How to Enhance Moisture-Wicking Properties in Kevlar Apparel?
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Kevlar Moisture-Wicking Evolution and Objectives
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s, has revolutionized various industries, particularly in protective gear and apparel. Initially designed for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, Kevlar's application in moisture-wicking apparel represents a significant evolution in its functionality. This technological progression aims to combine Kevlar's renowned durability with enhanced comfort for wearers in demanding environments.
The evolution of moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel has been driven by the increasing demand for multi-functional protective clothing. As users in military, law enforcement, and industrial sectors face diverse environmental challenges, the need for gear that offers both protection and comfort has become paramount. This dual requirement has spurred research and development efforts to modify Kevlar's inherently hydrophobic nature.
Historically, Kevlar's moisture management capabilities were limited, often necessitating the use of additional layers or treatments. The primary objective in enhancing these properties is to create a single-layer fabric that efficiently wicks moisture away from the skin while maintaining Kevlar's protective qualities. This goal aligns with the broader trend in technical textiles towards creating "smart" fabrics that adapt to user needs and environmental conditions.
Recent advancements have focused on several key areas: surface modification of Kevlar fibers, blending with hydrophilic materials, and innovative weaving techniques. These approaches aim to improve capillary action within the fabric structure, facilitating rapid moisture transport without compromising strength or protective properties. The ultimate objective is to develop Kevlar apparel that offers superior moisture management comparable to high-performance synthetic fabrics while retaining its unparalleled protective characteristics.
The technical challenges in this evolution are significant. Researchers must balance the need for moisture-wicking properties with the preservation of Kevlar's core strengths – its high tensile strength, low weight, and heat resistance. This balancing act requires a deep understanding of polymer science, textile engineering, and the specific needs of end-users in various applications.
Looking forward, the objectives for enhancing moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel include developing nanotechnology-based solutions for fiber modification, exploring bio-inspired designs for optimal moisture transport, and integrating smart textile technologies for adaptive moisture management. These ambitious goals reflect the ongoing commitment to pushing the boundaries of Kevlar's capabilities, ensuring its continued relevance in an ever-evolving landscape of protective and performance apparel.
The evolution of moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel has been driven by the increasing demand for multi-functional protective clothing. As users in military, law enforcement, and industrial sectors face diverse environmental challenges, the need for gear that offers both protection and comfort has become paramount. This dual requirement has spurred research and development efforts to modify Kevlar's inherently hydrophobic nature.
Historically, Kevlar's moisture management capabilities were limited, often necessitating the use of additional layers or treatments. The primary objective in enhancing these properties is to create a single-layer fabric that efficiently wicks moisture away from the skin while maintaining Kevlar's protective qualities. This goal aligns with the broader trend in technical textiles towards creating "smart" fabrics that adapt to user needs and environmental conditions.
Recent advancements have focused on several key areas: surface modification of Kevlar fibers, blending with hydrophilic materials, and innovative weaving techniques. These approaches aim to improve capillary action within the fabric structure, facilitating rapid moisture transport without compromising strength or protective properties. The ultimate objective is to develop Kevlar apparel that offers superior moisture management comparable to high-performance synthetic fabrics while retaining its unparalleled protective characteristics.
The technical challenges in this evolution are significant. Researchers must balance the need for moisture-wicking properties with the preservation of Kevlar's core strengths – its high tensile strength, low weight, and heat resistance. This balancing act requires a deep understanding of polymer science, textile engineering, and the specific needs of end-users in various applications.
Looking forward, the objectives for enhancing moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel include developing nanotechnology-based solutions for fiber modification, exploring bio-inspired designs for optimal moisture transport, and integrating smart textile technologies for adaptive moisture management. These ambitious goals reflect the ongoing commitment to pushing the boundaries of Kevlar's capabilities, ensuring its continued relevance in an ever-evolving landscape of protective and performance apparel.
