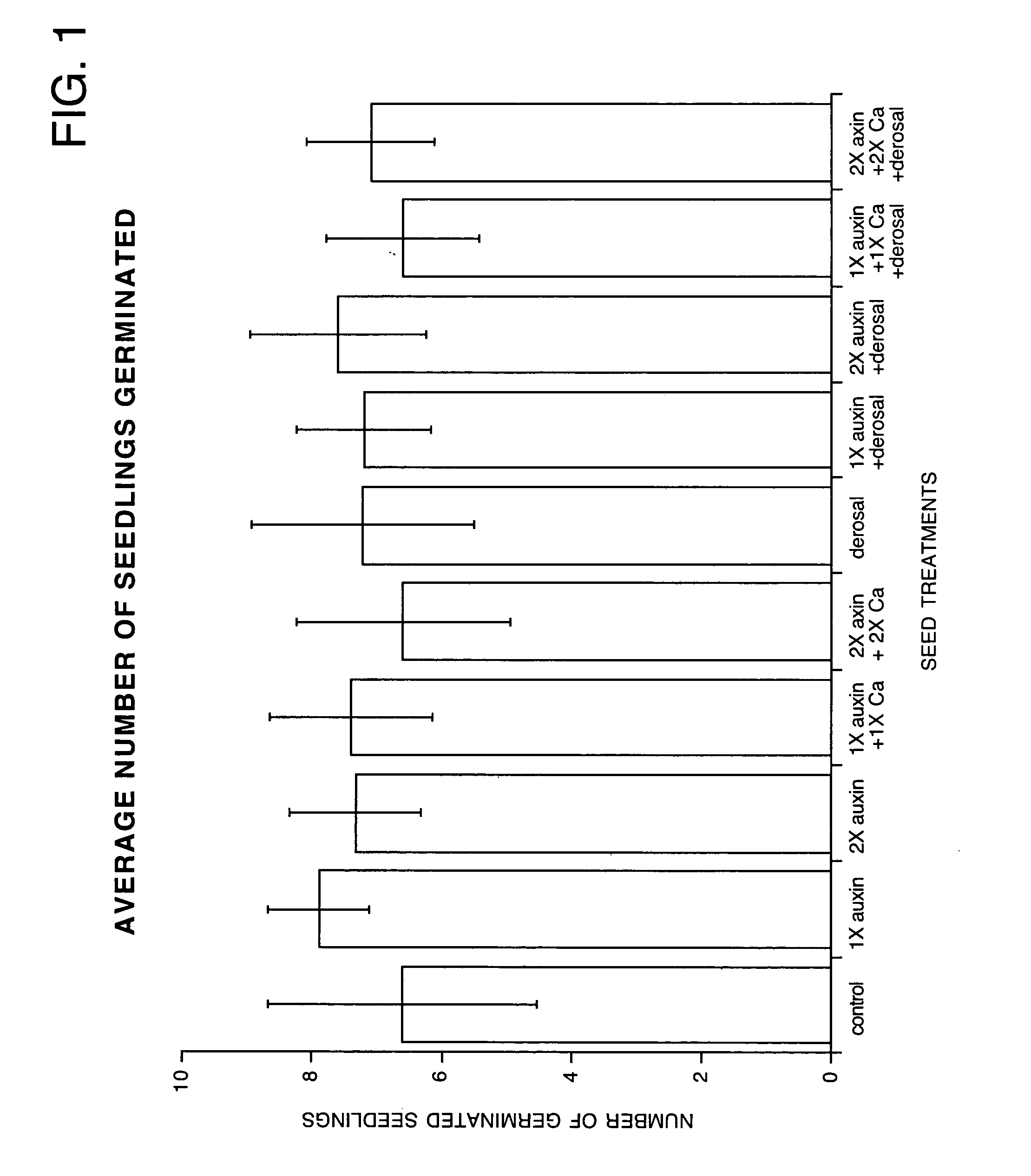
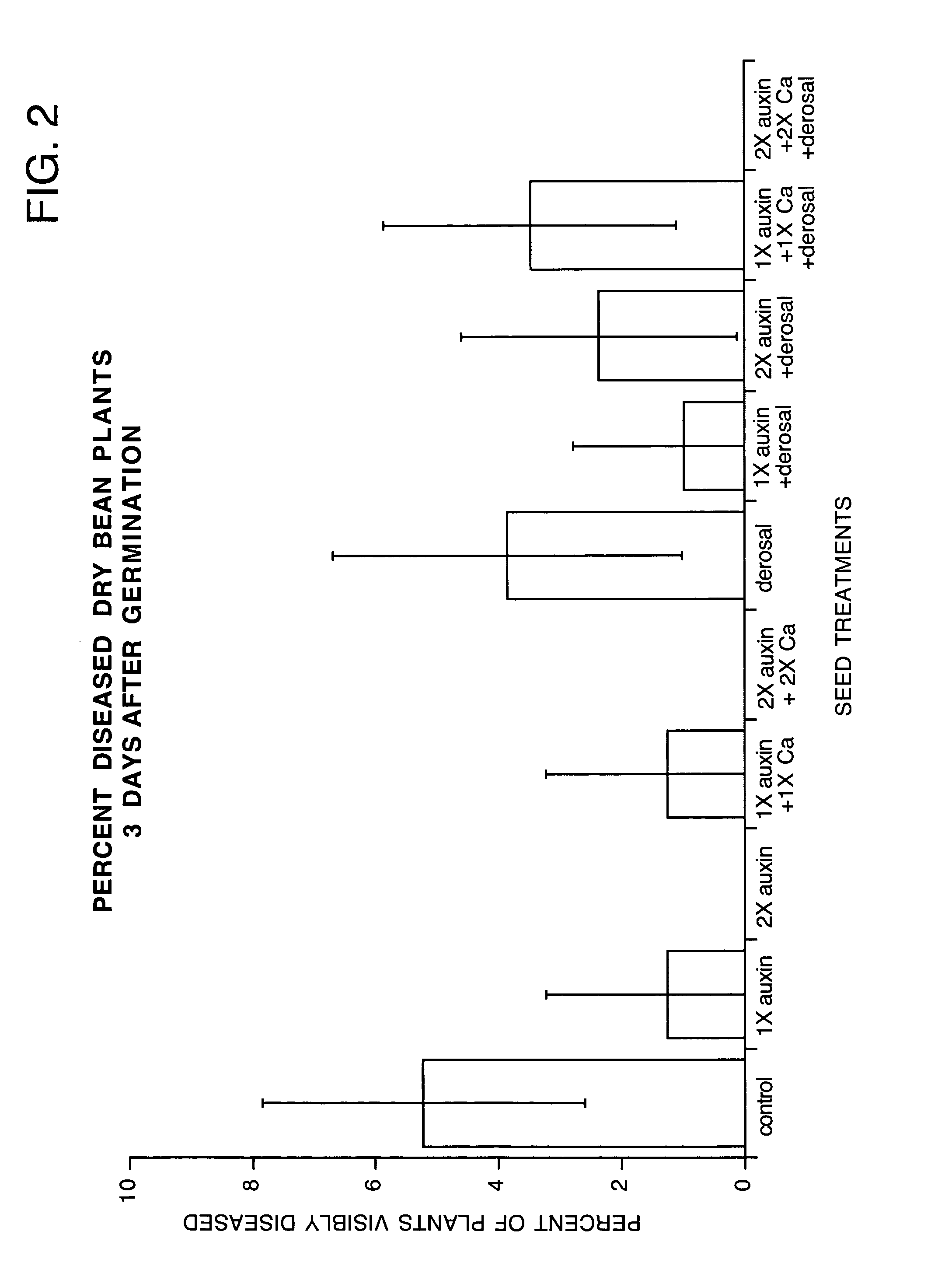
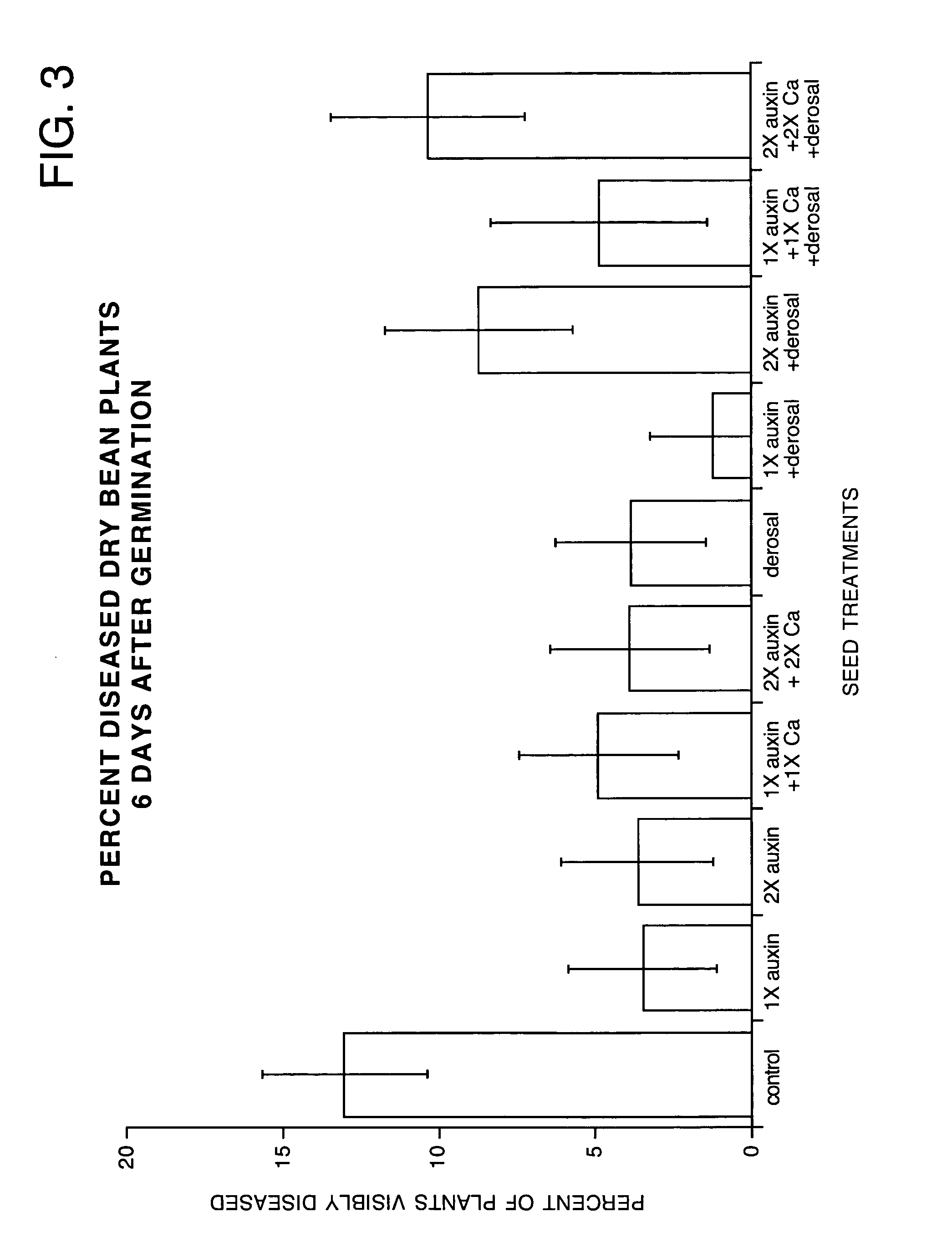
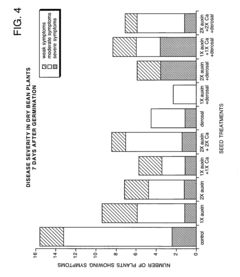
How Abscisic Acid Interacts with Auxin in Plant Development?
JUL 14, 20258 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ABA-Auxin Interaction Background and Objectives
The interaction between abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin in plant development represents a complex and crucial area of plant biology research. This interplay has been the subject of extensive study due to its significant impact on various aspects of plant growth, development, and stress responses. ABA, primarily known for its role in stress tolerance and seed dormancy, and auxin, a key regulator of plant growth and development, have long been recognized as essential phytohormones. However, their intricate interactions and combined effects on plant physiology have only recently begun to be unraveled.
