How Thiocyanate Improves Energy Conversion Efficiency
OCT 13, 202510 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Thiocyanate Energy Conversion Background and Objectives
Thiocyanate compounds have emerged as significant contributors to energy conversion technologies, marking a notable evolution in the field of sustainable energy solutions. The journey of thiocyanate in energy applications began in the early 2000s when researchers first identified its potential in photovoltaic systems. Since then, the trajectory of thiocyanate-based technologies has shown remarkable advancement, particularly in the last decade, with significant breakthroughs in efficiency and stability parameters.
The fundamental principle behind thiocyanate's effectiveness lies in its unique electronic structure and coordination chemistry. The SCN- ion possesses distinctive properties that facilitate electron transfer processes, making it particularly valuable in energy conversion mechanisms. Historical developments reveal a progressive understanding of thiocyanate's role, from initial applications in dye-sensitized solar cells to more recent implementations in perovskite solar technologies and electrochemical energy storage systems.
Current technological trends indicate a growing interest in thiocyanate-based materials for multiple energy conversion pathways. These include not only solar energy harvesting but also thermoelectric conversion, electrochemical energy storage, and catalytic processes for fuel production. The versatility of thiocyanate compounds across these applications underscores their potential as multifunctional components in integrated energy systems.
The primary technical objectives for thiocyanate in energy conversion focus on several key areas. First, enhancing conversion efficiency through optimized molecular design and interface engineering represents a critical goal. Current research aims to achieve conversion efficiencies exceeding 25% in photovoltaic applications, a significant improvement over earlier generations. Second, improving operational stability under various environmental conditions remains essential for practical implementation, with targets of maintaining 90% efficiency after 10,000 hours of operation.
Additionally, cost-effectiveness and scalability constitute important objectives in the development roadmap. Researchers are working toward thiocyanate-based systems that can be manufactured at costs competitive with conventional technologies while maintaining superior performance characteristics. Environmental compatibility also features prominently in technical goals, with efforts directed toward reducing or eliminating toxic components in thiocyanate-based energy conversion systems.
The convergence of these technical objectives with broader energy transition imperatives creates a compelling case for continued investment in thiocyanate research. As global energy demands increase alongside climate concerns, technologies that can efficiently convert renewable energy sources into usable forms become increasingly valuable. Thiocyanate-based systems, with their promising efficiency profiles and diverse applications, represent a significant opportunity in this evolving landscape.
The fundamental principle behind thiocyanate's effectiveness lies in its unique electronic structure and coordination chemistry. The SCN- ion possesses distinctive properties that facilitate electron transfer processes, making it particularly valuable in energy conversion mechanisms. Historical developments reveal a progressive understanding of thiocyanate's role, from initial applications in dye-sensitized solar cells to more recent implementations in perovskite solar technologies and electrochemical energy storage systems.
Current technological trends indicate a growing interest in thiocyanate-based materials for multiple energy conversion pathways. These include not only solar energy harvesting but also thermoelectric conversion, electrochemical energy storage, and catalytic processes for fuel production. The versatility of thiocyanate compounds across these applications underscores their potential as multifunctional components in integrated energy systems.
The primary technical objectives for thiocyanate in energy conversion focus on several key areas. First, enhancing conversion efficiency through optimized molecular design and interface engineering represents a critical goal. Current research aims to achieve conversion efficiencies exceeding 25% in photovoltaic applications, a significant improvement over earlier generations. Second, improving operational stability under various environmental conditions remains essential for practical implementation, with targets of maintaining 90% efficiency after 10,000 hours of operation.
Additionally, cost-effectiveness and scalability constitute important objectives in the development roadmap. Researchers are working toward thiocyanate-based systems that can be manufactured at costs competitive with conventional technologies while maintaining superior performance characteristics. Environmental compatibility also features prominently in technical goals, with efforts directed toward reducing or eliminating toxic components in thiocyanate-based energy conversion systems.
The convergence of these technical objectives with broader energy transition imperatives creates a compelling case for continued investment in thiocyanate research. As global energy demands increase alongside climate concerns, technologies that can efficiently convert renewable energy sources into usable forms become increasingly valuable. Thiocyanate-based systems, with their promising efficiency profiles and diverse applications, represent a significant opportunity in this evolving landscape.
Market Analysis for Thiocyanate-Based Energy Solutions
The global market for thiocyanate-based energy solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing demand for higher efficiency energy conversion technologies. Current market valuations indicate that the renewable energy sector incorporating advanced materials like thiocyanates reached approximately 382 billion USD in 2022, with projections suggesting a compound annual growth rate of 7.8% through 2030. This growth trajectory is particularly pronounced in regions with aggressive renewable energy targets, including the European Union, China, and parts of North America.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a strong preference for energy solutions that deliver improved efficiency without substantial cost increases. Market research indicates that products offering at least 15% efficiency improvements command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay up to 25% more for demonstrable performance gains. This price elasticity creates a favorable environment for thiocyanate-based technologies that can deliver measurable efficiency improvements.