Market Analysis for Enhanced Kevlar Apparel
The market for enhanced Kevlar apparel with improved moisture-wicking properties presents significant growth potential across various sectors. The global market for high-performance protective clothing, including Kevlar-based products, is experiencing steady expansion, driven by increasing safety concerns in industrial, military, and sports applications.
In the industrial sector, there is a growing demand for comfortable yet protective workwear, particularly in industries such as oil and gas, construction, and manufacturing. These sectors require apparel that not only provides protection against cuts, abrasions, and heat but also offers comfort during extended wear. The addition of moisture-wicking properties to Kevlar apparel addresses this need, potentially expanding market share in these industries.
The military and law enforcement sectors represent another substantial market for enhanced Kevlar apparel. These users require gear that maintains protective qualities while improving comfort and performance in diverse environmental conditions. Moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel can significantly enhance user experience, potentially leading to increased adoption and market growth in defense and security applications.
Sports and outdoor recreation industries also show promising market potential for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel. Activities such as motorcycling, extreme sports, and outdoor adventures require protective gear that doesn't compromise on comfort. The integration of moisture-wicking properties into Kevlar-based protective wear could open new market segments and attract consumers seeking high-performance, multi-functional apparel.
The market trend indicates a shift towards more versatile and comfortable protective clothing. Consumers and professional users alike are increasingly demanding apparel that offers protection without sacrificing comfort or mobility. This trend aligns well with the development of moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel, suggesting a receptive market for such innovations.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the high-performance protective clothing market, including Kevlar-based products. However, rapid industrialization and increasing safety regulations in Asia-Pacific regions, particularly in countries like China and India, are expected to drive significant market growth in these areas for enhanced Kevlar apparel.
The competitive landscape for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel is likely to involve both established players in the protective clothing industry and innovative startups. Major companies with expertise in advanced materials and protective gear are well-positioned to capitalize on this market opportunity, while smaller, agile firms may drive innovation in niche applications.
Overall, the market analysis suggests a strong potential for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel across multiple sectors. The combination of protection, comfort, and performance offered by such enhanced fabrics aligns well with current market trends and user demands, indicating favorable conditions for market growth and innovation in this space.
In the industrial sector, there is a growing demand for comfortable yet protective workwear, particularly in industries such as oil and gas, construction, and manufacturing. These sectors require apparel that not only provides protection against cuts, abrasions, and heat but also offers comfort during extended wear. The addition of moisture-wicking properties to Kevlar apparel addresses this need, potentially expanding market share in these industries.
The military and law enforcement sectors represent another substantial market for enhanced Kevlar apparel. These users require gear that maintains protective qualities while improving comfort and performance in diverse environmental conditions. Moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel can significantly enhance user experience, potentially leading to increased adoption and market growth in defense and security applications.
Sports and outdoor recreation industries also show promising market potential for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel. Activities such as motorcycling, extreme sports, and outdoor adventures require protective gear that doesn't compromise on comfort. The integration of moisture-wicking properties into Kevlar-based protective wear could open new market segments and attract consumers seeking high-performance, multi-functional apparel.
The market trend indicates a shift towards more versatile and comfortable protective clothing. Consumers and professional users alike are increasingly demanding apparel that offers protection without sacrificing comfort or mobility. This trend aligns well with the development of moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel, suggesting a receptive market for such innovations.
Geographically, North America and Europe currently dominate the high-performance protective clothing market, including Kevlar-based products. However, rapid industrialization and increasing safety regulations in Asia-Pacific regions, particularly in countries like China and India, are expected to drive significant market growth in these areas for enhanced Kevlar apparel.
The competitive landscape for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel is likely to involve both established players in the protective clothing industry and innovative startups. Major companies with expertise in advanced materials and protective gear are well-positioned to capitalize on this market opportunity, while smaller, agile firms may drive innovation in niche applications.
Overall, the market analysis suggests a strong potential for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel across multiple sectors. The combination of protection, comfort, and performance offered by such enhanced fabrics aligns well with current market trends and user demands, indicating favorable conditions for market growth and innovation in this space.