The historical context of ABA-auxin interaction research dates back to the mid-20th century when these hormones were first identified and characterized. Initially, they were studied in isolation, with researchers focusing on their individual roles. As our understanding of plant hormone signaling advanced, it became increasingly apparent that these hormones do not act in isolation but rather form a complex network of interactions.
The evolution of research in this field has been marked by several key milestones. Early studies in the 1970s and 1980s provided the first hints of crosstalk between ABA and auxin pathways. The advent of molecular biology techniques in the 1990s allowed for more detailed investigations into the mechanisms of hormone signaling and interaction. The turn of the 21st century saw a surge in research utilizing genetic and genomic approaches, leading to the identification of numerous genes and proteins involved in ABA and auxin signaling.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between ABA and auxin in various aspects of plant development. This includes understanding how these hormones influence each other's biosynthesis, transport, perception, and signaling pathways. Additionally, researchers aim to uncover the physiological consequences of this interaction on processes such as root development, shoot growth, fruit ripening, and responses to environmental stresses.
Another critical goal is to translate this fundamental knowledge into practical applications for agriculture and biotechnology. By understanding the ABA-auxin interplay, scientists hope to develop strategies for improving crop yield, stress tolerance, and overall plant performance. This could lead to the development of new plant growth regulators or the genetic modification of crops to optimize hormone responses.
