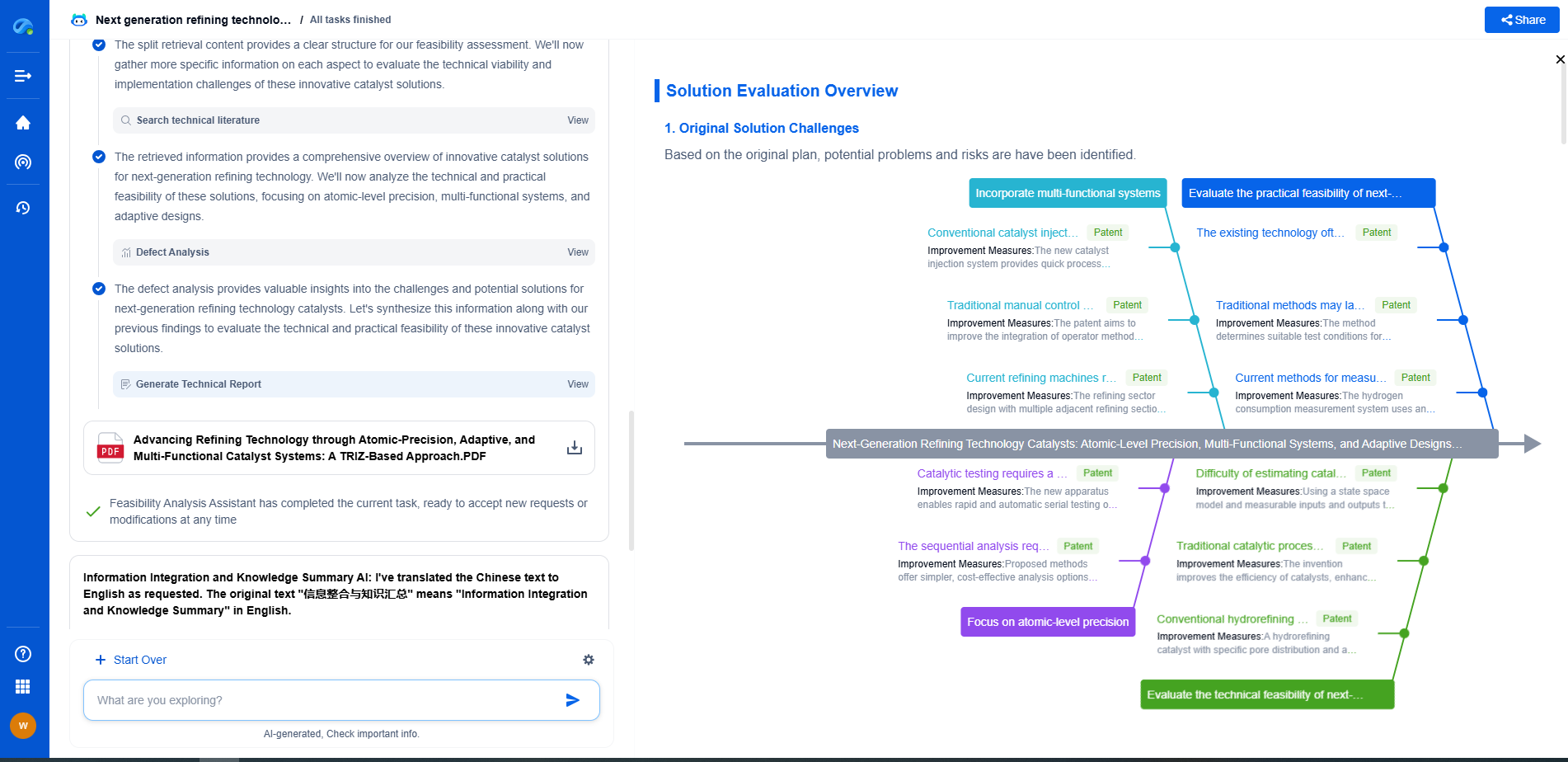
Why Your Ground Resistance Test Is Failing – And How to Fix It
JUL 9, 2025 |
Ground resistance testing is crucial for the safety and functionality of electrical systems. It ensures that electrical installations are properly earthed to prevent hazardous situations such as electric shocks, equipment failure, and fires. However, failing test results can be frustrating and often perplexing, especially when you believe all systems are in place. Let’s dive into why your ground resistance test might be failing and how you can address these issues effectively.