Current Challenges in Kevlar Moisture Management
Kevlar, renowned for its exceptional strength and heat resistance, faces significant challenges in moisture management when used in apparel applications. The primary issue stems from Kevlar's inherent hydrophobic nature, which inhibits its ability to effectively wick moisture away from the wearer's skin. This characteristic poses a considerable obstacle in developing comfortable and high-performance Kevlar-based garments for various industries, including military, firefighting, and extreme sports.
One of the main challenges is the limited surface area of Kevlar fibers for moisture absorption. Unlike natural fibers such as cotton, which have a porous structure that facilitates moisture absorption, Kevlar fibers have a smooth surface that repels water. This property, while beneficial for certain applications, becomes problematic when rapid moisture management is required in apparel.
Another significant hurdle is the difficulty in modifying Kevlar's chemical structure without compromising its core mechanical properties. Attempts to enhance hydrophilicity often result in a trade-off with strength and heat resistance, which are the primary reasons for using Kevlar in protective clothing. This delicate balance between improving moisture-wicking capabilities and maintaining structural integrity presents a complex challenge for material scientists and textile engineers.
The integration of Kevlar with other moisture-wicking materials also poses technical difficulties. While blending Kevlar with hydrophilic fibers can improve overall moisture management, achieving a homogeneous blend that maintains the protective properties of Kevlar while enhancing comfort remains a significant challenge. The disparate properties of Kevlar and moisture-wicking fibers often lead to inconsistent performance across the fabric.
Furthermore, the durability of moisture-wicking treatments on Kevlar fabrics is a persistent issue. Many surface treatments designed to improve hydrophilicity tend to degrade over time, especially under harsh conditions or frequent washing cycles. This degradation leads to a gradual loss of moisture-wicking properties, reducing the long-term effectiveness of the apparel.
The cost-effectiveness of enhancing moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel also presents a challenge. Advanced treatments and manufacturing processes required to improve moisture management can significantly increase production costs, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of such enhanced Kevlar fabrics in price-sensitive markets.
Lastly, the environmental impact of chemical treatments used to improve Kevlar's moisture-wicking properties is an emerging concern. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in textile manufacturing, developing eco-friendly methods to enhance Kevlar's moisture management capabilities without relying on harmful chemicals or processes is a critical challenge that researchers and manufacturers must address.
One of the main challenges is the limited surface area of Kevlar fibers for moisture absorption. Unlike natural fibers such as cotton, which have a porous structure that facilitates moisture absorption, Kevlar fibers have a smooth surface that repels water. This property, while beneficial for certain applications, becomes problematic when rapid moisture management is required in apparel.
Another significant hurdle is the difficulty in modifying Kevlar's chemical structure without compromising its core mechanical properties. Attempts to enhance hydrophilicity often result in a trade-off with strength and heat resistance, which are the primary reasons for using Kevlar in protective clothing. This delicate balance between improving moisture-wicking capabilities and maintaining structural integrity presents a complex challenge for material scientists and textile engineers.
The integration of Kevlar with other moisture-wicking materials also poses technical difficulties. While blending Kevlar with hydrophilic fibers can improve overall moisture management, achieving a homogeneous blend that maintains the protective properties of Kevlar while enhancing comfort remains a significant challenge. The disparate properties of Kevlar and moisture-wicking fibers often lead to inconsistent performance across the fabric.
Furthermore, the durability of moisture-wicking treatments on Kevlar fabrics is a persistent issue. Many surface treatments designed to improve hydrophilicity tend to degrade over time, especially under harsh conditions or frequent washing cycles. This degradation leads to a gradual loss of moisture-wicking properties, reducing the long-term effectiveness of the apparel.
The cost-effectiveness of enhancing moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel also presents a challenge. Advanced treatments and manufacturing processes required to improve moisture management can significantly increase production costs, potentially limiting the widespread adoption of such enhanced Kevlar fabrics in price-sensitive markets.
