How to Utilize LDAC for Broadcast Audio Solutions?
JUL 4, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
LDAC Technology Overview and Objectives
LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) is a cutting-edge audio coding technology developed by Sony Corporation, designed to deliver high-quality wireless audio transmission. As the demand for superior audio experiences in various broadcast scenarios continues to grow, LDAC has emerged as a promising solution to address the challenges of wireless audio transmission in professional broadcasting environments.
The primary objective of LDAC technology in broadcast audio solutions is to provide near-lossless audio quality while maintaining low latency and efficient bandwidth utilization. This technology aims to bridge the gap between wired and wireless audio transmission, offering broadcasters the flexibility and mobility of wireless systems without compromising on audio fidelity.
LDAC's development can be traced back to the increasing consumer demand for high-resolution audio content and the limitations of existing Bluetooth audio codecs. The technology was first introduced in 2015 and has since undergone continuous improvements to enhance its performance and compatibility across various devices and platforms.
In the context of broadcast audio solutions, LDAC seeks to address several key challenges faced by the industry. These include the need for higher audio quality in wireless transmissions, reduced latency for real-time applications, and improved efficiency in bandwidth usage. By tackling these issues, LDAC aims to enable broadcasters to deliver immersive audio experiences to their audiences while streamlining their production workflows.
The evolution of LDAC technology has been driven by advancements in digital signal processing, data compression algorithms, and wireless communication protocols. Its development has been closely aligned with the broader trends in the audio industry, including the shift towards high-resolution audio formats and the increasing adoption of wireless audio solutions in professional settings.
As the broadcast industry continues to embrace digital transformation, LDAC technology is positioned to play a crucial role in shaping the future of wireless audio transmission. Its potential applications extend beyond traditional broadcasting to include live events, sports coverage, and immersive audio experiences in virtual and augmented reality environments.
The ongoing development of LDAC technology is focused on further improving its performance metrics, expanding its compatibility with a wider range of devices and platforms, and addressing the specific requirements of professional broadcast applications. This includes efforts to reduce power consumption, enhance error resilience, and optimize the codec for various transmission scenarios encountered in broadcast environments.
The primary objective of LDAC technology in broadcast audio solutions is to provide near-lossless audio quality while maintaining low latency and efficient bandwidth utilization. This technology aims to bridge the gap between wired and wireless audio transmission, offering broadcasters the flexibility and mobility of wireless systems without compromising on audio fidelity.
LDAC's development can be traced back to the increasing consumer demand for high-resolution audio content and the limitations of existing Bluetooth audio codecs. The technology was first introduced in 2015 and has since undergone continuous improvements to enhance its performance and compatibility across various devices and platforms.
In the context of broadcast audio solutions, LDAC seeks to address several key challenges faced by the industry. These include the need for higher audio quality in wireless transmissions, reduced latency for real-time applications, and improved efficiency in bandwidth usage. By tackling these issues, LDAC aims to enable broadcasters to deliver immersive audio experiences to their audiences while streamlining their production workflows.
The evolution of LDAC technology has been driven by advancements in digital signal processing, data compression algorithms, and wireless communication protocols. Its development has been closely aligned with the broader trends in the audio industry, including the shift towards high-resolution audio formats and the increasing adoption of wireless audio solutions in professional settings.
As the broadcast industry continues to embrace digital transformation, LDAC technology is positioned to play a crucial role in shaping the future of wireless audio transmission. Its potential applications extend beyond traditional broadcasting to include live events, sports coverage, and immersive audio experiences in virtual and augmented reality environments.
The ongoing development of LDAC technology is focused on further improving its performance metrics, expanding its compatibility with a wider range of devices and platforms, and addressing the specific requirements of professional broadcast applications. This includes efforts to reduce power consumption, enhance error resilience, and optimize the codec for various transmission scenarios encountered in broadcast environments.
Market Analysis for LDAC Broadcast Audio
The LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) technology, developed by Sony, has gained significant traction in the consumer audio market, particularly in high-quality wireless audio transmission. As we analyze its potential in broadcast audio solutions, we observe a growing demand for improved audio quality and efficiency in various broadcasting scenarios.
