
Plasma display technology has been a game-changer in the world of visual display. Known for its vibrant colors, deep blacks, and wide viewing angles, plasma displays offer a viewing experience that has made them a popular choice for home entertainment, professional applications, and industrial uses. However, as display technology evolves, newer technologies like OLED and QLED have started to challenge the supremacy of plasma displays. This article explores the science behind plasma display technology, its advantages, applications, challenges, and the latest innovations driving this field forward.
Understanding Plasma Display Technology
Plasma displays use ionized gases to produce light. In each pixel of the screen, tiny cells contain gases like neon and xenon that are electrically charged to create plasma. The plasma emits ultraviolet (UV) light, which then excites phosphor materials to emit visible light. This process creates the vivid and dynamic images we see on plasma screens.
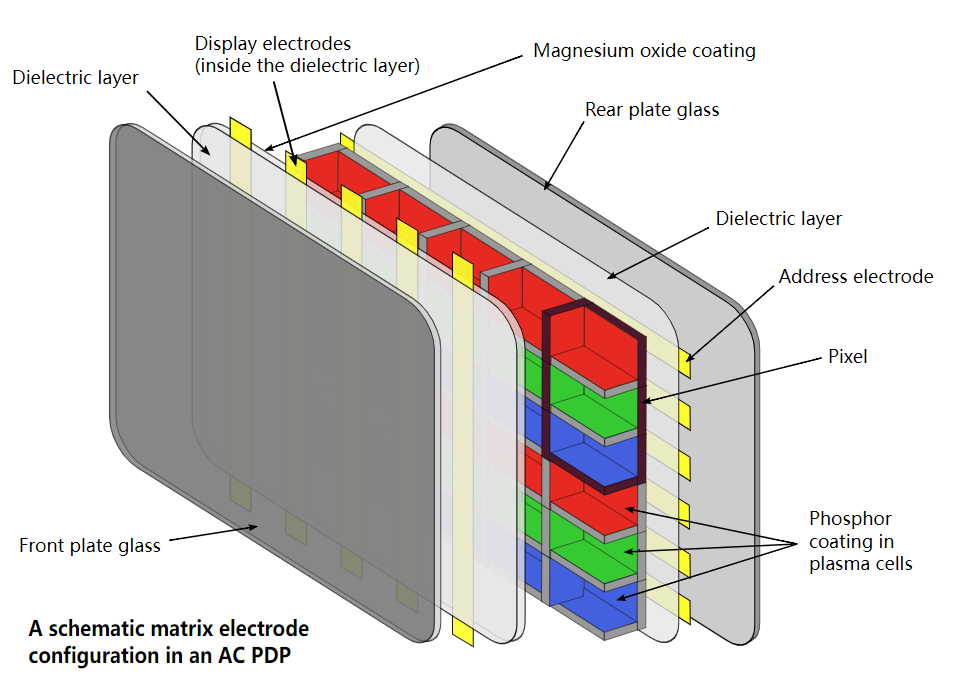
(Image Source: Wikipedia )
Key Characteristics of Plasma Displays:
- Excellent color reproduction and deep blacks. ✅
- Wide viewing angles without color distortion. ✅
- High contrast ratios for enhanced image clarity. ✅
- Heavier and thicker compared to other display technologies. ❌
- Higher power consumption, especially for large screens. ❌
The Science Behind Plasma Display Technology
At its core, plasma display technology works by electrically stimulating gas cells to create visible light. This method allows each pixel to operate independently, giving plasma displays an edge in terms of brightness, contrast, and color accuracy.