The historical context of ABA-auxin interaction research dates back to the mid-20th century when these hormones were first identified and characterized. Initially, they were studied in isolation, with researchers focusing on their individual roles. As our understanding of plant hormone signaling advanced, it became increasingly apparent that these hormones do not act in isolation but rather form a complex network of interactions.
The evolution of research in this field has been marked by several key milestones. Early studies in the 1970s and 1980s provided the first hints of crosstalk between ABA and auxin pathways. The advent of molecular biology techniques in the 1990s allowed for more detailed investigations into the mechanisms of hormone signaling and interaction. The turn of the 21st century saw a surge in research utilizing genetic and genomic approaches, leading to the identification of numerous genes and proteins involved in ABA and auxin signaling.
The primary objective of current research in this field is to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between ABA and auxin in various aspects of plant development. This includes understanding how these hormones influence each other's biosynthesis, transport, perception, and signaling pathways. Additionally, researchers aim to uncover the physiological consequences of this interaction on processes such as root development, shoot growth, fruit ripening, and responses to environmental stresses.
Another critical goal is to translate this fundamental knowledge into practical applications for agriculture and biotechnology. By understanding the ABA-auxin interplay, scientists hope to develop strategies for improving crop yield, stress tolerance, and overall plant performance. This could lead to the development of new plant growth regulators or the genetic modification of crops to optimize hormone responses.
Agricultural Demand for Hormone-Based Plant Growth Regulation
The agricultural sector has witnessed a growing demand for hormone-based plant growth regulation techniques, particularly those involving abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin interactions. This demand is driven by the need for improved crop yields, enhanced stress tolerance, and more efficient resource utilization in agriculture.
Farmers and agricultural companies are increasingly recognizing the potential of hormone-based approaches to optimize plant development and productivity. The ability to manipulate plant growth and development through the precise control of hormone levels offers significant advantages in terms of crop management and yield optimization.
One of the key drivers of this demand is the need for crops that can withstand environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. ABA plays a crucial role in plant stress responses, and its interaction with auxin can significantly influence plant resilience. As climate change continues to impact agricultural regions worldwide, the demand for stress-tolerant crops has surged, leading to increased interest in hormone-based solutions.
Moreover, the push for sustainable agriculture has further fueled the demand for hormone-based plant growth regulation. By optimizing plant growth and development, farmers can potentially reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, aligning with the growing trend towards environmentally friendly farming practices.
The horticultural industry has also shown significant interest in hormone-based plant growth regulation. Nurseries and greenhouse operators are seeking ways to control plant size, shape, and flowering time more precisely. The interaction between ABA and auxin offers potential solutions for producing compact, well-branched plants and controlling flowering in ornamental species.
In the fruit and vegetable sector, there is a growing demand for techniques that can improve fruit set, reduce premature fruit drop, and enhance overall fruit quality. The manipulation of ABA and auxin levels has shown promise in addressing these challenges, leading to increased interest from fruit and vegetable growers.
The seed industry is another area where hormone-based plant growth regulation is gaining traction. Seed companies are exploring ways to enhance seed vigor, germination rates, and seedling establishment through the careful modulation of hormone levels, including ABA and auxin.
As research continues to uncover the intricate mechanisms of ABA-auxin interactions in plant development, the agricultural sector is poised to benefit from new and innovative applications. This growing understanding is likely to drive further demand for hormone-based solutions in various aspects of crop production and management.
Farmers and agricultural companies are increasingly recognizing the potential of hormone-based approaches to optimize plant development and productivity. The ability to manipulate plant growth and development through the precise control of hormone levels offers significant advantages in terms of crop management and yield optimization.
One of the key drivers of this demand is the need for crops that can withstand environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. ABA plays a crucial role in plant stress responses, and its interaction with auxin can significantly influence plant resilience. As climate change continues to impact agricultural regions worldwide, the demand for stress-tolerant crops has surged, leading to increased interest in hormone-based solutions.
Moreover, the push for sustainable agriculture has further fueled the demand for hormone-based plant growth regulation. By optimizing plant growth and development, farmers can potentially reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, aligning with the growing trend towards environmentally friendly farming practices.
The horticultural industry has also shown significant interest in hormone-based plant growth regulation. Nurseries and greenhouse operators are seeking ways to control plant size, shape, and flowering time more precisely. The interaction between ABA and auxin offers potential solutions for producing compact, well-branched plants and controlling flowering in ornamental species.
In the fruit and vegetable sector, there is a growing demand for techniques that can improve fruit set, reduce premature fruit drop, and enhance overall fruit quality. The manipulation of ABA and auxin levels has shown promise in addressing these challenges, leading to increased interest from fruit and vegetable growers.
