How to Accelerate Gene Expression Studies with Abscisic Acid?
JUL 14, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
ABA Gene Expression Background and Objectives
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a crucial plant hormone that plays a vital role in regulating various physiological processes, including seed dormancy, germination, and stress responses. The study of gene expression in response to ABA has been a cornerstone of plant biology research for decades, providing invaluable insights into plant development and adaptation mechanisms.
The field of ABA-mediated gene expression has evolved significantly since the hormone's discovery in the 1960s. Initially, research focused on identifying ABA-responsive genes and characterizing their functions. As molecular biology techniques advanced, researchers began to unravel the complex signaling pathways and regulatory networks involved in ABA-mediated gene expression.
In recent years, the advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies and systems biology approaches has revolutionized our understanding of ABA-regulated gene expression. These advancements have enabled researchers to study global transcriptome changes in response to ABA, leading to the identification of numerous ABA-responsive genes and regulatory elements.
Despite these advances, accelerating gene expression studies with ABA remains a critical challenge in plant biology. The complexity of ABA signaling, the diversity of plant responses to ABA, and the intricate crosstalk with other hormonal pathways necessitate the development of more efficient and comprehensive research strategies.
The primary objectives of accelerating gene expression studies with ABA are multifaceted. First, researchers aim to develop high-throughput screening methods to rapidly identify and characterize ABA-responsive genes across different plant species and tissues. This would facilitate comparative studies and enhance our understanding of ABA-mediated responses in diverse plant systems.
Second, there is a pressing need to improve the temporal and spatial resolution of gene expression analyses. This involves developing techniques to monitor ABA-induced gene expression changes in real-time and at the single-cell level, providing a more nuanced understanding of ABA's effects on plant physiology.
Third, researchers seek to integrate multi-omics approaches to comprehensively study ABA-mediated gene expression. By combining transcriptomics with proteomics, metabolomics, and epigenomics data, scientists aim to construct holistic models of ABA signaling and its impact on gene regulation.
Lastly, accelerating gene expression studies with ABA has significant implications for crop improvement and stress tolerance. By elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying ABA-mediated stress responses, researchers hope to develop novel strategies for enhancing crop resilience to environmental challenges such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures.
The field of ABA-mediated gene expression has evolved significantly since the hormone's discovery in the 1960s. Initially, research focused on identifying ABA-responsive genes and characterizing their functions. As molecular biology techniques advanced, researchers began to unravel the complex signaling pathways and regulatory networks involved in ABA-mediated gene expression.
In recent years, the advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies and systems biology approaches has revolutionized our understanding of ABA-regulated gene expression. These advancements have enabled researchers to study global transcriptome changes in response to ABA, leading to the identification of numerous ABA-responsive genes and regulatory elements.
Despite these advances, accelerating gene expression studies with ABA remains a critical challenge in plant biology. The complexity of ABA signaling, the diversity of plant responses to ABA, and the intricate crosstalk with other hormonal pathways necessitate the development of more efficient and comprehensive research strategies.
The primary objectives of accelerating gene expression studies with ABA are multifaceted. First, researchers aim to develop high-throughput screening methods to rapidly identify and characterize ABA-responsive genes across different plant species and tissues. This would facilitate comparative studies and enhance our understanding of ABA-mediated responses in diverse plant systems.
Second, there is a pressing need to improve the temporal and spatial resolution of gene expression analyses. This involves developing techniques to monitor ABA-induced gene expression changes in real-time and at the single-cell level, providing a more nuanced understanding of ABA's effects on plant physiology.
Third, researchers seek to integrate multi-omics approaches to comprehensively study ABA-mediated gene expression. By combining transcriptomics with proteomics, metabolomics, and epigenomics data, scientists aim to construct holistic models of ABA signaling and its impact on gene regulation.
Lastly, accelerating gene expression studies with ABA has significant implications for crop improvement and stress tolerance. By elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying ABA-mediated stress responses, researchers hope to develop novel strategies for enhancing crop resilience to environmental challenges such as drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures.
Market Demand for Rapid Gene Expression Analysis
The market demand for rapid gene expression analysis, particularly in the context of abscisic acid (ABA) studies, has been steadily increasing in recent years. This growth is driven by the expanding applications of gene expression data in various fields, including agriculture, biotechnology, and pharmaceutical research. The ability to quickly and accurately analyze gene expression patterns in response to ABA treatment is crucial for understanding plant stress responses, developing drought-resistant crops, and advancing our knowledge of plant hormone signaling pathways.