Lastly, the environmental impact of chemical treatments used to improve Kevlar's moisture-wicking properties is an emerging concern. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in textile manufacturing, developing eco-friendly methods to enhance Kevlar's moisture management capabilities without relying on harmful chemicals or processes is a critical challenge that researchers and manufacturers must address.
Existing Moisture-Wicking Solutions for Kevlar
01 Moisture-wicking Kevlar fabric compositions
Innovative fabric compositions combining Kevlar with moisture-wicking materials to create apparel that offers both protection and comfort. These compositions often involve blending Kevlar fibers with synthetic or natural moisture-wicking fibers to enhance the overall performance of the garment.- Moisture-wicking Kevlar fabric compositions: Innovative fabric compositions combining Kevlar with moisture-wicking materials to create apparel that offers both protection and comfort. These compositions often involve blending Kevlar fibers with hydrophobic synthetic fibers or applying moisture-wicking treatments to Kevlar fabrics, resulting in garments that can effectively manage moisture while maintaining the protective properties of Kevlar.
- Layered structures for moisture management: Development of multi-layered fabric structures incorporating Kevlar and moisture-wicking layers. These designs typically feature a Kevlar outer layer for protection, combined with inner layers made of moisture-wicking materials. The layered approach allows for effective moisture transport away from the skin while maintaining the protective qualities of Kevlar on the exterior.
- Surface treatments for enhanced moisture-wicking: Application of specialized surface treatments to Kevlar fabrics to improve their moisture-wicking properties. These treatments can include hydrophobic coatings, nanotechnology-based finishes, or chemical modifications that enhance the fabric's ability to repel water and facilitate moisture transport, without compromising the inherent strength and protective qualities of Kevlar.
- Integration of moisture-wicking fibers with Kevlar: Techniques for integrating moisture-wicking synthetic fibers with Kevlar in the fabric construction process. This can involve methods such as core-spun yarns, where Kevlar forms the core surrounded by moisture-wicking fibers, or innovative weaving patterns that combine Kevlar with hydrophobic fibers to create a composite fabric with both protective and moisture-management properties.
- Moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel designs: Specific apparel designs that incorporate moisture-wicking properties into Kevlar-based protective clothing. These designs focus on garment construction techniques, strategic placement of moisture-wicking panels, and ventilation systems that work in conjunction with the moisture-wicking properties of the fabric to enhance overall comfort and performance in high-stress or high-temperature environments.
02 Layered structures for moisture management
Development of multi-layered fabric structures incorporating Kevlar and moisture-wicking layers. These designs typically feature a Kevlar outer layer for protection, combined with inner layers of moisture-wicking materials to enhance comfort and regulate body temperature.Expand Specific Solutions03 Surface treatments for enhanced moisture-wicking
Application of specialized surface treatments or coatings to Kevlar fabrics to improve their moisture-wicking properties. These treatments can modify the surface characteristics of Kevlar fibers to enhance their ability to transport moisture away from the skin.Expand Specific Solutions04 Integration of moisture-wicking technologies in Kevlar apparel design
Innovative apparel designs that strategically incorporate moisture-wicking technologies into Kevlar-based protective clothing. These designs focus on optimizing garment construction to maximize moisture management while maintaining the protective properties of Kevlar.Expand Specific Solutions05 Performance testing and evaluation methods
Development of specialized testing and evaluation methods to assess the moisture-wicking properties of Kevlar apparel. These methods aim to quantify and compare the moisture management performance of different Kevlar fabric compositions and garment designs.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Advanced Protective Apparel
The moisture-wicking properties enhancement in Kevlar apparel is currently in a growth phase, with increasing market demand driven by performance sportswear and protective gear industries. The global market size for moisture-wicking fabrics is projected to expand significantly in the coming years. Technologically, while moisture-wicking in synthetic fabrics is well-established, its application to Kevlar presents unique challenges due to Kevlar's inherent properties. Companies like 3M Innovative Properties Co., Northrop Grumman Systems Corp., and Indian Institutes of Technology are at the forefront of research and development in this field, focusing on innovative surface treatments and fiber modifications to improve Kevlar's moisture management capabilities.