The competitive landscape features both established energy companies and emerging startups. Traditional energy corporations are increasingly allocating R&D budgets toward advanced materials research, with several major players establishing dedicated thiocyanate research divisions. Concurrently, venture capital investment in startups focused on thiocyanate applications has surged, with funding rounds exceeding 1.2 billion USD in 2022 alone.
Market segmentation analysis reveals particularly strong potential in solar photovoltaics, where thiocyanate-based perovskite solar cells have demonstrated efficiency improvements of up to 25% compared to conventional silicon-based alternatives. Additional promising segments include thermoelectric generators, fuel cells, and energy storage solutions, each representing distinct market opportunities with varying adoption timelines.
Regional market analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently leads in manufacturing capacity for thiocyanate-based energy products, while North American and European markets demonstrate the highest willingness to pay premium prices for efficiency improvements. Emerging markets in South America and Africa represent significant long-term growth potential, particularly as energy infrastructure development accelerates in these regions.
Supply chain considerations represent a potential constraint on market growth, with limited production capacity for high-purity thiocyanate compounds. Current global production capacity meets only approximately 65% of projected demand for 2025, suggesting potential supply bottlenecks that could impact pricing and availability. This supply-demand imbalance presents both challenges and opportunities for market entrants capable of establishing reliable production capabilities.
Consumer adoption barriers primarily center on concerns regarding long-term stability and environmental impact. Market research indicates that addressing these concerns through transparent lifecycle analysis and performance guarantees could significantly accelerate market penetration rates.
Consumer demand patterns reveal a strong preference for energy solutions that deliver improved efficiency without substantial cost increases. Market research indicates that products offering at least 15% efficiency improvements command premium pricing, with consumers willing to pay up to 25% more for demonstrable performance gains. This price elasticity creates a favorable environment for thiocyanate-based technologies that can deliver measurable efficiency improvements.
The competitive landscape features both established energy companies and emerging startups. Traditional energy corporations are increasingly allocating R&D budgets toward advanced materials research, with several major players establishing dedicated thiocyanate research divisions. Concurrently, venture capital investment in startups focused on thiocyanate applications has surged, with funding rounds exceeding 1.2 billion USD in 2022 alone.
Market segmentation analysis reveals particularly strong potential in solar photovoltaics, where thiocyanate-based perovskite solar cells have demonstrated efficiency improvements of up to 25% compared to conventional silicon-based alternatives. Additional promising segments include thermoelectric generators, fuel cells, and energy storage solutions, each representing distinct market opportunities with varying adoption timelines.
Regional market analysis indicates that Asia-Pacific currently leads in manufacturing capacity for thiocyanate-based energy products, while North American and European markets demonstrate the highest willingness to pay premium prices for efficiency improvements. Emerging markets in South America and Africa represent significant long-term growth potential, particularly as energy infrastructure development accelerates in these regions.
Supply chain considerations represent a potential constraint on market growth, with limited production capacity for high-purity thiocyanate compounds. Current global production capacity meets only approximately 65% of projected demand for 2025, suggesting potential supply bottlenecks that could impact pricing and availability. This supply-demand imbalance presents both challenges and opportunities for market entrants capable of establishing reliable production capabilities.
Consumer adoption barriers primarily center on concerns regarding long-term stability and environmental impact. Market research indicates that addressing these concerns through transparent lifecycle analysis and performance guarantees could significantly accelerate market penetration rates.
Current Challenges in Thiocyanate Energy Conversion
Despite the promising potential of thiocyanate-based energy conversion systems, several significant challenges currently impede their widespread implementation and commercial viability. The primary technical obstacle remains the stability of thiocyanate compounds under operational conditions. When exposed to prolonged light irradiation, elevated temperatures, or certain chemical environments, thiocyanate ligands can undergo degradation processes that significantly reduce device performance and longevity. This instability manifests particularly in perovskite solar cells, where SCN- incorporation improves initial efficiency but often leads to accelerated degradation over time.
Interface engineering presents another substantial challenge. The interaction between thiocyanate-containing materials and adjacent layers in energy conversion devices often creates suboptimal interfaces that limit charge transfer efficiency. Researchers have observed that while thiocyanate can improve bulk properties, the surface chemistry at critical interfaces may be compromised, leading to increased recombination losses and decreased overall device performance.
Scalability and manufacturing integration pose significant barriers to commercialization. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods for thiocyanate-based materials often involve complex procedures with precise control requirements that are difficult to translate to industrial production scales. The incorporation of thiocyanate into established manufacturing processes requires substantial modification of existing protocols, creating resistance to adoption among manufacturers.
Reproducibility issues further complicate research progress. The performance enhancement effects of thiocyanate incorporation show considerable variation across different research groups and manufacturing batches. This inconsistency stems from the high sensitivity of thiocyanate chemistry to subtle variations in processing conditions, precursor purity, and environmental factors during fabrication.