In the agricultural sector, there is a pressing need for tools that can accelerate the development of stress-tolerant crop varieties. ABA plays a central role in plant responses to environmental stresses, particularly drought. Rapid gene expression analysis techniques enable researchers and breeders to identify key genes involved in ABA-mediated stress responses, potentially leading to the creation of more resilient crops. This has significant implications for food security and sustainable agriculture in the face of climate change.
The biotechnology industry has also shown increased interest in rapid gene expression analysis for ABA-related studies. Companies developing plant growth regulators and biostimulants require efficient methods to assess the effects of their products on gene expression. By accelerating these studies, companies can streamline their product development pipelines, bringing innovative solutions to market faster and gaining a competitive edge.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the demand for rapid gene expression analysis in ABA studies stems from the potential applications in drug discovery. ABA and its signaling pathways share similarities with certain human physiological processes, making it a valuable model for understanding cellular responses to stress. Accelerated gene expression studies can help identify novel drug targets and contribute to the development of new therapeutic approaches for stress-related disorders.
Academic research institutions are another significant driver of market demand for rapid gene expression analysis in ABA studies. The ability to quickly generate and analyze large-scale gene expression data enables researchers to conduct more comprehensive studies, test multiple hypotheses, and publish results more frequently. This acceleration of the research cycle contributes to faster scientific progress and a deeper understanding of plant biology and stress responses.
The market for rapid gene expression analysis tools and services is expected to grow as the importance of ABA-related research continues to increase. This demand is further fueled by advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies, bioinformatics, and automation, which have made gene expression studies more accessible and cost-effective. As a result, there is a growing need for integrated solutions that combine sample preparation, data generation, and analysis to provide researchers with actionable insights in a timely manner.
In the agricultural sector, there is a pressing need for tools that can accelerate the development of stress-tolerant crop varieties. ABA plays a central role in plant responses to environmental stresses, particularly drought. Rapid gene expression analysis techniques enable researchers and breeders to identify key genes involved in ABA-mediated stress responses, potentially leading to the creation of more resilient crops. This has significant implications for food security and sustainable agriculture in the face of climate change.
The biotechnology industry has also shown increased interest in rapid gene expression analysis for ABA-related studies. Companies developing plant growth regulators and biostimulants require efficient methods to assess the effects of their products on gene expression. By accelerating these studies, companies can streamline their product development pipelines, bringing innovative solutions to market faster and gaining a competitive edge.
In the pharmaceutical sector, the demand for rapid gene expression analysis in ABA studies stems from the potential applications in drug discovery. ABA and its signaling pathways share similarities with certain human physiological processes, making it a valuable model for understanding cellular responses to stress. Accelerated gene expression studies can help identify novel drug targets and contribute to the development of new therapeutic approaches for stress-related disorders.
Academic research institutions are another significant driver of market demand for rapid gene expression analysis in ABA studies. The ability to quickly generate and analyze large-scale gene expression data enables researchers to conduct more comprehensive studies, test multiple hypotheses, and publish results more frequently. This acceleration of the research cycle contributes to faster scientific progress and a deeper understanding of plant biology and stress responses.
The market for rapid gene expression analysis tools and services is expected to grow as the importance of ABA-related research continues to increase. This demand is further fueled by advancements in high-throughput sequencing technologies, bioinformatics, and automation, which have made gene expression studies more accessible and cost-effective. As a result, there is a growing need for integrated solutions that combine sample preparation, data generation, and analysis to provide researchers with actionable insights in a timely manner.
Current Challenges in ABA-Mediated Gene Expression Studies
Despite significant advancements in ABA-mediated gene expression studies, researchers still face several challenges that hinder the acceleration of these investigations. One of the primary obstacles is the complexity of ABA signaling pathways, which involve numerous components and intricate regulatory mechanisms. This complexity makes it difficult to isolate and study individual gene responses to ABA without considering the broader network effects.
Another major challenge is the temporal and spatial variability of ABA-induced gene expression. ABA responses can vary significantly depending on the tissue type, developmental stage, and environmental conditions. This variability complicates the design of experiments and the interpretation of results, as findings from one specific context may not be universally applicable.