Common Causes of Ground Resistance Test Failures
1. **Poor Soil Conditions**: The type of soil and its moisture content significantly affect ground resistance. Dry, rocky, or sandy soils typically have higher resistance compared to moist, clayey soils. Seasonal changes can exacerbate this problem, as soil resistivity increases with dryer conditions.
2. **Improper Installation**: If grounding electrodes are not installed at the correct depth or spacing, or if they are not connected properly, the resistance test can fail. Poor installation practices lead to inadequate contact with the earth, increasing resistance levels.
3. **Corrosion**: Over time, grounding rods and connections can corrode, increasing resistance and prompting test failures. Corrosion can be accelerated by soil chemical properties and environmental conditions.
4. **Inadequate Grounding System Design**: A poorly designed grounding system may not be able to handle the electrical load or fault currents, resulting in high resistance readings. Insufficient or improperly sized grounding conductors and electrodes could be the culprits.
5. **Electrical Noise and Interference**: Electrical noise from nearby equipment or power lines can interfere with test readings. This interference can produce inaccurate results, leading to perceived failures.
Troubleshooting and Solutions
1. **Soil Improvement**: When poor soil conditions are the issue, consider enhancing the soil around your grounding system. You can add moisture-enriching substances such as bentonite or chemical additives designed to reduce soil resistivity. Alternatively, use longer or additional ground rods to reach deeper, more conductive soil layers.
2. **Ensure Proper Installation**: Verify that all grounding components are installed correctly. Check the depth and spacing of grounding electrodes and ensure connections are secure. Periodically inspect the system to confirm it remains in good condition.
3. **Address Corrosion**: Regular maintenance is key to preventing and managing corrosion. Use corrosion-resistant materials such as copper-clad steel for grounding electrodes, and apply protective coatings where necessary. Conduct regular inspections to catch early signs of corrosion.
4. **Revise Grounding System Design**: Review the entire grounding system design to ensure it meets current standards and electricity load requirements. Consider consulting with an electrical engineer to make necessary adjustments or enhancements.
5. **Mitigate Electrical Noise**: To counteract electrical noise, conduct tests during periods of low electrical activity, such as early morning or late at night. Utilize test equipment with noise-cancelling features or employ alternative testing methods that are less susceptible to interference.
Best Practices for Reliable Ground Resistance Testing
- Conduct periodic tests to monitor changes over time, especially after weather events or construction activities.
- Use the right equipment for the environment and conditions. Ensure that test instruments are calibrated and in good working order.
- Maintain comprehensive records of all tests, including conditions and any modifications made to the grounding system.
Conclusion
Ground resistance testing is a vital part of maintaining a safe and effective electrical system. By understanding the factors that can cause test failures and implementing strategic solutions, you can ensure that your grounding system performs reliably. Regular maintenance and testing, coupled with a well-designed and installed system, will protect both people and equipment from electrical hazards. Taking these steps will not only help you pass ground resistance tests but also enhance the overall safety and efficiency of your electrical installations.
Navigating the evolving world of electrical measurement—from high-precision signal integrity to advanced test protocols like BERT or TDR—demands more than just expertise; it demands smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka empowers you to keep up—by turning complex patent data, technical parameters, and industry signals into actionable insight. It’s your AI partner for exploring what’s next in test, measurement, and electrical diagnostics.
💡 Try Patsnap Eureka for free and see how it transforms the way you work with electrical measurement technologies.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com