The seed industry is another area where hormone-based plant growth regulation is gaining traction. Seed companies are exploring ways to enhance seed vigor, germination rates, and seedling establishment through the careful modulation of hormone levels, including ABA and auxin.
As research continues to uncover the intricate mechanisms of ABA-auxin interactions in plant development, the agricultural sector is poised to benefit from new and innovative applications. This growing understanding is likely to drive further demand for hormone-based solutions in various aspects of crop production and management.
Current Understanding and Challenges in ABA-Auxin Crosstalk
The interaction between abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin in plant development represents a complex and intricate crosstalk that significantly influences various aspects of plant growth and responses to environmental stimuli. Current understanding of this interaction has revealed both synergistic and antagonistic effects, depending on the specific developmental context and environmental conditions.
Research has shown that ABA and auxin signaling pathways intersect at multiple levels, including transcriptional regulation, hormone biosynthesis, and transport mechanisms. For instance, ABA has been found to modulate auxin distribution by affecting the expression and localization of auxin transporters, such as PIN proteins. Conversely, auxin can influence ABA biosynthesis and signaling through the regulation of key genes involved in ABA metabolism.
One of the most well-documented interactions between ABA and auxin occurs during root development. ABA has been shown to inhibit primary root growth while promoting lateral root formation, a process that is also heavily influenced by auxin. The interplay between these two hormones in root architecture development involves complex feedback loops and the integration of multiple signaling pathways.
In shoot development, the ABA-auxin crosstalk plays a crucial role in regulating processes such as apical dominance, leaf senescence, and stomatal closure. For example, ABA-induced stomatal closure can be partially counteracted by auxin, highlighting the fine-tuning capabilities of this hormonal interaction in response to environmental stresses.
Despite significant advances in our understanding of ABA-auxin crosstalk, several challenges remain. One major obstacle is the difficulty in dissecting the direct effects of each hormone from their indirect interactions through other signaling pathways. The temporal and spatial specificity of hormone actions further complicates the analysis of their interactions.
Another challenge lies in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the integration of ABA and auxin signals at the cellular level. While some key players in this crosstalk have been identified, such as the ABI5 transcription factor and the AUX/IAA proteins, the complete picture of how these components work together to coordinate plant responses remains elusive.
Furthermore, the environmental context-dependency of ABA-auxin interactions poses a significant challenge in translating laboratory findings to field conditions. Factors such as light, temperature, and nutrient availability can dramatically alter the balance and outcomes of this hormonal crosstalk, necessitating more comprehensive studies under diverse environmental conditions.
Research has shown that ABA and auxin signaling pathways intersect at multiple levels, including transcriptional regulation, hormone biosynthesis, and transport mechanisms. For instance, ABA has been found to modulate auxin distribution by affecting the expression and localization of auxin transporters, such as PIN proteins. Conversely, auxin can influence ABA biosynthesis and signaling through the regulation of key genes involved in ABA metabolism.
One of the most well-documented interactions between ABA and auxin occurs during root development. ABA has been shown to inhibit primary root growth while promoting lateral root formation, a process that is also heavily influenced by auxin. The interplay between these two hormones in root architecture development involves complex feedback loops and the integration of multiple signaling pathways.
In shoot development, the ABA-auxin crosstalk plays a crucial role in regulating processes such as apical dominance, leaf senescence, and stomatal closure. For example, ABA-induced stomatal closure can be partially counteracted by auxin, highlighting the fine-tuning capabilities of this hormonal interaction in response to environmental stresses.
Despite significant advances in our understanding of ABA-auxin crosstalk, several challenges remain. One major obstacle is the difficulty in dissecting the direct effects of each hormone from their indirect interactions through other signaling pathways. The temporal and spatial specificity of hormone actions further complicates the analysis of their interactions.
Another challenge lies in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying the integration of ABA and auxin signals at the cellular level. While some key players in this crosstalk have been identified, such as the ABI5 transcription factor and the AUX/IAA proteins, the complete picture of how these components work together to coordinate plant responses remains elusive.
Furthermore, the environmental context-dependency of ABA-auxin interactions poses a significant challenge in translating laboratory findings to field conditions. Factors such as light, temperature, and nutrient availability can dramatically alter the balance and outcomes of this hormonal crosstalk, necessitating more comprehensive studies under diverse environmental conditions.