The dosage-dependent nature of ABA responses presents an additional hurdle. Different genes may respond to varying concentrations of ABA, and the threshold for activation can differ among genes and tissues. Determining the optimal ABA concentration for studying specific gene expression patterns requires extensive optimization, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, the crosstalk between ABA and other plant hormones adds another layer of complexity to gene expression studies. ABA interacts with various signaling pathways, including those of auxins, cytokinins, and ethylene. Disentangling the effects of ABA from those of other hormones can be challenging, particularly in whole-plant systems.
Technical limitations also impede progress in ABA-mediated gene expression studies. While high-throughput sequencing technologies have revolutionized transcriptomics, the analysis and interpretation of large-scale gene expression data remain challenging. Researchers often struggle with data normalization, identification of significant expression changes, and the functional annotation of novel ABA-responsive genes.
The lack of standardized protocols for ABA application and gene expression analysis across different plant species and experimental systems further complicates comparative studies. This inconsistency makes it difficult to draw broad conclusions about ABA-mediated gene regulation across diverse plant taxa.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of gene expression in response to ABA poses a significant challenge. Many ABA-responsive genes exhibit transient expression patterns, with rapid induction followed by quick downregulation. Capturing these dynamic changes requires precise timing and sophisticated experimental designs, which can be technically demanding and prone to variability between experiments.
Another major challenge is the temporal and spatial variability of ABA-induced gene expression. ABA responses can vary significantly depending on the tissue type, developmental stage, and environmental conditions. This variability complicates the design of experiments and the interpretation of results, as findings from one specific context may not be universally applicable.
The dosage-dependent nature of ABA responses presents an additional hurdle. Different genes may respond to varying concentrations of ABA, and the threshold for activation can differ among genes and tissues. Determining the optimal ABA concentration for studying specific gene expression patterns requires extensive optimization, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, the crosstalk between ABA and other plant hormones adds another layer of complexity to gene expression studies. ABA interacts with various signaling pathways, including those of auxins, cytokinins, and ethylene. Disentangling the effects of ABA from those of other hormones can be challenging, particularly in whole-plant systems.
Technical limitations also impede progress in ABA-mediated gene expression studies. While high-throughput sequencing technologies have revolutionized transcriptomics, the analysis and interpretation of large-scale gene expression data remain challenging. Researchers often struggle with data normalization, identification of significant expression changes, and the functional annotation of novel ABA-responsive genes.
The lack of standardized protocols for ABA application and gene expression analysis across different plant species and experimental systems further complicates comparative studies. This inconsistency makes it difficult to draw broad conclusions about ABA-mediated gene regulation across diverse plant taxa.
Lastly, the dynamic nature of gene expression in response to ABA poses a significant challenge. Many ABA-responsive genes exhibit transient expression patterns, with rapid induction followed by quick downregulation. Capturing these dynamic changes requires precise timing and sophisticated experimental designs, which can be technically demanding and prone to variability between experiments.
Existing Methods to Accelerate ABA Gene Expression Studies
01 High-throughput gene expression analysis
Advanced techniques for rapid and efficient analysis of gene expression patterns across multiple samples or conditions. These methods often involve automated processes and sophisticated data analysis tools to accelerate the study of gene expression on a large scale.- High-throughput gene expression analysis: Advanced techniques for rapid and efficient analysis of gene expression patterns across multiple samples or conditions. These methods often involve automated systems and parallel processing to accelerate data generation and analysis, enabling researchers to study large-scale gene expression changes in a time-efficient manner.
- Computational methods for gene expression data analysis: Development of sophisticated algorithms and software tools to process and interpret large-scale gene expression data quickly. These computational approaches can include machine learning, statistical modeling, and data visualization techniques to accelerate the identification of significant gene expression patterns and biological insights.
- Real-time gene expression monitoring: Technologies that enable continuous, rapid measurement of gene expression levels in living cells or organisms. These methods can provide immediate feedback on gene activity, allowing for faster experimental iterations and more dynamic studies of gene regulation and cellular responses.
- Microfluidic systems for gene expression analysis: Integration of gene expression studies with microfluidic technologies to miniaturize and accelerate experimental processes. These systems can handle small sample volumes, perform multiple assays in parallel, and reduce reaction times, thereby speeding up gene expression analysis workflows.
- Optimized sample preparation for gene expression studies: Development of improved methods for extracting and processing RNA samples for gene expression analysis. These techniques aim to reduce preparation time, increase RNA yield and quality, and enhance the overall efficiency of gene expression studies, leading to faster experimental turnaround times.
