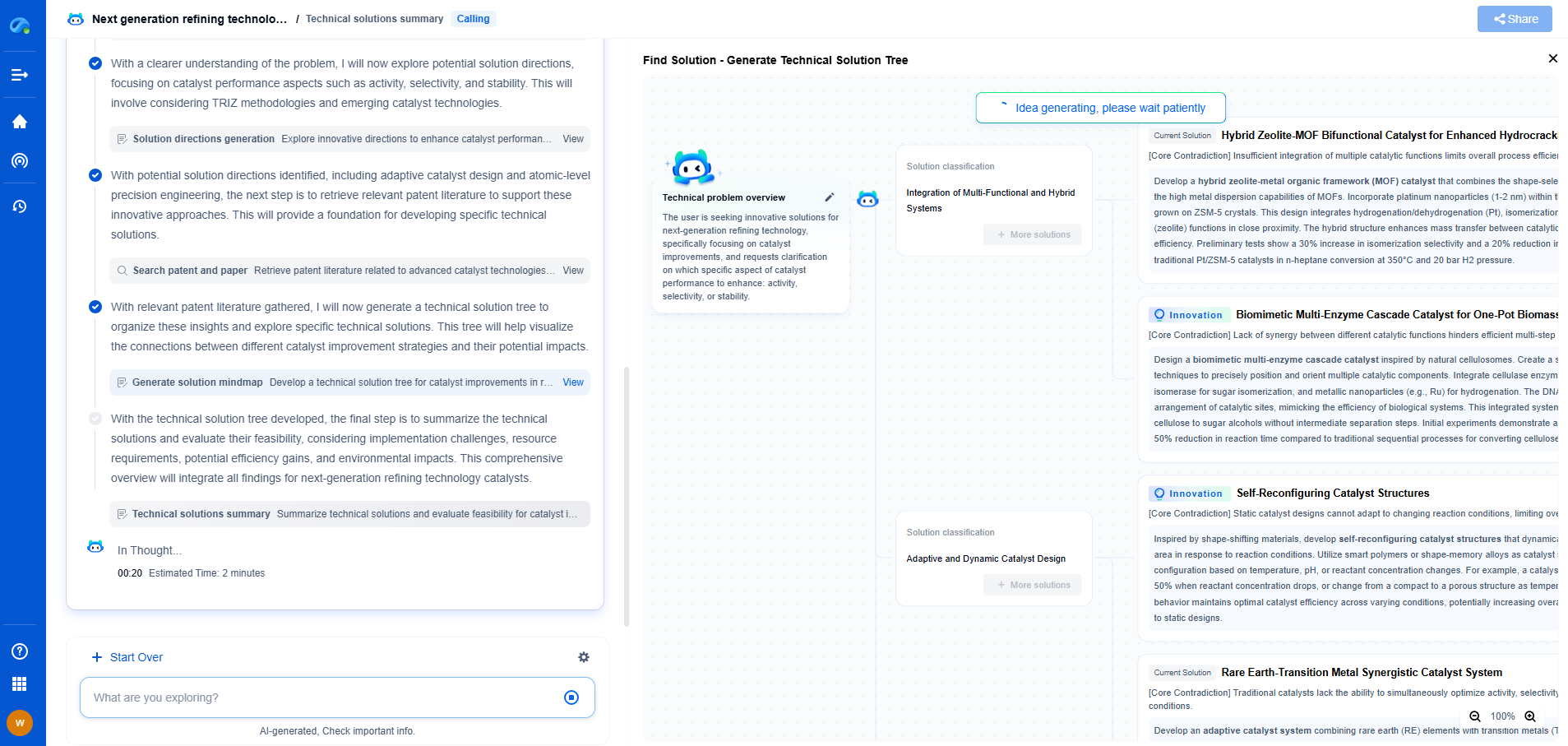
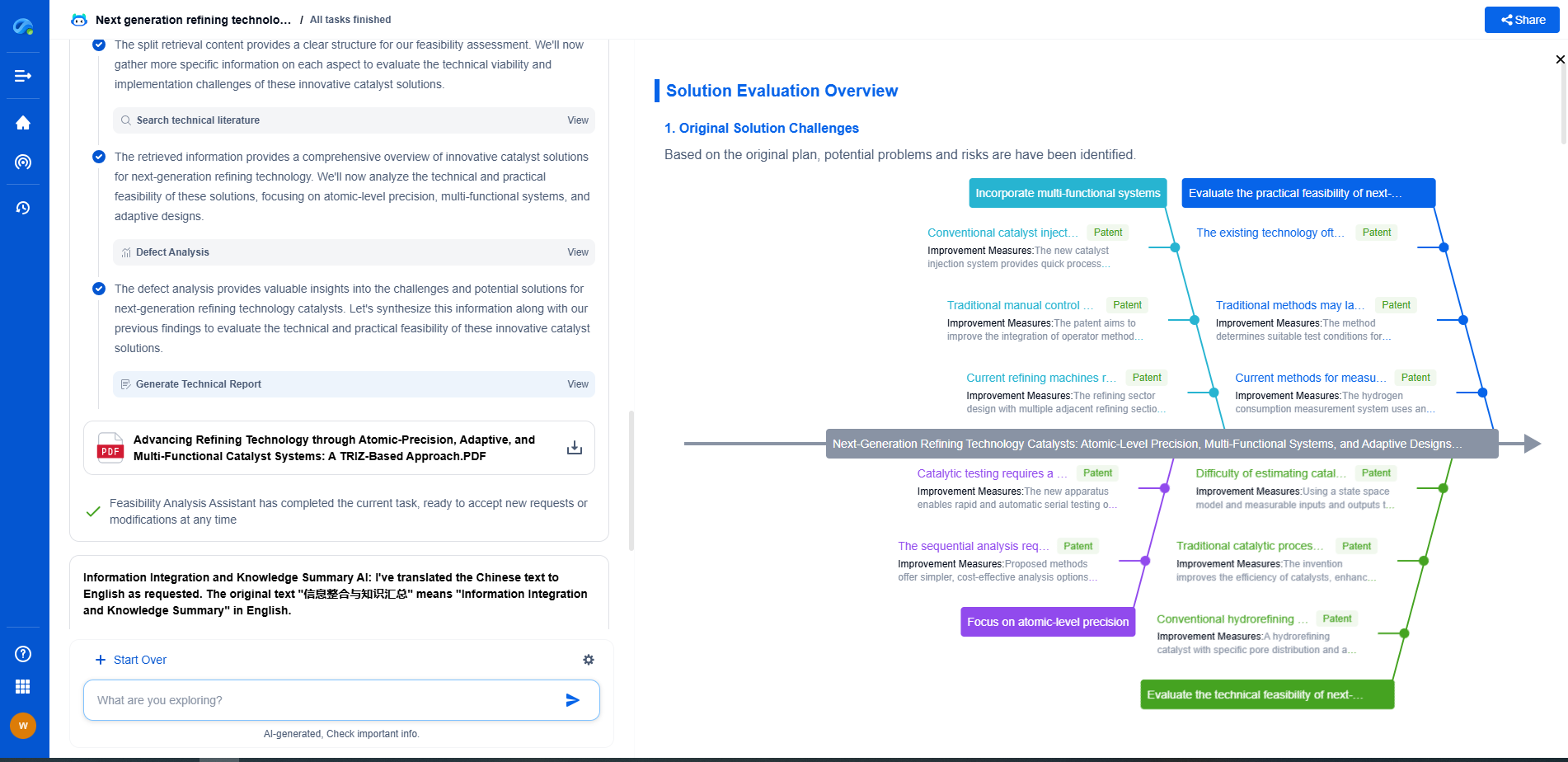
Wireless Sensor Interfaces: Bluetooth vs LoRaWAN vs Zigbee for Force Measurement
JUL 14, 2025 |
Understanding Wireless Sensor Interfaces
Wireless sensor interfaces serve as the communication medium between sensor nodes and data collection systems. When it comes to force measurement, accuracy, power consumption, range, and data rate are key factors to consider. Choosing the right interface can significantly impact the efficiency and reliability of the system.
Bluetooth: Ubiquitous and User-Friendly
Bluetooth technology is widely known for its ease of use and integration capabilities. It is particularly prevalent in consumer electronics and short-range communication systems. For force measurement applications, Bluetooth offers several advantages:
1. **Ease of Integration**: Bluetooth's widespread adoption means that it is often the default choice for many consumer devices. This can facilitate ease of integration and compatibility with existing systems.
2. **Low Power Consumption**: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is specifically designed to minimize power usage, making it suitable for battery-operated force measurement sensors.
3. **High Data Rate**: Bluetooth can handle relatively high data rates, which is beneficial for applications requiring real-time data transmission.
However, Bluetooth's limitation lies in its range. Typically, Bluetooth is effective over short distances (up to 100 meters in ideal conditions), which can be a constraint for applications requiring longer-range communication.
LoRaWAN: Long-Range and Low Power
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is specifically designed for long-range communication while maintaining low power consumption. It is particularly suitable for applications requiring data transmission over large areas, such as smart cities or industrial monitoring.
1. **Extended Range**: LoRaWAN can communicate over several kilometers, providing a significant advantage for remote force measurement applications.
2. **Scalability**: The network's ability to support thousands of devices makes it ideal for large-scale sensor deployments.
3. **Energy Efficiency**: LoRaWAN's low power consumption is advantageous for battery-powered sensors that need to operate over extended periods without maintenance.