The Key Benefits of Plasma Displays
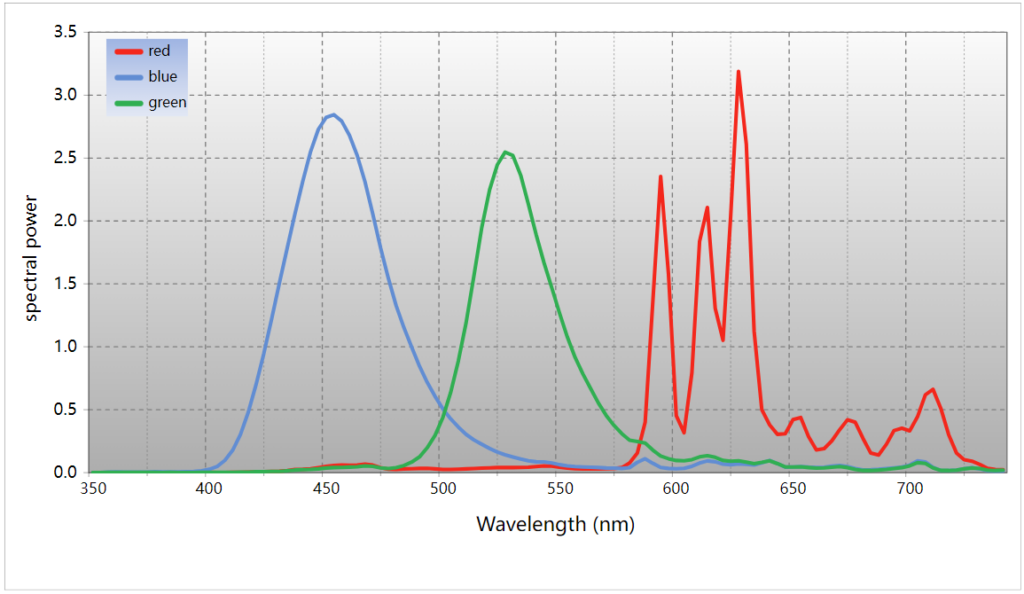
- Color Accuracy: Plasma displays are renowned for their rich and accurate color reproduction. This is due to the full-spectrum light emission of the plasma cells.
- Wide Viewing Angles: Unlike some other technologies, plasma screens maintain color consistency and image clarity even from extreme angles.
- Brightness and Contrast: Plasma displays can produce brighter images with deeper blacks, enhancing the contrast ratio and overall image quality.
While OLED and LED displays have gained popularity in recent years, plasma displays remain a strong contender in high-end applications due to their superior color accuracy and brightness levels.
Performance Comparison: Plasma Displays vs. Other Technologies
When comparing plasma displays to other technologies, Eureka Technical Q&A offers in-depth insights into their performance, durability, and suitability for different applications, helping you make informed decisions based on expert analysis.
| Parameter | Plasma | LCD | OLED |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luminous Efficacy | 1.5–3 lm/W | 3–5 lm/W (with LED backlight) | 10–15 lm/W (self-emissive) |
| Response Time | ~1 μs (gas discharge) | ~5–10 ms (liquid crystal inertia) | ~0.1 μs (organic electroluminescence) |
| Viewing Angles | 160°+ | ~120° (IPS/VA panels) | 180° (no backlight) |
| Power Consumption | High (sustain discharges) | Moderate (backlight-dependent) | Low (per-pixel emission) |
LCD: Relies on backlight modulation , achieving higher brightness but limited by liquid crystal opacity. Local dimming improves contrast but introduces blooming artifacts.
OLED: Superior infinite contrast and flexibility but faces challenges in burn-in and lifespan for static content.
Market Trends:
Plasma’s decline post-2015 stems from OLED’s thinner form factors and LCD’s cost scaling.
Applications in Different Industries
Home Entertainment
Plasma displays have been a popular choice for home theater systems due to their superior picture quality, especially for high-definition and 4K content. The large screen sizes available make them ideal for immersive movie-watching experiences.
Professional and Commercial Uses
- Digital Signage: Plasma displays are still used in commercial settings like shopping malls, airports, and stadiums where large, high-quality displays are needed.
- Medical Imaging: The high resolution and contrast of plasma displays make them suitable for medical diagnostics and imaging, where clarity is critical.
Industrial Applications
Plasma technology is also used in certain industrial sectors for specific applications, such as:
- Light Emitting Plasma Panels: Used in scientific research for energy-efficient light sources.