02 Real-time PCR optimization
Improved methods for optimizing real-time PCR processes, including enhanced primer design, reaction conditions, and data analysis algorithms. These advancements allow for faster and more accurate quantification of gene expression levels.Expand Specific Solutions03 Microarray technology enhancements
Developments in microarray technology to increase throughput and reduce processing time for gene expression studies. This includes improvements in array design, sample preparation, and data analysis methods to accelerate large-scale gene expression profiling.Expand Specific Solutions04 Machine learning in gene expression analysis
Integration of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to accelerate the analysis and interpretation of gene expression data. These computational approaches enable faster pattern recognition and prediction of gene function or disease associations.Expand Specific Solutions05 Single-cell RNA sequencing advancements
Innovations in single-cell RNA sequencing technologies to increase the speed and efficiency of gene expression analysis at the individual cell level. These advancements allow for rapid profiling of gene expression heterogeneity within complex tissues or cell populations.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in ABA and Gene Expression Research
The gene expression studies with Abscisic Acid (ABA) are in a mature stage of development, with a diverse competitive landscape. The market is characterized by a mix of established biotechnology companies, academic institutions, and research organizations. Key players like Valent BioSciences Corp., Pioneer Hi-Bred International, and Evogene Ltd. are driving innovation in this field. The market size is substantial, given ABA's critical role in plant stress responses and agricultural applications. Technological advancements by companies such as QIAGEN GmbH and Illumina, Inc. are accelerating research capabilities. Academic institutions like China Agricultural University and The Regents of the University of California are contributing significantly to the knowledge base, fostering collaborations between industry and academia to further accelerate gene expression studies with ABA.
China Agricultural University
Technical Solution: China Agricultural University has developed a novel approach to accelerate gene expression studies with abscisic acid (ABA) using CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology. They have created an ABA-inducible CRISPR activation system that allows for rapid and precise control of gene expression in response to ABA treatment[1]. This system utilizes a modified dCas9 fused with transcriptional activators and an ABA-responsive promoter. When ABA is applied, it triggers the expression of the dCas9 activator, which then binds to specific target genes and enhances their expression. This method enables researchers to study the effects of ABA-induced gene expression changes in a more controlled and efficient manner[3]. Additionally, they have optimized the ABA treatment conditions and developed high-throughput screening protocols to identify ABA-responsive genes more quickly[5].
Strengths: Precise control of gene expression, rapid response to ABA treatment, and compatibility with high-throughput screening. Weaknesses: May require optimization for different plant species and potential off-target effects of CRISPR technology.
The Regents of the University of California
Technical Solution: The University of California has developed a cutting-edge approach to accelerate gene expression studies with abscisic acid (ABA) using a combination of advanced genomics and bioinformatics tools. Their method involves the use of RNA-seq and ChIP-seq technologies to simultaneously analyze transcriptome changes and ABA-responsive transcription factor binding sites[2]. This integrated approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of ABA-mediated gene regulation. They have also developed a machine learning algorithm that predicts ABA-responsive genes based on promoter sequence features and epigenetic marks[4]. To further accelerate studies, they have created a high-throughput phenotyping platform that can rapidly assess ABA-induced physiological changes in plants, correlating these changes with gene expression data[6]. This multi-faceted approach significantly reduces the time required to identify and characterize ABA-responsive genes and their functions.
Strengths: Comprehensive analysis of ABA-mediated gene regulation, integration of multiple data types, and high-throughput capabilities. Weaknesses: Requires significant computational resources and expertise in bioinformatics.
Innovative Approaches in ABA-Induced Gene Expression
Method and constructs for increasing recombinant protein production in plants dehydration stress
PatentInactiveUS20110312095A1
Innovation
- Development of an inducible expression system utilizing a nucleic acid sequence isolated from alfalfa that includes a dehydrin promoter and terminator, which increases protein expression in response to cold, salt, or abscisic acid stress, allowing for targeted and efficient recombinant protein production.
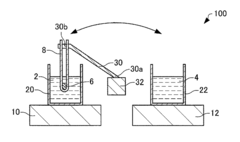
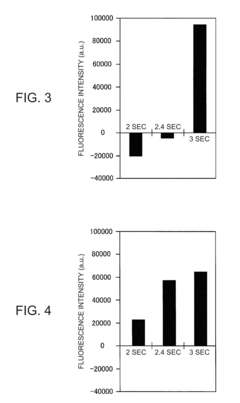
Nucleic acid amplification reaction method, reagent set, and method of using reagent set
PatentInactiveUS20180030508A1
Innovation
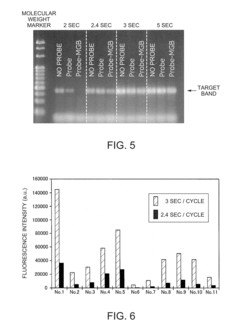
- A nucleic acid amplification reaction method that includes a thermal cycling step with cycles of 9 seconds or less, where the probe is added after amplification, and optimized primer and divalent cation concentrations to suppress probe inhibition, allowing for increased thermal cycling speed and sensitive fluorescence-based quantification.