3M Innovative Properties Co.
Technical Solution: 3M has developed a novel approach to enhance moisture-wicking properties in Kevlar apparel by incorporating hydrophilic nanofibers into the fabric structure. This technology involves electrospinning a blend of Kevlar and hydrophilic polymers to create a composite material with improved moisture management capabilities[1]. The resulting fabric maintains Kevlar's inherent strength and heat resistance while significantly improving its ability to transport moisture away from the skin. The company has also implemented a surface treatment process that modifies the Kevlar fibers to increase their hydrophilicity, further enhancing the fabric's moisture-wicking performance[3].
Strengths: Maintains Kevlar's core properties while significantly improving moisture management. Versatile application across various protective gear. Weaknesses: Potential increase in production costs due to additional processing steps. May slightly alter the fabric's texture or feel.
Northrop Grumman Systems Corp.
Technical Solution: Northrop Grumman has developed an innovative moisture-wicking system for Kevlar apparel, focusing on military and aerospace applications. Their approach involves a multi-layer fabric construction that combines Kevlar with specially engineered moisture-wicking layers[2]. The company utilizes advanced hydrophobic coatings on the outer Kevlar layer to repel external moisture, while incorporating a hydrophilic inner layer to draw sweat away from the body. This system is complemented by strategically placed ventilation channels within the fabric structure to enhance air circulation and accelerate moisture evaporation[4]. The technology also includes antimicrobial treatments to prevent odor buildup in high-moisture areas.
Strengths: Highly effective in extreme conditions, suitable for military and aerospace use. Integrated approach addressing both moisture-wicking and ventilation. Weaknesses: Potentially complex manufacturing process, which may lead to higher costs. May be overengineered for less demanding civilian applications.
Innovative Approaches in Kevlar Hydrophobicity
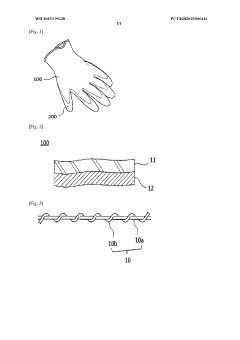
Coated gloves having excellent tear strength and heat resistance
PatentWO2015199438A1
Innovation
- A coated glove design featuring a core yarn of Kevlar, glass fiber, liquid crystal polyester yarn, or metal fiber, with a cover yarn twisted around the core yarn to enhance cutting strength and heat resistance, and a specific twist density to facilitate easy latex coating, where the first knitting part with the cover yarn is on the outside and the second part with span or nylon yarn is inside for improved comfort and coating properties.
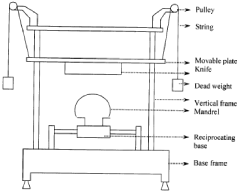
Design and development of an instrument to measure cut resistance of fabrics
PatentInactiveIN276DEL2008A
Innovation
- Development of an instrument to measure cut resistance by determining the load required and distance traveled to make a cut in fabrics, along with a model to analyze cutting forces and distance, which considers fabric construction, material parameters, and process parameters to optimize cut-resistant fabric design.
Environmental Impact of Moisture-Wicking Treatments
The environmental impact of moisture-wicking treatments in Kevlar apparel is a critical consideration in the development of enhanced moisture management solutions. These treatments, while improving the comfort and performance of the garments, can have significant implications for the environment throughout their lifecycle.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the use of chemical treatments to achieve moisture-wicking properties. Many of these treatments involve fluorochemicals, which have been linked to environmental persistence and potential toxicity. These chemicals can leach into water systems during production, use, and disposal of the apparel, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems and wildlife.
The production process of moisture-wicking treatments often requires substantial water and energy consumption. This can contribute to increased carbon emissions and strain on local water resources, particularly in regions where water scarcity is already a concern. Additionally, the use of synthetic materials in combination with these treatments may exacerbate the environmental footprint of the apparel.