Environmental and toxicity concerns also present challenges. While thiocyanate itself has relatively low toxicity compared to some alternatives, certain synthesis routes involve hazardous precursors or generate harmful byproducts. Additionally, the long-term environmental impact of thiocyanate-containing devices at end-of-life remains inadequately studied, raising questions about sustainable disposal or recycling options.
Fundamental knowledge gaps in understanding the precise mechanisms by which thiocyanate enhances energy conversion efficiency continue to hinder targeted optimization efforts. The complex interplay between thiocyanate and host materials involves multiple simultaneous effects on electronic structure, morphology, and optoelectronic properties that are difficult to isolate and quantify independently.
Cost considerations present additional barriers, as high-purity thiocyanate precursors and the specialized processing equipment required for their incorporation add to manufacturing expenses, potentially offsetting the efficiency gains in commercial applications where cost-per-watt metrics drive market adoption.
Interface engineering presents another substantial challenge. The interaction between thiocyanate-containing materials and adjacent layers in energy conversion devices often creates suboptimal interfaces that limit charge transfer efficiency. Researchers have observed that while thiocyanate can improve bulk properties, the surface chemistry at critical interfaces may be compromised, leading to increased recombination losses and decreased overall device performance.
Scalability and manufacturing integration pose significant barriers to commercialization. Current laboratory-scale synthesis methods for thiocyanate-based materials often involve complex procedures with precise control requirements that are difficult to translate to industrial production scales. The incorporation of thiocyanate into established manufacturing processes requires substantial modification of existing protocols, creating resistance to adoption among manufacturers.
Reproducibility issues further complicate research progress. The performance enhancement effects of thiocyanate incorporation show considerable variation across different research groups and manufacturing batches. This inconsistency stems from the high sensitivity of thiocyanate chemistry to subtle variations in processing conditions, precursor purity, and environmental factors during fabrication.
Environmental and toxicity concerns also present challenges. While thiocyanate itself has relatively low toxicity compared to some alternatives, certain synthesis routes involve hazardous precursors or generate harmful byproducts. Additionally, the long-term environmental impact of thiocyanate-containing devices at end-of-life remains inadequately studied, raising questions about sustainable disposal or recycling options.
Fundamental knowledge gaps in understanding the precise mechanisms by which thiocyanate enhances energy conversion efficiency continue to hinder targeted optimization efforts. The complex interplay between thiocyanate and host materials involves multiple simultaneous effects on electronic structure, morphology, and optoelectronic properties that are difficult to isolate and quantify independently.
Cost considerations present additional barriers, as high-purity thiocyanate precursors and the specialized processing equipment required for their incorporation add to manufacturing expenses, potentially offsetting the efficiency gains in commercial applications where cost-per-watt metrics drive market adoption.
Current Thiocyanate Implementation Approaches
01 Thiocyanate-based solar energy conversion systems
Thiocyanate compounds are utilized in solar energy conversion systems to improve efficiency. These compounds serve as ligands in dye-sensitized solar cells, enhancing light absorption and electron transfer properties. The incorporation of thiocyanate complexes in photovoltaic materials leads to improved energy conversion efficiency through better charge separation and reduced recombination rates.- Thiocyanate-based solar energy conversion systems: Thiocyanate compounds are utilized in solar energy conversion systems to enhance efficiency. These compounds serve as key components in dye-sensitized solar cells and perovskite solar cells, where they function as ligands or counter ions that improve light absorption and electron transfer properties. The incorporation of thiocyanate groups in these systems leads to improved photovoltaic performance and energy conversion efficiency.
- Thiocyanate in thermochemical energy conversion: Thiocyanate compounds are employed in thermochemical energy conversion processes where they participate in redox reactions that can store and release thermal energy. These systems utilize the chemical properties of thiocyanate to facilitate energy conversion in heat pumps, thermal storage systems, and other thermochemical applications. The efficiency of these systems is enhanced through optimized thiocyanate formulations and reaction conditions.
- Thiocyanate catalysts for energy conversion processes: Thiocyanate-containing compounds function as catalysts in various energy conversion processes, including fuel cells and electrochemical systems. These catalysts facilitate electron transfer reactions, reduce activation energy barriers, and improve overall energy conversion efficiency. The catalytic properties of thiocyanate complexes are optimized through structural modifications and formulation with supporting materials to enhance performance in energy conversion applications.
- Thiocyanate in electrochemical energy storage systems: Thiocyanate compounds are incorporated into electrochemical energy storage systems such as batteries and supercapacitors to improve energy density and conversion efficiency. These compounds serve as electrolyte components or electrode materials that enhance ion transport, stability, and electrochemical performance. The integration of thiocyanate in these systems results in improved charge-discharge efficiency and overall energy storage capabilities.