The broadcast audio market has been evolving rapidly, driven by the increasing consumption of digital content across multiple platforms. Traditional radio broadcasting, television, and emerging digital streaming services are all seeking ways to enhance their audio delivery capabilities. LDAC's ability to transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly with minimal loss presents a compelling value proposition for broadcasters looking to differentiate their offerings and meet the rising expectations of audiophiles and quality-conscious listeners.
In the radio broadcasting segment, the transition from analog to digital has opened new possibilities for audio quality improvement. LDAC could potentially be integrated into digital radio standards, offering a significant upgrade in audio fidelity over existing codecs. This would be particularly attractive for music-focused stations and public broadcasters who prioritize sound quality.
Television broadcasting, especially in the era of 4K and 8K video, is another area where LDAC could make substantial inroads. As viewers invest in high-end home theater systems, there's a growing expectation for audio quality to match the visual experience. LDAC's capacity to transmit 24-bit/96kHz audio could become a key selling point for premium TV content and live event broadcasts.
The burgeoning field of live streaming and internet radio presents another significant market opportunity for LDAC. As bandwidth capabilities improve globally, content creators and platforms are looking for ways to deliver studio-quality audio to their audiences. LDAC's efficient compression algorithm could allow for high-quality audio streaming without overwhelming network resources.
Professional audio applications within the broadcast industry, such as in-studio monitoring and remote production, could also benefit from LDAC technology. The low latency characteristic of LDAC is particularly valuable in these scenarios where timing and synchronization are critical.
However, the adoption of LDAC in broadcast audio faces several challenges. The proprietary nature of the technology may limit its widespread adoption, especially in industries that favor open standards. Additionally, the implementation costs and the need for compatible hardware on the receiving end could slow down market penetration.
Despite these challenges, the potential market size for LDAC in broadcast audio is substantial. As the global broadcast industry continues to grow and evolve, the demand for high-quality audio solutions is expected to increase proportionally. LDAC's unique positioning at the intersection of quality and efficiency makes it a technology worth watching in the broadcast audio landscape.
The broadcast audio market has been evolving rapidly, driven by the increasing consumption of digital content across multiple platforms. Traditional radio broadcasting, television, and emerging digital streaming services are all seeking ways to enhance their audio delivery capabilities. LDAC's ability to transmit high-resolution audio wirelessly with minimal loss presents a compelling value proposition for broadcasters looking to differentiate their offerings and meet the rising expectations of audiophiles and quality-conscious listeners.
In the radio broadcasting segment, the transition from analog to digital has opened new possibilities for audio quality improvement. LDAC could potentially be integrated into digital radio standards, offering a significant upgrade in audio fidelity over existing codecs. This would be particularly attractive for music-focused stations and public broadcasters who prioritize sound quality.
Television broadcasting, especially in the era of 4K and 8K video, is another area where LDAC could make substantial inroads. As viewers invest in high-end home theater systems, there's a growing expectation for audio quality to match the visual experience. LDAC's capacity to transmit 24-bit/96kHz audio could become a key selling point for premium TV content and live event broadcasts.
The burgeoning field of live streaming and internet radio presents another significant market opportunity for LDAC. As bandwidth capabilities improve globally, content creators and platforms are looking for ways to deliver studio-quality audio to their audiences. LDAC's efficient compression algorithm could allow for high-quality audio streaming without overwhelming network resources.
Professional audio applications within the broadcast industry, such as in-studio monitoring and remote production, could also benefit from LDAC technology. The low latency characteristic of LDAC is particularly valuable in these scenarios where timing and synchronization are critical.
However, the adoption of LDAC in broadcast audio faces several challenges. The proprietary nature of the technology may limit its widespread adoption, especially in industries that favor open standards. Additionally, the implementation costs and the need for compatible hardware on the receiving end could slow down market penetration.
Despite these challenges, the potential market size for LDAC in broadcast audio is substantial. As the global broadcast industry continues to grow and evolve, the demand for high-quality audio solutions is expected to increase proportionally. LDAC's unique positioning at the intersection of quality and efficiency makes it a technology worth watching in the broadcast audio landscape.
