
Technical Background and Objectives
Background
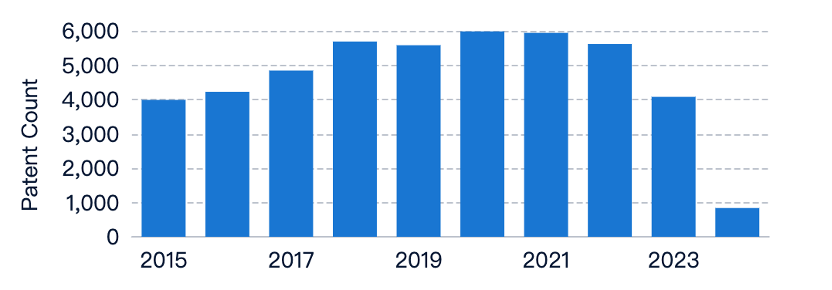
The technical field of ‘Easy fusion welding’ related to ‘fusion welding’ has seen a steady increase in patent applications over the years, indicating growing interest and research efforts. The number of patent applications peaked recently before a slight decline, suggesting an innovation boom with active development of new technologies to make fusion welding processes easier and more efficient. In contrast, literature publications have remained relatively low and stable, indicating that the field is more industry-driven. The divergence suggests that the industry is the primary driver of innovation, with companies investing heavily in research and development.
Objectives
The primary objective is to develop innovative techniques and methodologies for achieving easy fusion welding. This research aims to address challenges such as complex setup, stringent parameter control, and high operational costs, making the fusion welding process more accessible, cost-effective, and user-friendly without compromising the quality and strength of welded joints.
To get a detailed scientific explanations of Fusion Welding, try Eureka.
Technical Current Status Analysis
Fusion Welding Overview
Fusion welding is widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, shipbuilding, construction, and manufacturing. It involves melting and fusing the base materials to create a permanent joint, offering high strength and durability but requiring skilled operators for consistent and high-quality welds.
Applications and Impact:
- Automotive: Assembly of vehicle bodies, frames, and components. Easy fusion welding can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance weld quality.
- Aerospace: Fabrication of aircraft structures, engines, and critical components. Easy fusion welding ensures integrity and reliability under extreme conditions.
- Shipbuilding: Construction and repair of ships, offshore platforms, and marine structures. Easy fusion welding enhances productivity and durability.
- Construction: Structural steel fabrication, pipeline installation, and rebar joining. Easy fusion welding streamlines processes and improves safety.
- Manufacturing: Production of machinery, equipment, pressure vessels, and storage tanks. Easy fusion welding improves quality, reduces costs, and facilitates innovation.
Technical Characteristics and Challenges:
- Material Properties: Chemical composition, microstructure, and physical properties influence the fusion welding process.
- Joint Design and Accessibility: Geometry and configuration of the joint, as well as accessibility, can pose challenges.
- Heat Input and Thermal Management: Controlling heat input and managing thermal effects are crucial.
- Shielding Gas and Atmospheric Conditions: Proper shielding gas composition and coverage are essential.
- Operator Skill and Technique: Skilled operators are needed for consistent, high-quality welds.
- Automation and Process Control: Implementing and controlling automated systems requires robust strategies.
- Inspection and Quality Assurance: Ensuring integrity and quality of welded joints through non-destructive testing.
Technological Paths:
- Advanced Materials and Alloy Development: Developing new materials and alloys with improved weldability.
- Innovative Welding Processes and Techniques: Exploring techniques like friction stir welding and laser beam welding.
- Adaptive and Intelligent Control Systems: Implementing real-time monitoring and feedback systems.
- Simulation and Modeling: Using advanced simulation for process design and optimization.
- Automation and Robotics: Integrating advanced automation for consistency and efficiency.
- In-Process Monitoring and Inspection: Implementing real-time monitoring and inspection techniques.
- Workforce Training and Skill Development: Investing in comprehensive training programs.
Research Content
Research Objectives
Develop innovative techniques and methodologies for achieving easy fusion welding by exploring novel approaches to simplify the process.
Research Direction and Focus
Innovative Welding Techniques
- Investigate alternative welding techniques like laser or electron beam welding.
- Evaluate advanced welding processes like friction stir welding and explosive welding.
Welding Parameter Optimization
- Develop intelligent algorithms and machine learning models to optimize welding parameters.
- Create user-friendly software tools for automatic parameter recommendation.
Automated and Adaptive Welding Systems
- Develop automated and adaptive systems incorporating sensors and feedback mechanisms.
- Integrate robotics and computer vision for automated joint tracking and positioning.