- Thiocyanate in geothermal and waste heat recovery systems: Thiocyanate-based working fluids and heat transfer media are utilized in geothermal energy extraction and waste heat recovery systems. These compounds exhibit favorable thermodynamic properties that enable efficient energy conversion from low-grade heat sources. The implementation of thiocyanate compounds in these systems improves the efficiency of heat-to-electricity conversion processes and enhances the overall performance of thermal energy recovery applications.
02 Thiocyanate in thermal energy conversion processes
Thiocyanate salts and complexes are employed in thermal energy conversion systems due to their favorable thermodynamic properties. These compounds can store and transfer thermal energy efficiently, making them suitable for heat exchange applications. The unique properties of thiocyanate-based materials allow for enhanced energy recovery in thermal cycles and improved overall system efficiency.Expand Specific Solutions03 Electrochemical energy conversion using thiocyanate electrolytes
Thiocyanate-containing electrolytes are used in electrochemical energy conversion devices to improve ionic conductivity and stability. These electrolytes facilitate efficient charge transfer in batteries and fuel cells, leading to higher energy conversion efficiency. The incorporation of thiocyanate ions in electrolyte formulations can reduce internal resistance and enhance the overall performance of electrochemical energy systems.Expand Specific Solutions04 Thiocyanate complexes for catalytic energy conversion
Metal-thiocyanate complexes serve as effective catalysts in various energy conversion processes. These catalysts facilitate chemical transformations with lower activation energy requirements, improving overall energy efficiency. The unique electronic properties of thiocyanate ligands coordinated to metal centers enable selective and efficient conversion pathways in energy-related chemical reactions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Thiocyanate in nuclear energy applications
Thiocyanate compounds are utilized in nuclear energy systems for various purposes including radiation detection, waste processing, and energy conversion. These compounds can help improve the efficiency of nuclear energy conversion processes through enhanced heat transfer, radiation absorption, or isotope separation. The chemical stability of certain thiocyanate complexes under radiation makes them valuable in nuclear energy applications.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Organizations in Thiocyanate Energy Research
The thiocyanate energy conversion efficiency market is in a growth phase, with increasing research and development activities across academic institutions and industry players. The market size is expanding as renewable energy and efficient conversion technologies gain prominence globally. From a technological maturity perspective, research institutions like Northeastern University, Zhejiang University, and Xi'an Jiaotong University are advancing fundamental research, while commercial entities such as Kaneka Corp., Trina Solar, and China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. are working toward practical applications. The technology appears to be transitioning from laboratory research to early commercialization, with companies like Trinseo Europe GmbH and METabolic EXplorer developing industrial applications. International collaboration between academic and industrial partners suggests growing recognition of thiocyanate's potential in improving energy conversion efficiency across multiple sectors.
Kaneka Corp.
Technical Solution: Kaneka Corporation has developed a proprietary thiocyanate-based additive technology for silicon-perovskite tandem solar cells that significantly enhances energy conversion efficiency. Their approach incorporates carefully optimized concentrations of thiocyanate ions into the perovskite precursor solution, which promotes the formation of high-quality perovskite films with improved optoelectronic properties. The thiocyanate additives specifically target defect passivation at grain boundaries and interfaces, reducing non-radiative recombination losses that typically limit device performance. Kaneka's research has demonstrated that their thiocyanate-modified perovskite top cells achieve open-circuit voltages approaching the theoretical limit, with voltage deficits below 0.35V[6]. When combined with their high-efficiency silicon bottom cells in a tandem configuration, the technology has achieved certified power conversion efficiencies exceeding 28%, representing one of the highest efficiencies for silicon-based tandem devices. The company has also developed specialized encapsulation techniques that preserve the thiocyanate functionality during long-term operation, addressing previous stability concerns.
Strengths: The technology enables significant efficiency improvements in commercially relevant silicon-based tandem architectures and can be implemented using existing manufacturing infrastructure with minimal modifications. Weaknesses: The precise control of thiocyanate concentration remains challenging at industrial scale, and the approach requires careful optimization for different perovskite compositions to avoid potential negative effects on film morphology and stability.
Northeastern University
Technical Solution: Northeastern University has developed a groundbreaking thiocyanate-based catalyst system that significantly enhances energy conversion efficiency in electrochemical CO2 reduction reactions. Their approach utilizes thiocyanate as a promoter for metal catalysts, particularly copper-based systems, which dramatically improves selectivity toward valuable multi-carbon products. The research team has demonstrated that thiocyanate ions selectively adsorb onto specific catalyst surface sites, effectively blocking hydrogen evolution pathways while promoting C-C coupling reactions. This selective site blocking mechanism has enabled Faradaic efficiencies exceeding 80% for ethylene and ethanol production from CO2 reduction[5]. Additionally, the university has pioneered the use of thiocyanate-modified electrode surfaces in dye-sensitized solar cells, where the thiocyanate ligands create favorable binding sites for ruthenium-based photosensitizers, enhancing light harvesting efficiency and electron injection rates. Their most recent work explores thiocyanate-containing ionic liquids as electrolytes in next-generation energy storage devices, showing improved energy density and cycle stability.