Existing Models of ABA-Auxin Signaling Pathways
01 Interaction between abscisic acid and auxin in plant growth regulation
Abscisic acid and auxin interact to regulate various aspects of plant growth and development. This interaction plays a crucial role in processes such as root growth, shoot development, and stress responses. The balance between these two hormones is essential for optimal plant growth and adaptation to environmental conditions.- Interaction between abscisic acid and auxin in plant growth regulation: Abscisic acid and auxin interact to regulate various aspects of plant growth and development. This interaction plays a crucial role in processes such as root growth, shoot development, and stress responses. The balance between these two hormones is essential for optimal plant growth and adaptation to environmental conditions.
- Abscisic acid and auxin in stress tolerance mechanisms: Both abscisic acid and auxin are involved in plant stress tolerance mechanisms. Abscisic acid is particularly important in drought and salt stress responses, while auxin contributes to various stress adaptations. The interplay between these hormones helps plants to cope with adverse environmental conditions and maintain growth under stress.
- Synthetic analogs and derivatives of abscisic acid and auxin: Researchers have developed synthetic analogs and derivatives of abscisic acid and auxin to enhance their effectiveness or modify their properties. These synthetic compounds can be used to manipulate plant growth and development in agriculture and horticulture, offering potential improvements in crop yield and stress tolerance.
- Abscisic acid and auxin in seed dormancy and germination: Abscisic acid and auxin play important roles in regulating seed dormancy and germination. Abscisic acid generally promotes dormancy and inhibits germination, while auxin can promote or inhibit germination depending on the concentration and context. Understanding the balance between these hormones is crucial for improving seed quality and germination rates in agriculture.
- Methods for measuring and manipulating abscisic acid and auxin levels: Various methods have been developed to measure and manipulate abscisic acid and auxin levels in plants. These include analytical techniques for hormone quantification, genetic engineering approaches to alter hormone biosynthesis or signaling, and exogenous application of hormones or their inhibitors. These methods are valuable tools for studying hormone function and improving plant traits in agriculture and biotechnology.
02 Abscisic acid and auxin in stress tolerance
Both abscisic acid and auxin are involved in plant stress tolerance mechanisms. Abscisic acid is particularly important in drought and salt stress responses, while auxin contributes to various stress adaptations. The interplay between these hormones helps plants cope with adverse environmental conditions and maintain growth under stress.Expand Specific Solutions03 Synthetic analogs and derivatives of abscisic acid and auxin
Researchers have developed synthetic analogs and derivatives of abscisic acid and auxin to enhance their effectiveness or modify their properties. These synthetic compounds can be used to manipulate plant growth and development for agricultural or horticultural purposes, offering potential improvements in crop yield and quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Abscisic acid and auxin in fruit ripening and senescence
Abscisic acid and auxin play important roles in fruit ripening and senescence processes. The balance between these hormones influences fruit development, maturation, and post-harvest quality. Understanding and manipulating their interactions can lead to improved fruit quality and extended shelf life.Expand Specific Solutions05 Methods for measuring and modulating abscisic acid and auxin levels
Various techniques have been developed to measure and modulate abscisic acid and auxin levels in plants. These methods include analytical techniques for hormone quantification, genetic approaches to alter hormone biosynthesis or signaling, and exogenous application of hormones or their inhibitors. Such tools are valuable for studying hormone functions and developing agricultural applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Research Institutions and Scientists in Plant Hormone Studies
The interaction between abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin in plant development represents a complex and competitive landscape in the field of plant biology. The market is in a growth phase, with increasing research focus and potential agricultural applications. The global plant growth regulators market, which includes ABA and auxin, is projected to reach significant market size in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Valent BioSciences Corp., Stoller Enterprises, Inc., and Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. leading in commercial applications. Academic institutions such as China Agricultural University and Fudan University are contributing to fundamental research. The interplay between industry and academia is driving innovation, with companies like Riken Corp. and Syngenta Participations AG bridging the gap between research and practical applications.
China Agricultural University
Technical Solution: China Agricultural University has made significant contributions to understanding the interaction between abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin in plant development. Their research focuses on the molecular mechanisms underlying this interaction, particularly in stress responses and root development. They have identified key transcription factors and signaling components that mediate the crosstalk between ABA and auxin pathways[1]. Their studies have revealed that ABA can modulate auxin transport and signaling, affecting lateral root formation and root architecture under drought stress[2]. Additionally, they have explored the role of ABA-auxin interaction in regulating stomatal closure and plant water use efficiency[3].
Strengths: Strong focus on molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. Comprehensive research on stress responses and root development. Weaknesses: May need more translational research to apply findings to crop improvement.