Current LDAC Implementation Challenges
LDAC, developed by Sony, is a high-resolution audio codec designed for Bluetooth transmission. While it offers superior audio quality compared to standard Bluetooth codecs, implementing LDAC for broadcast audio solutions presents several challenges.
One of the primary obstacles is the limited bandwidth of broadcast channels. LDAC requires a higher bitrate than traditional codecs to deliver its high-quality audio, which can be problematic in broadcast scenarios where bandwidth is often constrained. This limitation may necessitate compromises in audio quality or require innovative solutions to optimize data transmission.
Compatibility issues also pose a significant challenge. LDAC is not universally supported across all devices and platforms, which can lead to inconsistent user experiences in broadcast environments. Broadcasters must consider how to handle devices that do not support LDAC, potentially requiring fallback options or parallel transmission of multiple audio formats.
Latency is another critical concern when implementing LDAC for broadcast audio. While LDAC offers low latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, it may still introduce delays that are unacceptable in live broadcast scenarios, particularly for applications requiring precise audio-video synchronization.
The complexity of LDAC's encoding and decoding processes presents additional challenges. Implementing LDAC in broadcast equipment requires significant computational resources, which may increase hardware costs and power consumption. This complexity can also lead to potential stability issues, especially in 24/7 broadcast operations where reliability is paramount.
Licensing and intellectual property considerations further complicate LDAC implementation. As a proprietary technology, integrating LDAC into broadcast solutions may involve negotiating licensing agreements with Sony, which can be time-consuming and potentially costly for broadcasters.
Adapting LDAC for variable network conditions in broadcast scenarios is also challenging. Broadcast environments often face fluctuating signal strengths and interference, which can impact the stability of high-bitrate audio transmission. Developing robust error correction and adaptive bitrate mechanisms for LDAC in these conditions is crucial but technically demanding.
Lastly, the integration of LDAC with existing broadcast infrastructure and workflows presents significant hurdles. Many broadcasters have established systems and processes optimized for traditional audio codecs. Incorporating LDAC may require substantial modifications to these systems, potentially disrupting operations and necessitating staff retraining.
One of the primary obstacles is the limited bandwidth of broadcast channels. LDAC requires a higher bitrate than traditional codecs to deliver its high-quality audio, which can be problematic in broadcast scenarios where bandwidth is often constrained. This limitation may necessitate compromises in audio quality or require innovative solutions to optimize data transmission.
Compatibility issues also pose a significant challenge. LDAC is not universally supported across all devices and platforms, which can lead to inconsistent user experiences in broadcast environments. Broadcasters must consider how to handle devices that do not support LDAC, potentially requiring fallback options or parallel transmission of multiple audio formats.
Latency is another critical concern when implementing LDAC for broadcast audio. While LDAC offers low latency compared to some other high-quality codecs, it may still introduce delays that are unacceptable in live broadcast scenarios, particularly for applications requiring precise audio-video synchronization.
The complexity of LDAC's encoding and decoding processes presents additional challenges. Implementing LDAC in broadcast equipment requires significant computational resources, which may increase hardware costs and power consumption. This complexity can also lead to potential stability issues, especially in 24/7 broadcast operations where reliability is paramount.
Licensing and intellectual property considerations further complicate LDAC implementation. As a proprietary technology, integrating LDAC into broadcast solutions may involve negotiating licensing agreements with Sony, which can be time-consuming and potentially costly for broadcasters.
Adapting LDAC for variable network conditions in broadcast scenarios is also challenging. Broadcast environments often face fluctuating signal strengths and interference, which can impact the stability of high-bitrate audio transmission. Developing robust error correction and adaptive bitrate mechanisms for LDAC in these conditions is crucial but technically demanding.
Lastly, the integration of LDAC with existing broadcast infrastructure and workflows presents significant hurdles. Many broadcasters have established systems and processes optimized for traditional audio codecs. Incorporating LDAC may require substantial modifications to these systems, potentially disrupting operations and necessitating staff retraining.