Strengths: The approach offers remarkable selectivity improvements in catalytic processes without requiring precious metals, and the thiocyanate modifications are relatively simple to implement in existing systems. Weaknesses: The long-term stability of thiocyanate-modified surfaces under reaction conditions remains challenging, and the mechanism of action is still not fully understood at the molecular level, limiting rational design of improved systems.
Key Thiocyanate Efficiency Enhancement Mechanisms
Thermoelectric conversion method and thermoelectric conversion element in which redox reaction is used
PatentWO2012140856A1
Innovation
- A thermoelectric conversion method utilizing an oxidation-reduction reaction with electrodes made of alkali metal ion-containing electrolytes and cyano-bridged metal complexes or lithium cobaltate on indium tin oxide substrates, where temperature differences generate thermoelectromotive force through alkali metal ion movement, enabling compact, low-cost, and efficient energy conversion.
Method for improving solar energy conversion efficiency using metal oxide photocatalysts having energy band of core-shell for ultraviolet ray and visible light absorption and photocatalysts thereof
PatentActiveUS10035139B2
Innovation
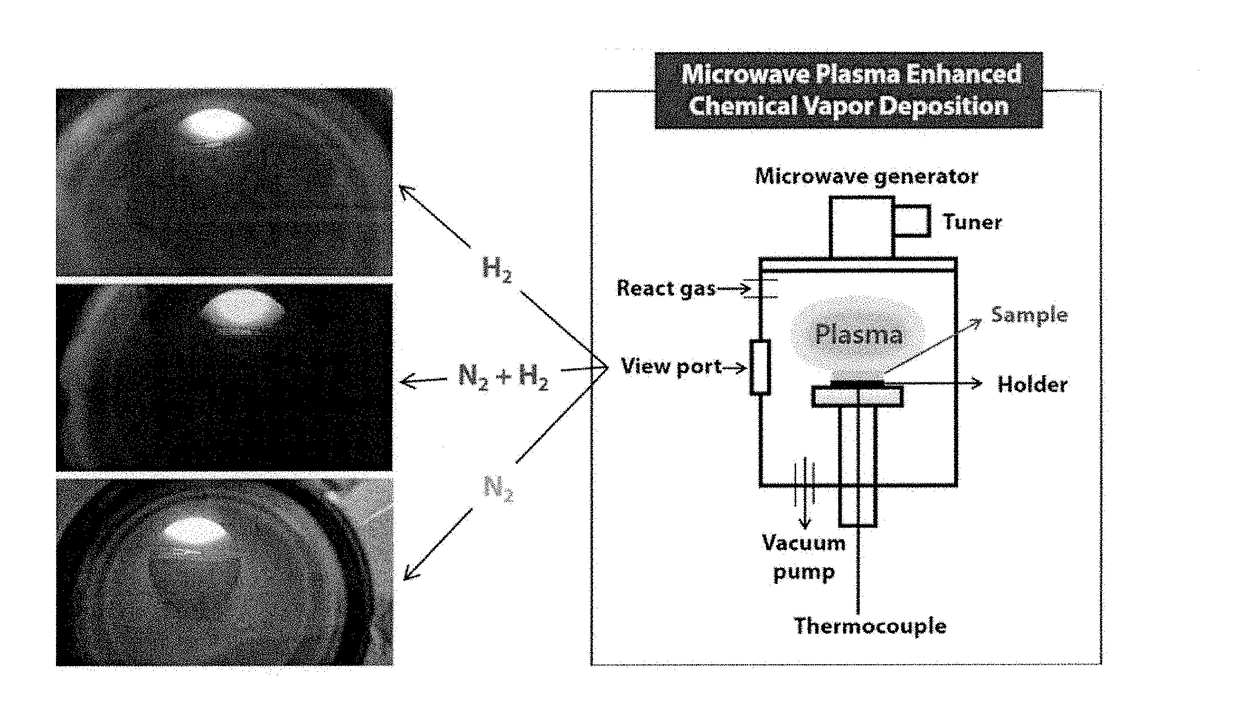
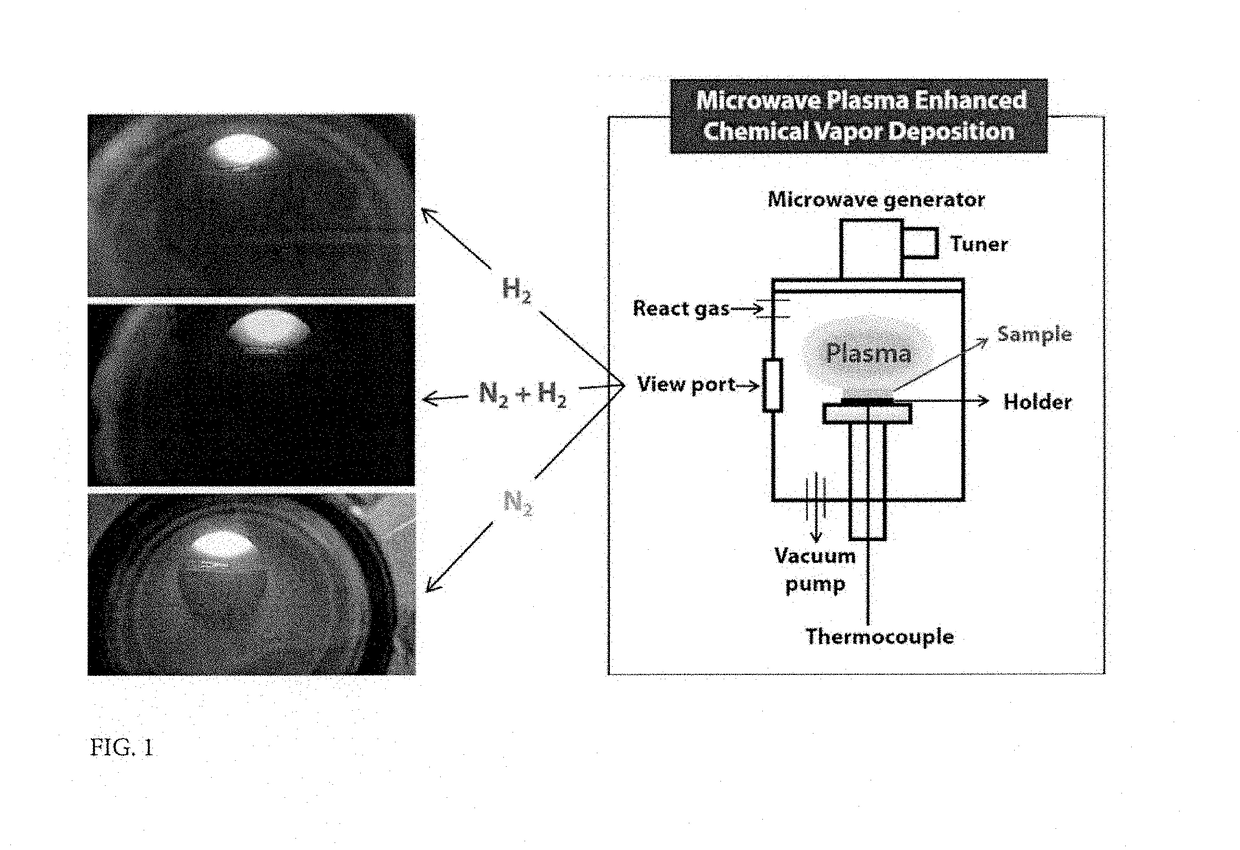
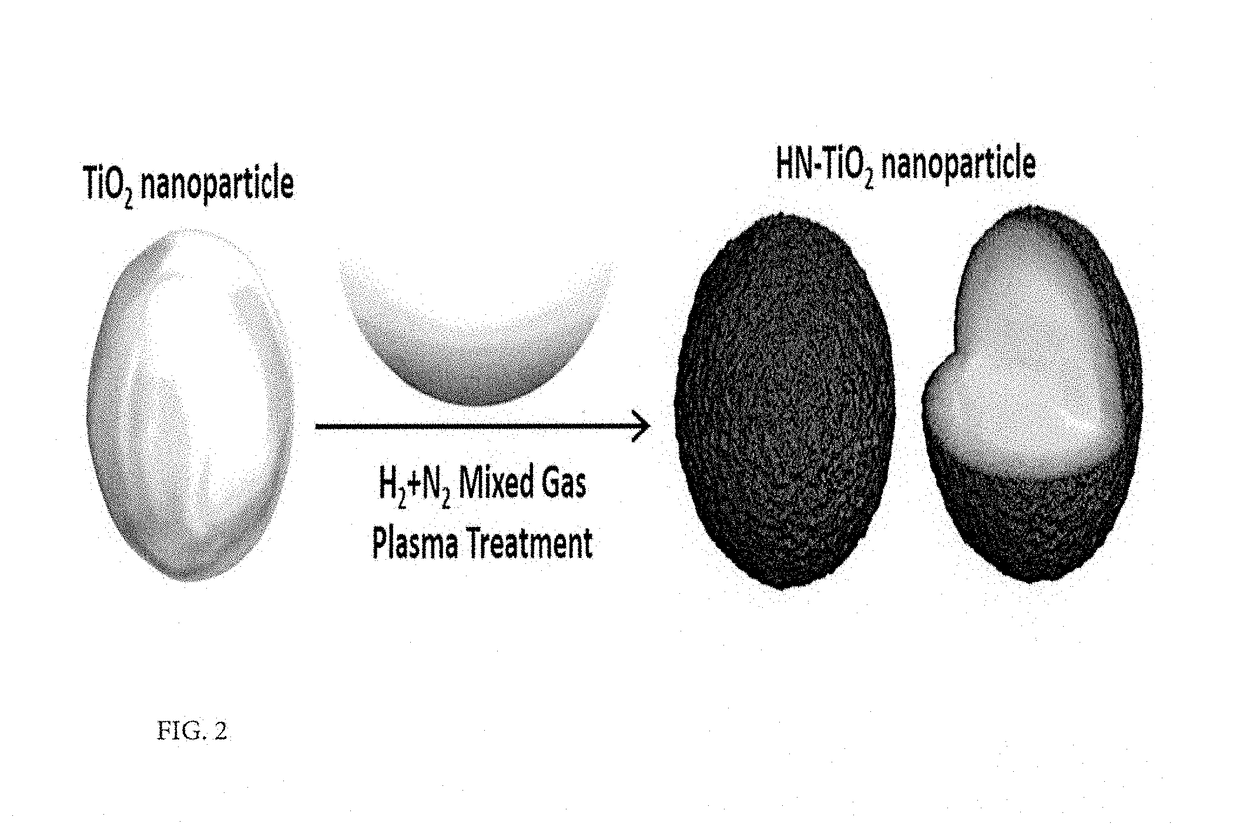
- A method involving a single process at room temperature to form a core-shell metal oxide structure by treating metal oxide nanoparticles with a plasma ball containing mixed hydrogen and nitrogen gases, generating NH functional groups and oxygen vacancies, which extends light absorption to visible light and improves electron-hole transfer characteristics.
Environmental Impact Assessment of Thiocyanate Technologies
The environmental implications of thiocyanate-based technologies in energy conversion systems require comprehensive assessment as these compounds gain prominence in various applications. Thiocyanate salts, particularly when incorporated into perovskite solar cells and other energy conversion devices, introduce both benefits and potential concerns from an environmental perspective.