Regulatory Considerations for Gene Expression Studies
Gene expression studies involving abscisic acid (ABA) are subject to various regulatory considerations that researchers must navigate to ensure compliance and scientific integrity. These regulations encompass a wide range of aspects, from laboratory safety protocols to ethical considerations in plant research.
One primary regulatory concern is the safe handling and storage of ABA. As a plant hormone, ABA is classified as a biochemical, and its use in research settings is governed by laboratory safety regulations. Researchers must adhere to proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety. This includes maintaining appropriate documentation of ABA usage and implementing proper personal protective equipment protocols.
Genetic modification techniques often employed in ABA-related gene expression studies fall under the purview of biosafety regulations. Many countries have established guidelines for genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which may apply to plants modified to alter ABA-related gene expression. Researchers must obtain necessary permits and approvals before conducting experiments involving genetic modifications, and ensure proper containment measures are in place to prevent unintended release of modified organisms.
Ethical considerations also play a crucial role in gene expression studies. While plant research generally faces fewer ethical hurdles compared to animal studies, researchers must still consider the potential ecological impacts of their work, particularly when studying genes that could affect plant stress responses or agricultural productivity. Institutional review boards may require researchers to address these concerns in their experimental designs.
Data management and sharing regulations are increasingly important in the field of gene expression studies. Many funding agencies and journals now require researchers to make their data publicly available, adhering to FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles. This necessitates careful planning for data storage, curation, and sharing, often requiring researchers to deposit data in recognized repositories and provide detailed metadata.
Intellectual property considerations are another critical aspect of regulatory compliance in ABA-related gene expression research. Researchers must be aware of existing patents on ABA-related genes, methodologies, or applications, and navigate potential conflicts or licensing requirements. Additionally, they should consider how their own discoveries might be protected through patents or other forms of intellectual property rights.
Lastly, researchers must adhere to good laboratory practice (GLP) guidelines to ensure the reliability and reproducibility of their results. This includes maintaining detailed records of experimental procedures, calibrating equipment regularly, and implementing quality control measures. Compliance with these standards is crucial for the credibility of research findings and may be required for regulatory submissions or publication in high-impact journals.
One primary regulatory concern is the safe handling and storage of ABA. As a plant hormone, ABA is classified as a biochemical, and its use in research settings is governed by laboratory safety regulations. Researchers must adhere to proper storage, handling, and disposal procedures to minimize environmental impact and ensure worker safety. This includes maintaining appropriate documentation of ABA usage and implementing proper personal protective equipment protocols.
Genetic modification techniques often employed in ABA-related gene expression studies fall under the purview of biosafety regulations. Many countries have established guidelines for genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which may apply to plants modified to alter ABA-related gene expression. Researchers must obtain necessary permits and approvals before conducting experiments involving genetic modifications, and ensure proper containment measures are in place to prevent unintended release of modified organisms.
Ethical considerations also play a crucial role in gene expression studies. While plant research generally faces fewer ethical hurdles compared to animal studies, researchers must still consider the potential ecological impacts of their work, particularly when studying genes that could affect plant stress responses or agricultural productivity. Institutional review boards may require researchers to address these concerns in their experimental designs.
Data management and sharing regulations are increasingly important in the field of gene expression studies. Many funding agencies and journals now require researchers to make their data publicly available, adhering to FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles. This necessitates careful planning for data storage, curation, and sharing, often requiring researchers to deposit data in recognized repositories and provide detailed metadata.
Intellectual property considerations are another critical aspect of regulatory compliance in ABA-related gene expression research. Researchers must be aware of existing patents on ABA-related genes, methodologies, or applications, and navigate potential conflicts or licensing requirements. Additionally, they should consider how their own discoveries might be protected through patents or other forms of intellectual property rights.