Existing LDAC Broadcast Solutions
01 Audio codec technology for wireless devices
LDAC is an advanced audio codec technology developed for high-quality wireless audio transmission. It enables the transmission of high-resolution audio content over Bluetooth connections, offering improved sound quality compared to standard Bluetooth codecs. LDAC supports higher bitrates and a wider frequency range, resulting in a more detailed and immersive audio experience for users of compatible devices.- Audio codec technology for wireless devices: LDAC is an advanced audio codec technology developed for high-quality wireless audio transmission. It enables the transmission of high-resolution audio data over Bluetooth connections, providing improved sound quality compared to standard Bluetooth codecs. LDAC supports higher bitrates and a wider frequency range, resulting in a more detailed and immersive audio experience for users of compatible devices.
- Integration with smart home and IoT devices: LDAC technology is being integrated into various smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) devices to enhance audio streaming capabilities. This integration allows for improved audio quality in wireless speakers, soundbars, and other connected audio devices within smart home ecosystems. The technology enables seamless high-quality audio transmission between different devices, enhancing the overall user experience in smart homes.
- Application in mobile devices and wearables: LDAC is increasingly being implemented in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets, as well as in wearable technology like wireless earbuds and smartwatches. This implementation allows for improved audio quality in portable devices, enhancing the listening experience for music, podcasts, and other audio content. The technology is particularly beneficial for users who prioritize high-fidelity audio in their mobile devices.
- Compatibility with various audio formats: LDAC technology is designed to be compatible with a wide range of audio formats, including high-resolution audio files. This compatibility ensures that users can enjoy high-quality audio across different file types and sources. The codec's ability to handle various audio formats makes it versatile for different applications and user preferences in the audio industry.
- Energy efficiency in audio transmission: LDAC technology incorporates energy-efficient algorithms for audio transmission, balancing high-quality sound with power consumption. This feature is particularly important for battery-powered devices, as it allows for extended playback times without compromising on audio quality. The energy-efficient design of LDAC makes it suitable for use in a wide range of portable and wireless audio devices.
02 Integration with smart home and IoT devices
LDAC technology is being integrated into various smart home and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This integration allows for high-quality audio streaming in connected home environments, enhancing the user experience in applications such as multi-room audio systems, smart speakers, and home entertainment setups. The technology enables seamless audio transmission between different devices within the smart home ecosystem.Expand Specific Solutions03 Automotive audio applications
LDAC is finding applications in automotive audio systems, providing high-quality wireless audio streaming for in-car entertainment. The technology allows for improved audio performance in vehicle infotainment systems, enabling passengers to enjoy high-resolution audio content from their mobile devices through the car's audio system. This application enhances the overall driving and passenger experience.Expand Specific Solutions04 Energy-efficient implementation
Efforts are being made to implement LDAC technology in an energy-efficient manner, particularly for battery-powered devices. This involves optimizing the codec's performance while minimizing power consumption, ensuring that users can enjoy high-quality audio without significantly impacting device battery life. Such implementations are crucial for portable audio devices and wireless headphones.Expand Specific Solutions05 Compatibility and interoperability improvements
Ongoing developments in LDAC technology focus on improving compatibility and interoperability with various devices and platforms. This includes efforts to make LDAC more widely supported across different operating systems, audio equipment manufacturers, and streaming services. These improvements aim to create a more seamless and universal high-quality audio ecosystem for consumers.Expand Specific Solutions
Key LDAC Technology Players
The LDAC (Low Latency Audio Codec) broadcast audio solutions market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for high-quality wireless audio transmission. The market size is expanding as more consumer electronics manufacturers adopt LDAC technology. In terms of technical maturity, LDAC is well-established but still evolving. Key players like Sony, the technology's developer, and Qualcomm are leading the market. Other major companies such as Samsung, LG Electronics, and Harman Becker Automotive Systems are also integrating LDAC into their products, indicating its growing acceptance in the industry. The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of established electronics giants and specialized audio technology firms, all vying to enhance their product offerings with LDAC capabilities.
QUALCOMM, Inc.