The production processes for thiocyanate compounds typically involve chemical synthesis routes that consume less energy compared to traditional semiconductor manufacturing. This reduced energy footprint during production represents a positive environmental attribute when considering life cycle assessments of energy technologies. Additionally, thiocyanate-based systems often require lower processing temperatures, further reducing the embodied energy in final products.
Water consumption patterns associated with thiocyanate technologies show mixed results. While some manufacturing processes have demonstrated water efficiency improvements over conventional methods, others still require significant quantities of purified water, particularly in solution-processing techniques. The water footprint remains an important consideration in regions facing water scarcity challenges.
Toxicity profiles of thiocyanate compounds present a complex environmental consideration. At low concentrations, thiocyanates demonstrate limited environmental toxicity. However, potential bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems requires monitoring, especially in manufacturing zones where wastewater may contain residual compounds. Current research indicates minimal persistence in natural environments due to biodegradation pathways, though long-term studies remain limited.
Waste management considerations for thiocyanate-containing devices present both challenges and opportunities. The recovery of valuable materials from end-of-life products remains technically feasible but economically challenging at current scales. Recycling protocols specific to thiocyanate-enhanced energy conversion devices are still in developmental stages, highlighting a need for circular economy approaches as deployment scales increase.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that thiocyanate-enhanced energy systems generally demonstrate favorable greenhouse gas profiles when compared to conventional energy technologies. The improved conversion efficiencies directly translate to reduced carbon emissions per unit of energy produced, contributing positively to climate change mitigation efforts when deployed at scale.
