
What Is Barium Phosphate?
Barium phosphate (Ba₃(PO₄)₂) is an inorganic compound known for its white, odorless appearance and water insolubility. Widely used in various industrial applications, this compound plays a significant role in fields like ceramics, pigments, and more. In this article, we’ll explore the chemical properties, uses, and key characteristics of Ba₃(PO₄)₂, offering valuable insights into its applications and significance in different industries.
Properties of Barium Phosphate
- Crystal structure: It crystallizes in the orthorhombic system
- Thermal properties: It exhibits a diffuse phase transition behavior
- Dielectric and conductivity properties: It shows temperature and frequency-dependent dielectric constant, dielectric loss, and AC conductivity
- Morphology: Nanostructured one can form irregular flakes or particles in the range of 20-100 nm
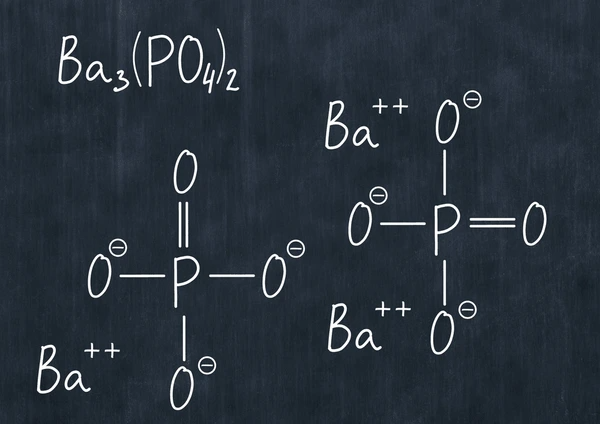
Safety Concerns and Handling Barium Phosphate
Toxicity and Health Risks: Barium compounds, including phosphate forms, can be toxic if ingested, inhaled, or contact skin. As a heavy metal, barium accumulates in the body, potentially damaging the cardiovascular, nervous, and muscular systems.
Handling and Exposure: Always wear proper personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and a lab coat when handling phosphate compounds. Ensure good ventilation to prevent inhaling dust or fumes, and follow safe handling procedures.
Comparison with Sodium Phosphate
Similarities: Both phosphate compounds have applications in medical and industrial fields. They share similar chemical properties and pose health risks if mishandled.
Differences: Sodium phosphate is often used in medical procedures like bowel cleansing but can cause renal issues and electrolyte imbalances. On the other hand, phosphate compounds like barium are primarily used in industrial applications, with fewer medical uses.
Applications of Barium Phosphate
Electro-optic Applications
- Piezoelectric Properties: Barium phosphate has strong piezoelectric properties, making it ideal for sensors and actuators. It converts mechanical stress into electrical charge, crucial for applications like sonar, pressure sensors, and precision engineering actuators.
- Electro-optic Devices: This material is also used in electro-optic devices, such as modulators and switches. Its ability to alter the refractive index under an electric field supports high-speed optical communication and laser technology.
Thermoelectric Applications
- Thermistors: Phosphate ceramics are commonly used in thermistors, which measure temperature. Their ability to change electrical resistance with temperature ensures precise control in electronic systems.
- Thermoelectric Generators: The material can convert heat into electricity, making it valuable for waste heat recovery systems and remote power generation.
Electrochemical Applications
- Batteries: Barium phosphate enhances lithium-ion battery technology. It improves efficiency, performance, and safety by increasing cycle life and thermal stability.
- Electrolyte Additives: As an electrolyte additive, it boosts ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability, enabling faster-charging, higher-energy-density batteries.
Catalysis and Materials Science
- Catalytic Applications: Barium phosphate acts as a catalyst or support in chemical reactions, speeding up processes and enhancing selectivity. This is useful in chemical synthesis, fuel processing, and environmental cleanup.
- Material Synthesis: The unique structure of this material aids in synthesizing advanced materials, offering tailored properties for specialized applications.
Application Cases
| Product/Project | Technical Outcomes | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|
| Barium Phosphate Catalysts | Enables efficient alkoxylation of organic compounds, and preparation of unsaturated carboxylic acids/esters with high selectivity. | Organic synthesis, fine chemical production, and polymer industry. |
| Barium Phosphate Phosphors | Exhibits high emission intensity, heat stability, and eliminates need for rare earth elements in phosphor materials. | Imaging plates for computed radiography, energy-efficient light sources. |
| Barium Phosphate Contrast Agents | Provides excellent contrast for visualizing blood vessels and microvasculature in ex vivo micro-CT imaging. | Biomedical imaging, preclinical studies, and vascular research. |
| Barium Phosphate Fillers | Imparts desirable properties like opacity, density, and durability to plastics, coatings, paints, and paper products. | Polymer composites, protective coatings, and paper manufacturing. |
| Barium Phosphate Pigments | Acts as a stable substrate for colored pigment formulations and coatings with improved opacity and durability. | Decorative coatings, paints, and inks for various applications. |
Latest Technical Innovations of Barium Phosphate
Synthesis Methods and Process Innovations
- Cyclic Production Method: This method prepares barium sulfate and lithium-iron phosphate by adding barium hydroxide to a heated lithium/sulfate solution. It ensures controlled output at high temperatures (above 50°C).
- Biosynthesis: Nanoparticles are bio-synthesized using centrifuged bacteria solutions at controlled pH, producing irregular, flake-like nanostructures (20-100nm in size).
- Catalytic Conversion: Barium sulfate converts to barium metaphosphate through high-temperature calcination (500°C) with ammonium dihydrogen phosphate in a single step.
- Continuous Precipitation: Barium and sulfate solutions mix under controlled pH (1-5), flow rates, and stirring, producing microcrystals with precise size and morphology.
Structural and Compositional Modifications
- Doping: Synthesis of cadmium-doped barium phosphate crystals exhibiting diffuse phase transition and relaxor behavior, with tunable dielectric properties.
- Composite Formation: Preparation of barium phosphate-based chemically bonded phosphate ceramics incorporating barium for improved radiation shielding.
- Phosphor Development: Synthesis of phosphate phosphors like Ba(TiZr)PO with controlled Zr doping (x) for tunable emission intensity and thermal stability without rare earth elements.
Separation and Purification Techniques
- Colloidal Separation: Separation of colloidal barium phosphate/sodium phosphate catalysts from alkoxylated products by water-induced breaking of the colloidal state.
- Acid Treatment: Treatment of di-barium phosphate with volatile acids (HCl, HNO3) to produce soluble barium salts with regeneration of phosphoric acid.
Technical Challenges of Barium Phosphate
| Synthesis of Barium Phosphate Nanoparticles | Developing efficient and scalable methods for the biosynthesis of barium phosphate nanoparticles with controlled size, morphology, and crystallinity. |
| Continuous Precipitation of Barium Phosphate Microcrystals | Optimising the continuous precipitation process for producing barium phosphate microcrystals with precise control over size, shape, and size distribution. |
| Catalytic Conversion of Barium Sulfate to Barium Phosphates | Exploring efficient catalytic routes for the one-step conversion of barium sulfate to barium metaphosphate or other barium phosphate compounds. |
| Doping and Structural Modifications of Barium Phosphates | Investigating the effects of doping and compositional modifications on the structural, dielectric, and relaxor properties of barium phosphate crystals. |
| Cyclic Production of Barium Sulfate and Lithium Phosphates | Developing a cyclic process for the co-production of barium sulfate and lithium-iron phosphate compounds with improved efficiency and yield. |
To get detailed scientific explanations of the barium phosphate, try Patsnap Eureka.

