
A rectifier diode is a semiconductor device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction. It is a fundamental component in power supplies, battery charging circuits, and electronic devices that require DC power. This article explores the working principle, types, applications, and safety considerations of rectifier diodes.
What is a Rectifier Diode?
A rectifier diode is a PN-junction diode designed to handle high voltage and current during rectification. It allows current to flow in the forward direction while blocking it in the reverse direction, making it ideal for converting AC to DC.
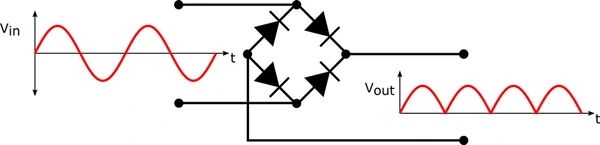
Working Principle
- Forward Bias: When you connect the anode (P-side) to the positive terminal and the cathode (N-side) to the negative terminal, the diode conducts electricity.
- Reverse Bias: When you reverse the polarity, the diode blocks current flow and prevents backflow.
Types of Rectifier Diodes
- Standard Silicon Rectifier Diode
- Handles moderate voltage and current
- Used in general power supply circuits
- Schottky Diode
- Has low forward voltage drop (0.2V–0.3V)
- Used in high-frequency applications and power efficiency circuits
- Fast Recovery Diode
- Has short reverse recovery time
- Used in switching power supplies and inverters
- Bridge Rectifier
- Consists of four diodes in a bridge configuration
- Provides full-wave rectification for AC to DC conversion
- Zener Diode (as a Rectifier)
- Can be used in voltage regulation and rectification
- Allows controlled current flow in the reverse direction when breakdown voltage is reached
Comparison: Half-Wave vs. Full-Wave Rectifier
| Parameter | Half-Wave Rectifier | Full-Wave Rectifier |
|---|---|---|
| Diodes Required | 1 | 2 (center-tap) or 4 (bridge) |
| Efficiency | Lower (~40%) | Higher (~80%) |
| DC Output | Pulsating | Smoother |
| Application | Simple circuits | Power supplies |
Applications of Rectifier Diodes
Looking to dive deeper into rectifier diodes? Eureka Technical Q&A offers expert insights to help you understand their applications and optimize their performance in various systems.
Power Supply Units
Rectifier diodes are essential in power supply units. They convert AC mains voltage into the DC voltage that electronic devices require. This conversion typically uses a rectifier bridge configuration for efficiency.
Signal Processing
In signal processing, rectifier diodes extract the envelope of amplitude-modulated (AM) signals. They also detect both positive and negative peaks in signals.
Temperature Measurement
Rectifier diodes play a role in temperature measurement, especially at cryogenic temperatures. Despite variability between samples, they accurately measure temperature changes in these conditions.
Automotive Applications
In the automotive industry, rectifier diodes power daytime running lights (DRL) and battery charging systems. Advanced technologies, such as Super Barrier Rectifiers (SBR), boost efficiency and reliability.
Telecommunications
Rectifier diodes are integral in telecommunications equipment. They rectify signals and provide stable power to various components.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics like smartphones, tablets, and televisions, rectifier diodes convert AC to DC. This conversion powers internal circuits efficiently.
Industrial Applications
Industries use rectifier diodes in power control systems and motor drives. They ensure reliable DC power conversion in various industrial applications.
Renewable Energy Systems
Rectifier diodes are critical in renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind. They convert the variable DC output from renewable sources into stable DC or AC power for grid integration.
Medical Devices
Medical electronics rely on rectifier diodes for devices like ECG machines and pacemakers. They ensure a reliable power supply for these critical applications.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace and defense, rectifier diodes are used for power conditioning and conversion in electronic systems. They enhance the performance and reliability of these systems.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Integrated Transformer/Rectifier Teledyne UK Ltd. | Integrates diodes within secondary winding, uses parallel diodes for compact design, addressing capacitance and cost issues in high voltage applications | High voltage applications requiring efficient and cost-effective power conversion |
| Cryogenic Temperature Sensor Tampere University of Technology | Utilizes common rectifier diodes for temperature sensing below 50K, providing a cost-effective alternative to calibrated cryogenic sensors | Quench detection and temperature change sensing in cryogenic environments |
| Parallel Diode Rectifier Assembly Associated Equipment Corp. | Uses current-regulating plate and links to balance current flow, enabling operation with unmatched diodes and handling excessive currents | High-current applications requiring robust rectification and thermal runaway prevention |
| Self-bootstrapping Field Effect Diode STMicroelectronics International NV | Employs field-effect devices with positive feedback, reducing voltage drop and leakage current while simplifying circuitry | Power conversion applications requiring high efficiency and cost-effectiveness |
| HSMS-2860 Schottky Diode Rectifier La Roche University | Achieves 36.2 mV output and 1.3% conversion efficiency at -20 dBm input power using single stub matching circuit or radial stubs low pass filter | Low-power energy harvesting applications at 2.45 GHz |
Safety Considerations for Rectifier Diodes
- Voltage Rating: Use a diode with a higher breakdown voltage than the circuit voltage.
- Current Rating: Ensure the diode can handle the maximum forward current without overheating.
- Heat Dissipation: Use heat sinks or cooling mechanisms for high-power diodes.
- Reverse Voltage Protection: Prevents damage from voltage spikes in inductive loads.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a rectifier diode and a normal diode?
A rectifier diode handles higher currents and voltages, while normal diodes are used for signal processing and low-power applications.
2. How do I choose a rectifier diode?
Consider the maximum voltage, current rating, recovery time, and power dissipation needed for your circuit.
3. What is the most commonly used rectifier diode?
The 1N4007 is widely used in general rectification due to its high voltage rating (1000V) and 1A current capacity.
4. Can a Zener diode be used as a rectifier?
Yes, but it primarily serves voltage regulation, not power rectification.
5. What happens if a rectifier diode fails?
A failed diode can cause circuit malfunction, overheating, or complete power failure in rectified circuits.
Conclusion
Rectifier diodes are essential components in power electronics, enabling the conversion of AC to DC in a wide range of applications. Choosing the right type of rectifier diode ensures efficient performance and circuit reliability. Proper voltage, current ratings, and heat management are crucial for safe and long-lasting operation.
To get detailed scientific explanations of Rectifier diodes, try Patsnap Eureka.


