Kevlar is a para-aramid synthetic fiber first developed by DuPont in the 1960s, renowned for its exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, thermal stability, and resistance to wear and chemical degradation. Originally used in ballistic armor, Kevlar has evolved into a strategic material for various sectors demanding lightweight, durable, and high-performance solutions.
As industries move toward safer, more resilient, and environmentally conscious technologies, Kevlar is increasingly integrated into cutting-edge applications—from next-gen vehicles and protective gear to medical devices and smart textiles.
This article explores Kevlar’s structural properties, diverse application domains, comparative benefits and challenges, future innovation trends, and how tools like PatSnap Eureka AI Agent can accelerate Kevlar-related breakthroughs.
Material Composition & Key Properties
Kevlar is composed of long chains of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide. Key features include:
- High tensile strength: ~3,620 MPa
- Thermal resistance: Stable up to 500°F (260°C)
- Lightweight: Five times stronger than steel on an equal weight basis
- Chemical resistance: Resists most acids, alkalis, and organic solvents
- Low flammability: Self-extinguishing in nature
Kevlar fibers are produced via a solution spinning process, forming liquid crystal polymers that align during extrusion for optimal mechanical performance.

Application Domains
🛡️ Defense & Personal Protection
Modern combat and law enforcement demand lightweight armor with high energy absorption capacity. Kevlar’s ballistic resistance makes it ideal for bulletproof vests, helmets, and blast-resistant panels.
Current Research: Innovations include breathable armor weaves, moisture-resistant laminates, and AI-modeled fiber layouts for customizable protection.
Explore More in:
- Kevlar Innovations for Next-Gen Ballistic Protection
- Kevlar’s Role in Advancing Military Vehicle Armor
- How Kevlar Enhances Protection in Explosive Environments?
- Maximize Kevlar Efficiency in Extreme Environment Applications
- Kevlar’s Contribution to Lightweight Personal Armor Design
- How to Engineer Bulletproof Kevlar Solutions for Civilian Use?
- Kevlar Innovations Influencing Modern Architecture Trends
✈️ Aerospace, Automotive & Industrial Engineering
Industries prioritize weight reduction without compromising performance. Kevlar-reinforced composites are used in aerospace panels, vehicle reinforcements, and industrial equipment for superior crashworthiness and longevity.
Current Research: Emerging trends include nanocomposite Kevlar, 3D-woven Kevlar cores, and fireproof formulations for ultra-high-temperature zones.
Explore More in:
- Exploring Kevlar’s Role in Advanced Aerospace Applications
- Breakthroughs in Kevlar Aerospace Composite Materials
- Kevlar as a Game-Changer in Eco-Friendly Vehicle Design
- Kevlar Fiber Technology in Modern Manufacturing Processes
- Ultralight Kevlar Composites for Aerospace Efficiency
- Kevlar’s Expansion into High-Temperature Environments
- Kevlar’s Role in Enhancing Mining Safety Instruments
🚨 Smart Textiles & Wearable Technology
Wearables require breathable, strong, and flexible substrates. Kevlar enables protective apparel, stretchable smart fabrics, and RFID-compatible clothing.
Current Research: AI-designed weaves, conductive fiber integration, and heat-sealable smart threads are driving innovation in this space.
Explore More in:
- How to Integrate Kevlar into Smart Protective Clothing?
- Kevlar and Its Role in New Age Environmental Protection Gear
- How to Innovate Kevlar-Based Smart Fabrics for Health Monitoring?
⚕️ Medical, Bioengineering & Filtration
Kevlar’s biocompatibility, porosity, and durability enable applications in surgical instruments, implants, prosthetics, and wound dressings.
Current Research: Focus areas include Kevlar meshes for tissue regeneration, fiber-functionalized drug delivery, and next-gen filtration membranes.
Explore More in:
- Future of Kevlar in Medical Device Engineering
- Kevlar’s Enhancement of Electric Vehicle Fire Safety Measures
- Kevlar in Developing High-Performance Outdoor Gear
- Kevlar Applications in the Development of Advanced Orthotics
- Kevlar Applications in Breakthrough Wound Treatment Devices
- Kevlar-Based Filtration Systems for Industrial Applications
🏗️ Construction & Infrastructure
Modern infrastructure must balance strength, weight, and resilience. Kevlar reinforcements in concrete, seismic dampers, and tension cables extend structural durability.
Current Research: Green Kevlar composites and 4D-woven meshes are tested for earthquake-proofing and long-term material aging resistance.
Explore More in:
- How to Improve Durability in Kevlar-Based Gear?