Disposal of Kevlar apparel with moisture-wicking treatments presents another environmental challenge. The durability of Kevlar, combined with the added chemicals, can make these garments difficult to recycle or biodegrade. This contributes to the growing problem of textile waste in landfills and the release of microfibers into the environment during washing and wear.
However, there are ongoing efforts to develop more environmentally friendly moisture-wicking solutions. Bio-based treatments derived from natural sources are being explored as alternatives to synthetic chemicals. These treatments aim to provide similar performance benefits while reducing environmental impact and improving biodegradability.
Advancements in nanotechnology are also offering promising avenues for enhancing moisture-wicking properties with minimal environmental impact. Nanostructured surfaces can be engineered to repel moisture without the need for chemical treatments, potentially reducing the use of harmful substances in the production process.
The adoption of closed-loop manufacturing systems and water recycling technologies in the production of moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel can significantly reduce water consumption and minimize the release of chemicals into the environment. Furthermore, innovations in dyeing and finishing processes are focusing on reducing energy use and minimizing chemical waste.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, there is increasing pressure on manufacturers to develop sustainable moisture-wicking solutions. This has led to a rise in eco-friendly certifications and standards for textile treatments, encouraging the industry to prioritize environmental considerations alongside performance metrics.
One of the primary environmental concerns is the use of chemical treatments to achieve moisture-wicking properties. Many of these treatments involve fluorochemicals, which have been linked to environmental persistence and potential toxicity. These chemicals can leach into water systems during production, use, and disposal of the apparel, potentially affecting aquatic ecosystems and wildlife.
The production process of moisture-wicking treatments often requires substantial water and energy consumption. This can contribute to increased carbon emissions and strain on local water resources, particularly in regions where water scarcity is already a concern. Additionally, the use of synthetic materials in combination with these treatments may exacerbate the environmental footprint of the apparel.
Disposal of Kevlar apparel with moisture-wicking treatments presents another environmental challenge. The durability of Kevlar, combined with the added chemicals, can make these garments difficult to recycle or biodegrade. This contributes to the growing problem of textile waste in landfills and the release of microfibers into the environment during washing and wear.
However, there are ongoing efforts to develop more environmentally friendly moisture-wicking solutions. Bio-based treatments derived from natural sources are being explored as alternatives to synthetic chemicals. These treatments aim to provide similar performance benefits while reducing environmental impact and improving biodegradability.
Advancements in nanotechnology are also offering promising avenues for enhancing moisture-wicking properties with minimal environmental impact. Nanostructured surfaces can be engineered to repel moisture without the need for chemical treatments, potentially reducing the use of harmful substances in the production process.
The adoption of closed-loop manufacturing systems and water recycling technologies in the production of moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel can significantly reduce water consumption and minimize the release of chemicals into the environment. Furthermore, innovations in dyeing and finishing processes are focusing on reducing energy use and minimizing chemical waste.
As consumer awareness of environmental issues grows, there is increasing pressure on manufacturers to develop sustainable moisture-wicking solutions. This has led to a rise in eco-friendly certifications and standards for textile treatments, encouraging the industry to prioritize environmental considerations alongside performance metrics.
Durability and Performance Testing Methods
Durability and performance testing methods for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel are crucial in evaluating the effectiveness and longevity of these specialized garments. The testing process typically involves a combination of standardized procedures and custom-designed experiments to assess both the moisture management capabilities and the overall durability of the fabric.
One of the primary testing methods is the Moisture Management Test (MMT), which measures the liquid moisture transport properties of fabrics in multiple directions. This test evaluates the absorption rate, spreading speed, and one-way transport capability of the material. For Kevlar apparel with enhanced moisture-wicking properties, the MMT results should indicate rapid moisture absorption, efficient spreading, and quick transfer from the inner to the outer surface of the fabric.