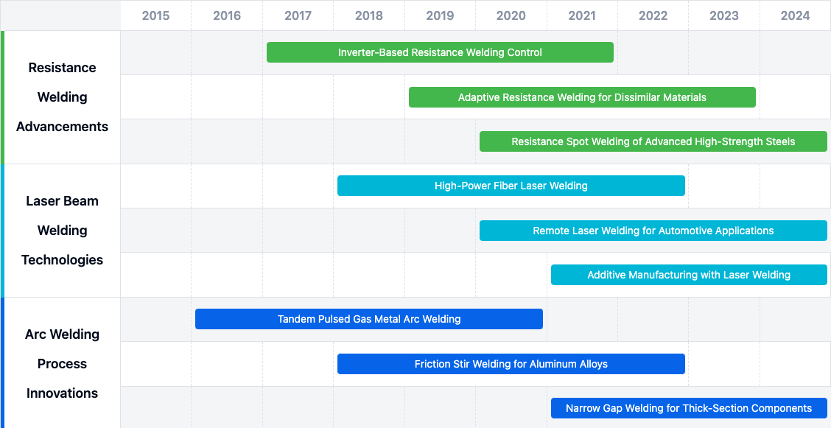
Technical Development Roadmap
Key Areas of Advancement
- Laser Beam Welding Technologies: High-power fiber laser welding and remote laser welding for automotive applications.
- Resistance Welding Advancements: Inverter-based control systems and techniques for dissimilar materials.
- Arc Welding Process Innovations: Tandem pulsed gas metal arc welding and narrow gap welding for thick-section components.
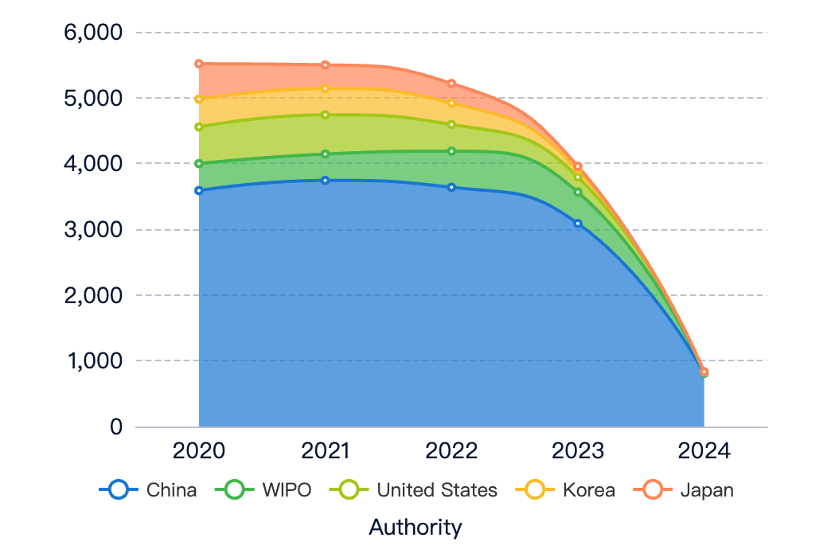
Main Player Analysis
Key Players and Focus
- Annamalai University: Research on GMAW, GTAW, and FSW for different materials, focusing on mechanical properties and optimization techniques.
- LG Energy Solution Ltd.: Focus on developing and patenting advanced welding technologies for various applications.
- Harbin Institute of Technology: Research on electron beam welding, laser brazing, and hybrid welding for advanced materials.
- Canon Inc.: Extensive patent portfolio on welding processes, equipment design, and process optimization.
- NIPPON STEEL CORP.: Focus on welding technologies for steel, covering a wide range of processes and applications.
Current Technical Solution Overview
Fusion Welding Methods and Techniques
- Controlling Welding Process: Techniques for controlling fusion depth, weld seam formation, and weld penetration.
- Fusion Welding Machines and Apparatus: Innovations in seam fusion-welding machines, fusion welding machines for cladding, and machines for specific applications.
- Fusion Welding of Plastic and Resin Materials: Methods for welding resin articles and large plastic parts.
- Fusion Welding Devices and Systems: Optimizing the welding process and devices for specific applications.
- Fusion Welding for Specific Applications: Techniques for TIG welding with nuclear fusion, welding of pipe parts, and fusion welding for metallurgical inspection.
Fusion Welding of Specific Materials
- Techniques for Specific Materials: Methods for welding superalloys, molybdenum alloys, and other challenging materials.
- Devices and Methods for Fusion Welding: Innovations in welding torches, automatic systems, and methods for specific materials like thermoplastics and aluminum alloys.
- Processes for Optical Fibers: Techniques for aligning and welding optical fibers with precision.