Lastly, researchers must adhere to good laboratory practice (GLP) guidelines to ensure the reliability and reproducibility of their results. This includes maintaining detailed records of experimental procedures, calibrating equipment regularly, and implementing quality control measures. Compliance with these standards is crucial for the credibility of research findings and may be required for regulatory submissions or publication in high-impact journals.
Environmental Impact of ABA Research Acceleration
The acceleration of gene expression studies with abscisic acid (ABA) has significant environmental implications that warrant careful consideration. As research in this field progresses rapidly, it is crucial to assess the potential ecological impacts and sustainability of these accelerated studies.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the increased production and use of synthetic ABA in laboratory settings. While ABA is a naturally occurring plant hormone, the large-scale synthesis required for accelerated research may lead to chemical waste and energy consumption. Proper disposal and management of these synthetic compounds are essential to prevent contamination of soil and water systems.
Furthermore, the intensified focus on ABA-related gene expression studies may inadvertently lead to a narrower scope of plant research. This could potentially result in reduced attention to other important aspects of plant biology and ecology, which may have long-term consequences for our understanding of ecosystem dynamics and biodiversity conservation.
The acceleration of ABA research also raises questions about the potential for unintended ecological consequences. As scientists gain the ability to manipulate ABA-related gene expression more rapidly, there is a risk of creating plants with altered stress responses that could disrupt natural ecosystems if released. Careful containment measures and risk assessments are necessary to mitigate these potential threats.
On the positive side, accelerated ABA research could lead to the development of more drought-resistant crops, which could have significant environmental benefits. By reducing water requirements and increasing crop yields in water-stressed regions, these advancements could help conserve water resources and reduce the need for agricultural expansion into natural habitats.
The rapid pace of research may also lead to faster discoveries in plant adaptation to climate change. This could provide valuable insights for conservation efforts and help in developing strategies to protect vulnerable ecosystems from the impacts of global warming.
However, the increased demand for experimental plant material may lead to greater resource consumption in terms of energy, water, and growth media. Research facilities may need to expand, potentially leading to land use changes and increased carbon footprints. It is crucial for institutions to implement sustainable practices and green technologies to offset these environmental costs.
In conclusion, while the acceleration of gene expression studies with ABA holds great promise for advancing our understanding of plant biology and developing resilient crops, it is imperative to balance these benefits with careful consideration of the environmental impacts. Implementing sustainable research practices, conducting thorough environmental risk assessments, and maintaining a holistic approach to plant science will be key to ensuring that the acceleration of ABA research contributes positively to both scientific progress and environmental stewardship.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the increased production and use of synthetic ABA in laboratory settings. While ABA is a naturally occurring plant hormone, the large-scale synthesis required for accelerated research may lead to chemical waste and energy consumption. Proper disposal and management of these synthetic compounds are essential to prevent contamination of soil and water systems.
Furthermore, the intensified focus on ABA-related gene expression studies may inadvertently lead to a narrower scope of plant research. This could potentially result in reduced attention to other important aspects of plant biology and ecology, which may have long-term consequences for our understanding of ecosystem dynamics and biodiversity conservation.
The acceleration of ABA research also raises questions about the potential for unintended ecological consequences. As scientists gain the ability to manipulate ABA-related gene expression more rapidly, there is a risk of creating plants with altered stress responses that could disrupt natural ecosystems if released. Careful containment measures and risk assessments are necessary to mitigate these potential threats.
On the positive side, accelerated ABA research could lead to the development of more drought-resistant crops, which could have significant environmental benefits. By reducing water requirements and increasing crop yields in water-stressed regions, these advancements could help conserve water resources and reduce the need for agricultural expansion into natural habitats.
The rapid pace of research may also lead to faster discoveries in plant adaptation to climate change. This could provide valuable insights for conservation efforts and help in developing strategies to protect vulnerable ecosystems from the impacts of global warming.
However, the increased demand for experimental plant material may lead to greater resource consumption in terms of energy, water, and growth media. Research facilities may need to expand, potentially leading to land use changes and increased carbon footprints. It is crucial for institutions to implement sustainable practices and green technologies to offset these environmental costs.
In conclusion, while the acceleration of gene expression studies with ABA holds great promise for advancing our understanding of plant biology and developing resilient crops, it is imperative to balance these benefits with careful consideration of the environmental impacts. Implementing sustainable research practices, conducting thorough environmental risk assessments, and maintaining a holistic approach to plant science will be key to ensuring that the acceleration of ABA research contributes positively to both scientific progress and environmental stewardship.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!