- Kevlar-Based Nano-Composites for Strength and Flexibility
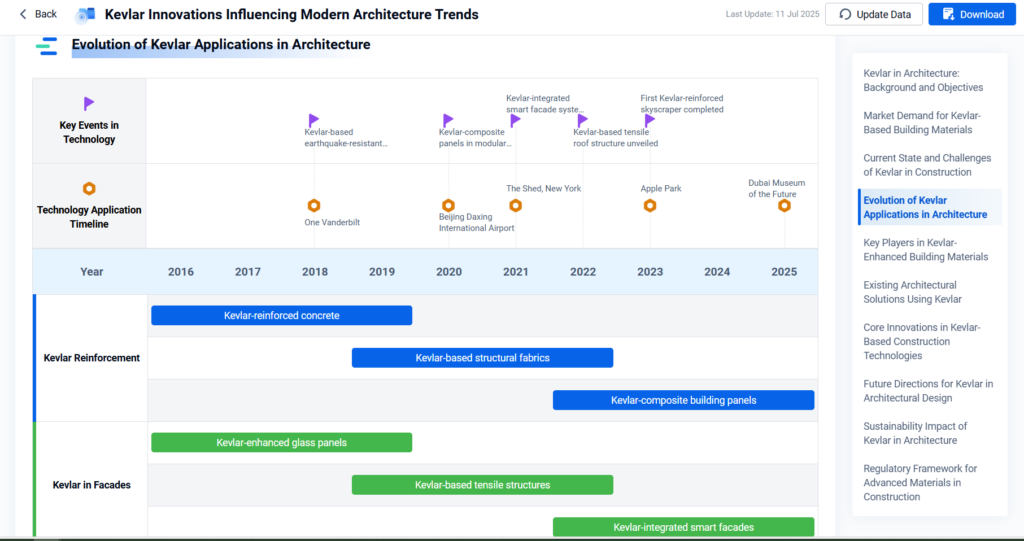
- Kevlar Reinforcement in Modern Concrete Construction
- How to Optimize Kevlar Weaving Techniques for Increased Toughness?
- Deploying Kevlar for Enhanced Earthquake-Resilient Structures
- Kevlar’s Role in Strengthening Power Transmission Lines
- Kevlar’s Contribution to High-Stress Construction Environments
Comparative Advantages & Limitations
Kevlar’s advantages make it indispensable in applications where failure is not an option. However, its limitations must be acknowledged to make informed engineering and research decisions.
Advantages:
- Exceptional Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Kevlar’s tensile strength exceeds that of steel while being significantly lighter, making it ideal for aerospace, military, and sports applications where weight saving is critical.
- Thermal Stability: Performs reliably in high-temperature environments up to 500°C without degradation, a major plus for firefighting gear, automotive parts, and industrial seals.
- Cut, Abrasion & Impact Resistance: It protects against sharp objects and high-velocity impacts, which is why it’s a material of choice in body armor, gloves, and mechanical wear protection.
- Chemical Inertness: Resistant to many corrosive agents including acids, fuels, and solvents. This expands its application in harsh environments like oil & gas and mining.
- Design Flexibility: Can be spun into yarns, woven into fabrics, layered into composites, or even used in laminates with carbon fiber for ultra-performance applications.
Limitations:
- UV Degradation: Kevlar degrades under prolonged UV exposure unless specially treated, making it less suitable for long-term outdoor use without protective coatings.
- Hydrophilic Nature: While chemically resistant, it can absorb moisture, which may reduce mechanical performance in humid conditions unless encapsulated.
- Cost & Processing: Kevlar is more expensive than many alternatives and requires specialized equipment for fabrication, particularly in advanced composite applications.
- Limited Electrical Properties: Though durable, it is not conductive or suitable for applications requiring electrical functionality unless combined with conductive materials.
- Recyclability Challenges: Although durable, end-of-life Kevlar products are difficult to recycle and require innovation in reuse or decomposition methods to improve circularity.
Future Outlook & Research Frontiers
Kevlar’s trajectory is expanding through both application-specific and cross-disciplinary innovation:
Emerging Directions:
- Smart sensor-embedded fabrics for military/healthcare
- Biodegradable or recyclable Kevlar analogs
- Enhanced 3D printing filaments with Kevlar strands
- Acoustic damping in space and defense environments
Commercial Breakthrough Areas:
- AI-designed fiber topology for performance targeting
- Low-cost green synthesis methods
- Multi-material Kevlar hybrids for energy and electronics
Conclusion & Key Takeaways
Kevlar has become a benchmark for safety, strength, and adaptability across industries. From life-saving ballistic vests to aerospace breakthroughs and medical devices, its high-performance capabilities continue to inspire innovation.
Now is the time for researchers, engineers, and manufacturers to reevaluate Kevlar’s potential in sustainable and high-stakes environments.
Accelerate Innovation with PatSnap Eureka AI Agent
Ready to unlock the full potential of Kevlar?
PatSnap Eureka AI Agent empowers your R&D team to uncover hidden white spaces, visualize patent activity in real time, and benchmark against global innovations across materials science and defense tech.
👉 Request a free PatSnap Eureka AI Agent demo today and future-proof your next material breakthrough.