Vertical wicking tests are also commonly employed to assess the fabric's ability to transport moisture vertically against gravity. In this test, a strip of fabric is suspended with its lower end immersed in a colored liquid. The height of liquid rise over time is measured, providing insights into the fabric's capillary action and wicking performance. Kevlar apparel with superior moisture-wicking properties should demonstrate rapid and sustained vertical wicking.
Durability testing for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel often includes abrasion resistance tests, such as the Martindale abrasion test or the Taber abrasion test. These methods simulate wear and tear on the fabric surface, allowing researchers to evaluate how the moisture-wicking properties are affected by repeated use and friction. The goal is to ensure that the enhanced wicking capabilities remain effective even after prolonged wear and multiple wash cycles.
Wash durability tests are particularly important for assessing the longevity of moisture-wicking treatments applied to Kevlar fabrics. These tests involve subjecting the apparel to multiple wash cycles according to standardized protocols, followed by re-evaluation of moisture management properties. The retention of moisture-wicking performance after washing is a critical factor in determining the overall effectiveness of the enhancement techniques.
Thermal and evaporative resistance tests, such as those performed using a sweating guarded hotplate, provide valuable data on the fabric's ability to manage heat and moisture simultaneously. These tests simulate the heat and moisture produced by the human body during physical activity, offering insights into the comfort and performance characteristics of the moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel under various environmental conditions.
Additionally, tensile strength and tear resistance tests are essential for evaluating the structural integrity of the enhanced Kevlar fabric. These tests ensure that the moisture-wicking treatments do not compromise the inherent strength and protective properties of Kevlar, which are crucial for many of its applications in protective clothing and equipment.
By employing this comprehensive suite of testing methods, researchers and manufacturers can thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of moisture-wicking enhancements in Kevlar apparel, ensuring that the final products meet the demanding requirements for both performance and durability in real-world applications.
One of the primary testing methods is the Moisture Management Test (MMT), which measures the liquid moisture transport properties of fabrics in multiple directions. This test evaluates the absorption rate, spreading speed, and one-way transport capability of the material. For Kevlar apparel with enhanced moisture-wicking properties, the MMT results should indicate rapid moisture absorption, efficient spreading, and quick transfer from the inner to the outer surface of the fabric.
Vertical wicking tests are also commonly employed to assess the fabric's ability to transport moisture vertically against gravity. In this test, a strip of fabric is suspended with its lower end immersed in a colored liquid. The height of liquid rise over time is measured, providing insights into the fabric's capillary action and wicking performance. Kevlar apparel with superior moisture-wicking properties should demonstrate rapid and sustained vertical wicking.
Durability testing for moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel often includes abrasion resistance tests, such as the Martindale abrasion test or the Taber abrasion test. These methods simulate wear and tear on the fabric surface, allowing researchers to evaluate how the moisture-wicking properties are affected by repeated use and friction. The goal is to ensure that the enhanced wicking capabilities remain effective even after prolonged wear and multiple wash cycles.
Wash durability tests are particularly important for assessing the longevity of moisture-wicking treatments applied to Kevlar fabrics. These tests involve subjecting the apparel to multiple wash cycles according to standardized protocols, followed by re-evaluation of moisture management properties. The retention of moisture-wicking performance after washing is a critical factor in determining the overall effectiveness of the enhancement techniques.
Thermal and evaporative resistance tests, such as those performed using a sweating guarded hotplate, provide valuable data on the fabric's ability to manage heat and moisture simultaneously. These tests simulate the heat and moisture produced by the human body during physical activity, offering insights into the comfort and performance characteristics of the moisture-wicking Kevlar apparel under various environmental conditions.
Additionally, tensile strength and tear resistance tests are essential for evaluating the structural integrity of the enhanced Kevlar fabric. These tests ensure that the moisture-wicking treatments do not compromise the inherent strength and protective properties of Kevlar, which are crucial for many of its applications in protective clothing and equipment.
By employing this comprehensive suite of testing methods, researchers and manufacturers can thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness of moisture-wicking enhancements in Kevlar apparel, ensuring that the final products meet the demanding requirements for both performance and durability in real-world applications.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!