- Techniques for Pipe and Tube Applications: Methods for welding thermoplastic pipes, electro-fusion welding, and welding of fittings.
- Advancements in Fusion Welding Processes: Optimizing parameters, using specialized materials, and enhancing quality and efficiency.
Fusion Welding Equipment and Apparatus
- Equipment for Specific Materials: Specialized equipment for aluminum alloys and coiled materials.
- Automatic and Simulation Equipment: Equipment for automatic operations and simulation for training.
- Integrated Functions: Equipment combining welding and cutting or edge sealing.
- Equipment for Specific Applications: Tools for welding optical fibers, piping systems, and jewelry.
- Advanced Control and Adjustment Systems: Equipment with precise control systems for consistent welds.
Fusion Welding of Plastic and Synthetic Materials
- Methods and Devices for Plastic Pipes and Fittings: Techniques for welding pipes to saddles, branch pipes, and other fittings.
- Joining Plastic Components: Methods for welding synthetic resin sheets and molded products.
- Fusion Welding of Plastic Coatings and Films: Techniques for welding plastic coatings or films.
- Welding Synthetic Plastic Materials: Methods for welding thermoplastic resins and synthetic fibers.
- Welding 3D Printed Plastic Components: Techniques for welding plastic components from 3D printing.
Fusion Welding of Metal Components and Structures
- Methods for Metal Components: Techniques for butt-welding, cladding, and joining dissimilar metals.
- Fusion Welding Apparatus and Devices: Innovations in welding machines and clamping devices.
- Filler Materials and Compositions: Specialized filler materials for improved weld quality.
- Processes for Specific Applications: Methods for welding pipes, screen materials, and high-tensile alloy steel members.
Key Patent Interpretation
Patent Highlights
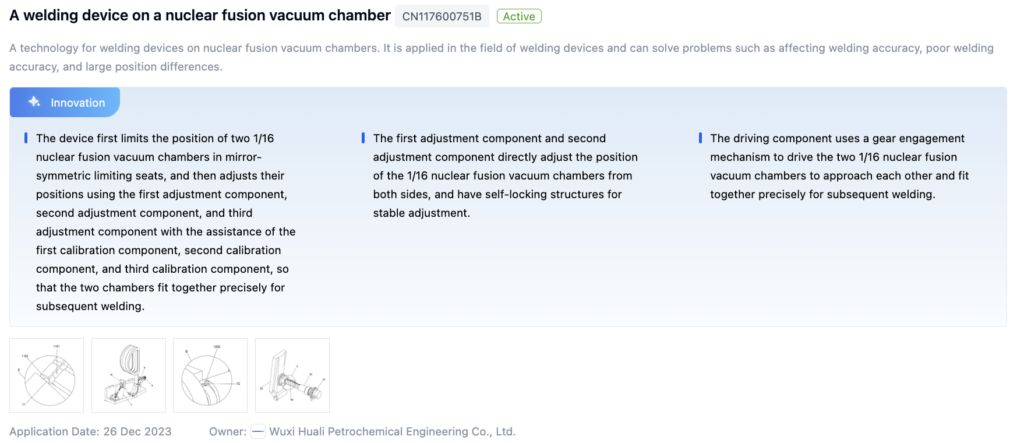
Patent 1: Welding Device on a Nuclear Fusion Vacuum Chamber
- Core Invention Points:
- Adjusts the position of nuclear fusion vacuum chambers using calibration components for precise fit and welding.
- Self-locking adjustment components ensure stable positioning.
- Gear engagement mechanism drives the chambers together for precise welding.
Patent 2: Titanium Steel Composite Tube Welding Method
- Core Invention Points:
- Trapezoidal groove on the steel pipe reduces required welding thickness.
- Hybrid welding process using friction stir welding and fusion welding for optimized weld performance.

Patent 3: Method of Cladding and Fusion Welding of Superalloys
- Core Invention Points:
- Uses filler material with controlled amounts of melting point depressants to reduce solidification cracking.
- Achieves crack-free welding of low ductility superalloys.
Possible Research Directions
- Fusion Welding Methods and Techniques: Developing techniques for butt welding, seam welding, and arc welding.
- Fusion Welding Control and Optimization: Techniques for controlling fusion depth and optimizing weld strength.
- Fusion Welding of Specific Materials: Methods for welding superalloys, molybdenum alloys, and other materials.
- Fusion Welding Equipment and Apparatus: Innovations in welding machines and devices.
- Fusion Welding of Plastic and Synthetic Materials: Techniques for welding plastic pipes, molded products, and other components.
If you want an in-depth research or a technical report, you can always get what you want in Eureka Technical Research. Try now!