- High-Performance Displays: Employed in sectors like aviation for advanced cockpit displays and control systems.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Display Panel LG Electronics, Inc. | Dividing scan electrodes into blocks and applying gradually falling signals improves address discharge stability and enhances luminance. | Large-screen televisions and public information displays requiring high brightness and contrast. |
| VIERA Plasma TV Panasonic (Japan) | Constant reduction in cost and efforts to realize larger sizes have made plasma displays dominant in the market. | Home entertainment systems and professional display applications requiring large screen sizes. |
| ADS (Address Display-Period Separation) PDP Fujitsu Ltd. | Developed technologies providing three times the luminous efficacy compared to latest PDP products and innovative manufacturing processes for cost reduction. | Large screen flat panel display market, particularly for high-end consumer and commercial applications. |
| Plasma Display Device Samsung SDI Co., Ltd. | Uses complementary colors in filters and phosphors for effective light absorption, enhancing image quality and reducing manufacturing complexity. | High-contrast display applications in both consumer and professional settings. |
| Advanced Color PDP Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. | Improved PDP technologies supporting a growing market, with market value reaching $10 billion in 2005. | Plasma televisions and large-format displays for both industrial and consumer markets. |
Challenges and Limitations of Plasma Displays
While plasma displays offer excellent image quality, they come with some challenges:
❌ Power Consumption: Plasma displays are generally more power-hungry than other display types, which makes them less energy-efficient.
❌ Thick and Heavy: The design of plasma displays is bulkier compared to newer technologies like OLED, which can lead to challenges in space-limited environments.
❌ Burn-in Issues: Plasma screens are prone to burn-in, where static images can leave permanent marks on the screen over time.
Despite these limitations, plasma displays continue to be a strong choice for certain applications where picture quality is paramount.
Future Trends in Plasma Display Technology
Researchers and innovators continue to enhance the performance of plasma displays, even as newer technologies gradually phase them out. Some future trends include:
- Energy-Efficient Plasma Technology: Researchers are focusing on developing energy-efficient plasma displays to reduce their power consumption while maintaining image quality.
- Advanced Phosphor Materials: Researchers are developing new phosphor coatings to enhance color accuracy and lifespan.
- Integration with Smart Technology: Plasma displays are expected to integrate AI and IoT devices, offering smarter, more connected viewing experiences.
How Eureka by PatSnap Accelerates Innovation in Plasma Display Technology
What is Eureka by PatSnap?
Eureka by PatSnap is an AI-powered innovation intelligence tool that helps R&D teams discover the latest advancements in plasma display technology. With its data-driven insights, Eureka supports companies in staying competitive by providing access to patent analysis, market trends, and future technology roadmaps.
How It Benefits Plasma Display R&D
- Patent Analysis: Eureka helps researchers identify cutting-edge patents in the plasma display field, allowing companies to stay ahead of industry trends.
- Competitive Intelligence: By offering insights into competitor activities and technologies, Eureka helps manufacturers benchmark against top players in the display technology market.
- Technology Roadmapping: Eureka assists in strategic planning by providing valuable data on emerging technologies and market shifts, ensuring companies remain on the cutting edge of plasma display innovation.
For R&D teams focused on advancing plasma display technology, Eureka by PatSnap can significantly accelerate research and development processes, enabling quicker, more informed innovation strategies.
Conclusion
Plasma display technology remains a powerful solution in various industries, offering superior picture quality and vibrant colors. Despite its challenges, such as high power consumption and limited lifespan, plasma displays continue to be the go-to option for applications that demand the highest image quality. As new technologies like OLED and LED continue to develop, plasma displays will likely continue to evolve, with advancements focused on energy efficiency and integration with smart technologies. Tools like Eureka by PatSnap provide invaluable support for R&D teams, enabling them to stay ahead in the rapidly changing world of display technology.
🚀 Want to stay updated on the latest trends in display technology? Sign up for Eureka by PatSnap today to accelerate your innovation journey!
FAQs
1️⃣ Why are plasma displays so expensive?
Plasma displays tend to be more expensive due to their advanced technology, superior picture quality, and larger screen sizes.
2️⃣ How long do plasma displays last?
Plasma displays typically last between 30,000 and 60,000 hours, depending on usage and model.
3️⃣ Are plasma displays better than OLED?
Plasma displays offer superior color accuracy and brightness, but OLED displays are more energy-efficient and have thinner profiles.
4️⃣ Can plasma displays be used for gaming?
Yes, plasma displays offer excellent response times and color accuracy, making them suitable for high-quality gaming experiences.
5️⃣ How can I stay updated on plasma display innovations?
AI-powered tools like Eureka by PatSnap can keep you informed about the latest developments and trends in the plasma display industry.
To get detailed scientific explanations of plasma display, try Patsnap Eureka.