Institute of Crop Science, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences
Technical Solution: The Institute of Crop Science has conducted extensive research on the ABA-auxin interaction in crop plants. They have developed novel approaches to manipulate this interaction for improving crop stress tolerance and yield. Their studies have revealed that fine-tuning the balance between ABA and auxin can enhance drought resistance in major crops like rice and wheat[4]. They have also identified specific genes involved in the ABA-auxin crosstalk that can be targeted for crop improvement[5]. Their research extends to the application of exogenous ABA and auxin analogs to optimize plant growth and development under various environmental conditions[6].
Strengths: Strong focus on practical applications in crop improvement. Extensive research on major crop species. Weaknesses: May need more basic research to fully understand the underlying mechanisms.
Breakthrough Discoveries in ABA-Auxin Molecular Mechanisms
Methods for improving growth and crop productivity of plants by adjusting plant hormone levels, ratios and/or co-factors
PatentInactiveEP1667520A2
Innovation
- A model and method utilizing hormone gradients, particularly auxin and cytokinin ratios, applied through roots or aerial tissues, to manipulate plant growth, using naturally occurring or synthetic hormones like indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), often combined with boron to stabilize and enhance hormone activity, thereby influencing plant architecture and productivity.
Controlling plant pathogens and pests with applied or induced auxins
PatentInactiveUS20050043177A1
Innovation
- Applying effective amounts of auxins or other plant growth regulators, such as indole-3-acetic acid or cytokinins, to modulate the auxin-to-cytokinin ratio in plant tissues, thereby enhancing the plant's natural defense mechanisms against pathogens and pests.
Environmental Factors Influencing ABA-Auxin Balance
The interaction between abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin in plant development is significantly influenced by various environmental factors. These external conditions play a crucial role in modulating the balance between these two important plant hormones, thereby affecting plant growth and development.
Light is a key environmental factor that impacts the ABA-auxin balance. High light intensity tends to promote ABA biosynthesis while suppressing auxin production. This shift in hormone balance often leads to reduced stem elongation and increased stress tolerance. Conversely, low light conditions typically favor auxin accumulation, promoting cell elongation and shade avoidance responses.
Temperature also exerts a strong influence on the ABA-auxin interplay. Heat stress generally increases ABA levels, triggering stomatal closure and enhancing plant tolerance to high temperatures. In contrast, cooler temperatures can promote auxin-mediated growth responses, such as increased root development and lateral branching.
Water availability is another critical factor affecting the ABA-auxin balance. Drought conditions stimulate ABA production, leading to stomatal closure and reduced water loss. This increase in ABA often antagonizes auxin-mediated growth processes, resulting in slower overall plant growth but improved drought tolerance. Conversely, well-watered conditions generally favor auxin-mediated growth responses.
Nutrient availability in the soil also impacts the ABA-auxin balance. Nitrogen deficiency, for instance, can lead to increased ABA levels and reduced auxin sensitivity, affecting root architecture and shoot growth. Phosphorus deficiency may alter the balance by promoting changes in root system architecture, often mediated by both ABA and auxin signaling pathways.
Atmospheric CO2 concentration is an increasingly important factor influencing the ABA-auxin balance. Elevated CO2 levels can affect stomatal development and function, processes regulated by both ABA and auxin. This altered hormone balance under high CO2 conditions can lead to changes in plant water use efficiency and overall growth patterns.
Biotic factors, such as pathogen infection or herbivory, can also impact the ABA-auxin balance. These stresses often trigger complex hormonal responses, including changes in ABA and auxin levels, which can affect plant defense mechanisms and growth patterns.
Understanding these environmental influences on the ABA-auxin balance is crucial for predicting and managing plant responses to changing climatic conditions. This knowledge can be applied in agriculture and horticulture to optimize plant growth and stress tolerance under various environmental scenarios.
Light is a key environmental factor that impacts the ABA-auxin balance. High light intensity tends to promote ABA biosynthesis while suppressing auxin production. This shift in hormone balance often leads to reduced stem elongation and increased stress tolerance. Conversely, low light conditions typically favor auxin accumulation, promoting cell elongation and shade avoidance responses.
Temperature also exerts a strong influence on the ABA-auxin interplay. Heat stress generally increases ABA levels, triggering stomatal closure and enhancing plant tolerance to high temperatures. In contrast, cooler temperatures can promote auxin-mediated growth responses, such as increased root development and lateral branching.
Water availability is another critical factor affecting the ABA-auxin balance. Drought conditions stimulate ABA production, leading to stomatal closure and reduced water loss. This increase in ABA often antagonizes auxin-mediated growth processes, resulting in slower overall plant growth but improved drought tolerance. Conversely, well-watered conditions generally favor auxin-mediated growth responses.