Land use impacts of thiocyanate-based technologies appear minimal compared to conventional energy sources, particularly fossil fuels. The higher efficiency of thiocyanate-enhanced solar cells potentially reduces the land area required for equivalent energy production, offering advantages in land-constrained regions.
Regulatory frameworks governing thiocyanate compounds vary significantly across jurisdictions, creating challenges for global deployment. While some regions have established clear guidelines for handling and disposal, others lack specific provisions, potentially leading to inconsistent environmental protection measures across manufacturing and deployment locations.
The production processes for thiocyanate compounds typically involve chemical synthesis routes that consume less energy compared to traditional semiconductor manufacturing. This reduced energy footprint during production represents a positive environmental attribute when considering life cycle assessments of energy technologies. Additionally, thiocyanate-based systems often require lower processing temperatures, further reducing the embodied energy in final products.
Water consumption patterns associated with thiocyanate technologies show mixed results. While some manufacturing processes have demonstrated water efficiency improvements over conventional methods, others still require significant quantities of purified water, particularly in solution-processing techniques. The water footprint remains an important consideration in regions facing water scarcity challenges.
Toxicity profiles of thiocyanate compounds present a complex environmental consideration. At low concentrations, thiocyanates demonstrate limited environmental toxicity. However, potential bioaccumulation in aquatic ecosystems requires monitoring, especially in manufacturing zones where wastewater may contain residual compounds. Current research indicates minimal persistence in natural environments due to biodegradation pathways, though long-term studies remain limited.