However, LoRaWAN's data rate is relatively low compared to Bluetooth and Zigbee, which might not be suitable for applications requiring high-frequency data transmission or real-time analytics.
Zigbee: Balance Between Range and Data Rate
Zigbee technology offers a middle ground between Bluetooth and LoRaWAN, providing a balance of range, power consumption, and data rate. It is widely used in industrial applications and home automation.
1. **Mesh Networking**: Zigbee supports mesh networks, enabling devices to relay data through multiple nodes, thus extending the effective communication range and enhancing network reliability.
2. **Moderate Data Rate**: Zigbee offers a moderate data rate, which is sufficient for most force measurement applications that do not require high-speed data transmission.
3. **Low Power Consumption**: Like LoRaWAN, Zigbee is designed for energy efficiency, making it suitable for battery-powered devices.
Zigbee's maximum range is typically shorter than LoRaWAN, but its ability to form mesh networks compensates for this limitation in many scenarios.
Selecting the Right Interface for Force Measurement
Choosing between Bluetooth, LoRaWAN, and Zigbee for force measurement involves analyzing the specific requirements of the application. Considerations include:
- **Range Requirements**: For applications with sensors spread over large areas, LoRaWAN is advantageous. For shorter distances, Bluetooth and Zigbee are more appropriate.
- **Data Rate Needs**: High data rate requirements favor Bluetooth, while Zigbee offers a balanced option, and LoRaWAN is suited for applications where low data rate suffices.
- **Power Consumption**: All three technologies offer low power options, but the specific application context—such as battery life expectations and maintenance capabilities—will guide the choice.
- **Integration and Compatibility**: Existing infrastructure and system requirements may inherently favor one technology over the others.
Ultimately, the choice of wireless sensor interface should align with the operational goals, environmental conditions, and technical requirements of the force measurement application. By understanding the strengths and limitations of Bluetooth, LoRaWAN, and Zigbee, engineers and developers can make informed decisions that enhance the performance and reliability of their systems.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com