Nutrient availability in the soil also impacts the ABA-auxin balance. Nitrogen deficiency, for instance, can lead to increased ABA levels and reduced auxin sensitivity, affecting root architecture and shoot growth. Phosphorus deficiency may alter the balance by promoting changes in root system architecture, often mediated by both ABA and auxin signaling pathways.
Atmospheric CO2 concentration is an increasingly important factor influencing the ABA-auxin balance. Elevated CO2 levels can affect stomatal development and function, processes regulated by both ABA and auxin. This altered hormone balance under high CO2 conditions can lead to changes in plant water use efficiency and overall growth patterns.
Biotic factors, such as pathogen infection or herbivory, can also impact the ABA-auxin balance. These stresses often trigger complex hormonal responses, including changes in ABA and auxin levels, which can affect plant defense mechanisms and growth patterns.
Understanding these environmental influences on the ABA-auxin balance is crucial for predicting and managing plant responses to changing climatic conditions. This knowledge can be applied in agriculture and horticulture to optimize plant growth and stress tolerance under various environmental scenarios.
Biotechnological Applications of ABA-Auxin Interaction Knowledge
The knowledge gained from understanding the interaction between abscisic acid (ABA) and auxin in plant development has significant biotechnological applications. This interaction plays a crucial role in various aspects of plant growth and stress responses, offering potential for improving crop productivity and resilience.
One of the primary applications is in the development of drought-resistant crops. By manipulating the ABA-auxin signaling pathways, researchers can enhance plants' ability to withstand water stress. This could lead to the creation of crops that require less irrigation, a valuable trait in regions facing water scarcity or unpredictable rainfall patterns.
The ABA-auxin interaction also influences root architecture, presenting opportunities for optimizing nutrient uptake and soil anchorage. Biotechnological interventions targeting this interaction could result in plants with more efficient root systems, capable of better nutrient absorption and improved stability in various soil conditions.
In the realm of fruit ripening and post-harvest technology, understanding the ABA-auxin interplay offers potential for controlling fruit maturation processes. This knowledge could be applied to develop techniques for delaying or accelerating ripening, extending shelf life, and improving fruit quality.
The role of ABA and auxin in plant responses to various environmental stresses, including salinity and temperature extremes, provides avenues for developing crops with enhanced stress tolerance. This application is particularly relevant in the context of climate change, where crops need to adapt to increasingly variable and extreme weather conditions.
In plant tissue culture and micropropagation, manipulating the balance between ABA and auxin can optimize in vitro plant regeneration and growth. This has implications for the mass production of elite plant varieties and the conservation of rare or endangered plant species.
The interaction between ABA and auxin also influences seed dormancy and germination. Biotechnological applications in this area could lead to improved seed technologies, enhancing germination rates and seedling vigor, which are crucial for agricultural productivity.
Furthermore, understanding this hormonal interplay can contribute to the development of novel plant growth regulators. These synthetic compounds, designed to mimic or modulate ABA-auxin interactions, could offer more precise control over specific aspects of plant growth and development.
One of the primary applications is in the development of drought-resistant crops. By manipulating the ABA-auxin signaling pathways, researchers can enhance plants' ability to withstand water stress. This could lead to the creation of crops that require less irrigation, a valuable trait in regions facing water scarcity or unpredictable rainfall patterns.
The ABA-auxin interaction also influences root architecture, presenting opportunities for optimizing nutrient uptake and soil anchorage. Biotechnological interventions targeting this interaction could result in plants with more efficient root systems, capable of better nutrient absorption and improved stability in various soil conditions.
In the realm of fruit ripening and post-harvest technology, understanding the ABA-auxin interplay offers potential for controlling fruit maturation processes. This knowledge could be applied to develop techniques for delaying or accelerating ripening, extending shelf life, and improving fruit quality.
The role of ABA and auxin in plant responses to various environmental stresses, including salinity and temperature extremes, provides avenues for developing crops with enhanced stress tolerance. This application is particularly relevant in the context of climate change, where crops need to adapt to increasingly variable and extreme weather conditions.
In plant tissue culture and micropropagation, manipulating the balance between ABA and auxin can optimize in vitro plant regeneration and growth. This has implications for the mass production of elite plant varieties and the conservation of rare or endangered plant species.
The interaction between ABA and auxin also influences seed dormancy and germination. Biotechnological applications in this area could lead to improved seed technologies, enhancing germination rates and seedling vigor, which are crucial for agricultural productivity.
Furthermore, understanding this hormonal interplay can contribute to the development of novel plant growth regulators. These synthetic compounds, designed to mimic or modulate ABA-auxin interactions, could offer more precise control over specific aspects of plant growth and development.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!