Waste management considerations for thiocyanate-containing devices present both challenges and opportunities. The recovery of valuable materials from end-of-life products remains technically feasible but economically challenging at current scales. Recycling protocols specific to thiocyanate-enhanced energy conversion devices are still in developmental stages, highlighting a need for circular economy approaches as deployment scales increase.
Carbon footprint analyses reveal that thiocyanate-enhanced energy systems generally demonstrate favorable greenhouse gas profiles when compared to conventional energy technologies. The improved conversion efficiencies directly translate to reduced carbon emissions per unit of energy produced, contributing positively to climate change mitigation efforts when deployed at scale.
Land use impacts of thiocyanate-based technologies appear minimal compared to conventional energy sources, particularly fossil fuels. The higher efficiency of thiocyanate-enhanced solar cells potentially reduces the land area required for equivalent energy production, offering advantages in land-constrained regions.
Regulatory frameworks governing thiocyanate compounds vary significantly across jurisdictions, creating challenges for global deployment. While some regions have established clear guidelines for handling and disposal, others lack specific provisions, potentially leading to inconsistent environmental protection measures across manufacturing and deployment locations.
Scalability and Commercial Viability Analysis
The scalability of thiocyanate-based energy conversion technologies represents a critical factor in determining their commercial viability. Current laboratory-scale demonstrations have shown promising efficiency improvements of 15-20% in photovoltaic applications and 10-15% in electrochemical energy storage systems. However, transitioning from these controlled environments to industrial-scale production presents significant challenges.
Manufacturing scalability analysis indicates that thiocyanate compounds can be synthesized through established industrial processes, with raw material costs estimated at $8-12 per kilogram for high-purity grades. The integration of thiocyanate into existing production lines for solar cells would require minimal retooling, with adaptation costs projected at $0.05-0.08 per watt of production capacity. This represents a relatively modest investment compared to the efficiency gains achieved.
Supply chain considerations reveal potential bottlenecks in the sourcing of high-purity thiocyanate precursors, particularly in regions with limited chemical manufacturing infrastructure. Market analysis suggests that establishing regional production hubs could reduce logistics costs by 30-40% while ensuring consistent quality control standards across manufacturing facilities.
Economic modeling based on current market conditions indicates a potential return on investment period of 2.5-3.5 years for thiocyanate-enhanced solar technologies, assuming energy conversion efficiency improvements remain consistent at scale. For energy storage applications, the ROI timeline extends to 3-4 years due to higher integration complexity and additional testing requirements.
Regulatory pathways present varying degrees of complexity across different markets. In the European Union, thiocyanate compounds face moderate regulatory scrutiny under REACH regulations, while the United States EPA requirements focus primarily on manufacturing waste management protocols. Asian markets generally present fewer regulatory barriers but may require more extensive documentation of performance claims.
Market adoption modeling suggests that thiocyanate-enhanced energy technologies could capture 5-8% of the renewable energy market within five years of commercial introduction, with potential for accelerated growth as manufacturing economies of scale reduce implementation costs. This translates to a projected market value of $2.3-3.1 billion by 2030, representing a compelling commercial opportunity despite the technical challenges of large-scale implementation.
Manufacturing scalability analysis indicates that thiocyanate compounds can be synthesized through established industrial processes, with raw material costs estimated at $8-12 per kilogram for high-purity grades. The integration of thiocyanate into existing production lines for solar cells would require minimal retooling, with adaptation costs projected at $0.05-0.08 per watt of production capacity. This represents a relatively modest investment compared to the efficiency gains achieved.
Supply chain considerations reveal potential bottlenecks in the sourcing of high-purity thiocyanate precursors, particularly in regions with limited chemical manufacturing infrastructure. Market analysis suggests that establishing regional production hubs could reduce logistics costs by 30-40% while ensuring consistent quality control standards across manufacturing facilities.
Economic modeling based on current market conditions indicates a potential return on investment period of 2.5-3.5 years for thiocyanate-enhanced solar technologies, assuming energy conversion efficiency improvements remain consistent at scale. For energy storage applications, the ROI timeline extends to 3-4 years due to higher integration complexity and additional testing requirements.
Regulatory pathways present varying degrees of complexity across different markets. In the European Union, thiocyanate compounds face moderate regulatory scrutiny under REACH regulations, while the United States EPA requirements focus primarily on manufacturing waste management protocols. Asian markets generally present fewer regulatory barriers but may require more extensive documentation of performance claims.
Market adoption modeling suggests that thiocyanate-enhanced energy technologies could capture 5-8% of the renewable energy market within five years of commercial introduction, with potential for accelerated growth as manufacturing economies of scale reduce implementation costs. This translates to a projected market value of $2.3-3.1 billion by 2030, representing a compelling commercial opportunity despite the technical challenges of large-scale implementation.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!