Technical Solution: Qualcomm has developed a solution that incorporates LDAC into their Bluetooth audio SoCs, particularly in their QCC series. Their approach focuses on integrating LDAC decoding capabilities into their chips, allowing for seamless implementation in various audio devices. Qualcomm's solution includes optimizations for power efficiency, crucial for portable devices using LDAC[4]. They have also implemented LDAC alongside their own aptX codec, providing manufacturers with flexible options for high-quality audio transmission. Qualcomm's implementation supports LDAC's variable bit rate feature, allowing devices to adjust audio quality based on connection stability and battery life considerations[5].
Strengths: Wide adoption in mobile and audio devices, power-efficient implementation, integration with other audio technologies. Weaknesses: Dependent on Sony's LDAC licensing, potential competition with Qualcomm's own aptX codec.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Technical Solution: Samsung has integrated LDAC support into their Galaxy series smartphones and various audio products, including wireless earbuds and speakers. Their approach to utilizing LDAC for broadcast audio solutions involves optimizing the codec for their Exynos processors, ensuring efficient decoding and minimal battery drain[6]. Samsung has also developed a seamless pairing system that automatically detects and enables LDAC when compatible devices are connected. For broadcast scenarios, Samsung has implemented multi-device connectivity, allowing users to stream high-quality audio to multiple LDAC-enabled devices simultaneously[7]. Additionally, Samsung has worked on enhancing the user interface to make LDAC settings more accessible and user-friendly in their devices.
Strengths: Wide ecosystem of compatible devices, optimized performance on Samsung hardware, user-friendly implementation. Weaknesses: Limited to Samsung's ecosystem for full feature set, potential conflicts with Samsung's own audio technologies.
LDAC Core Patents and Innovations
Current-measuring device
PatentActiveUS11881926B2
Innovation
- A redundant communication link is established using both VoIP and analogue communication signals, with an evaluation unit deciding which signal to forward based on quality criteria, ensuring secure and clear communication by utilizing existing IP-based aeronautical data networks and future communication standards like LTE and 5G.
Real-time audio interaction method of multi-Bluetooth audio equipment
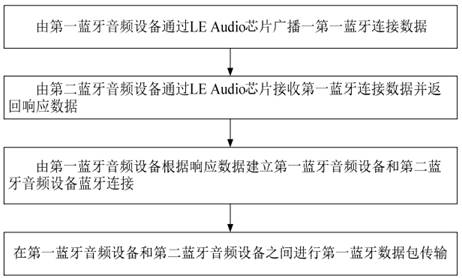
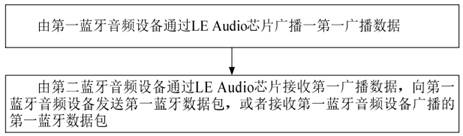
PatentActiveCN112135285A
Innovation
- It adopts LE Audio chip and uses low-complexity LC3 encoder and decoder to decompress, encode, decode and transmit audio data, reduce the transmission delay of audio data, and realize multiple independent audio streaming transmission. It supports Bluetooth broadcast function to ensure Real-time interaction of audio data.
LDAC Licensing and Adoption Strategies
LDAC licensing and adoption strategies play a crucial role in the widespread implementation of this advanced audio codec technology in broadcast solutions. Sony, the developer of LDAC, has established a licensing program that allows manufacturers to integrate LDAC into their products. This program typically involves licensing fees and compliance with technical specifications to ensure consistent performance across devices.
For broadcast audio solutions, adopting LDAC requires careful consideration of licensing terms and costs. Manufacturers must evaluate the potential benefits of improved audio quality against the associated licensing expenses. The licensing strategy often includes tiered options, allowing for different levels of integration based on the specific needs of broadcast equipment manufacturers.
To facilitate adoption, Sony has implemented a certification process for LDAC-enabled devices. This certification ensures that products meet the required technical standards and can deliver the promised audio quality. For broadcast equipment manufacturers, obtaining this certification can be a key differentiator in the market, demonstrating their commitment to high-quality audio transmission.
Collaboration with industry partners is another essential aspect of LDAC adoption strategies. Sony has been actively working with various audio equipment manufacturers, chipset providers, and software developers to expand the LDAC ecosystem. This collaborative approach helps in creating a more diverse range of LDAC-compatible products and solutions for the broadcast industry.
Education and awareness campaigns form an integral part of the adoption strategy. Sony and its partners often conduct workshops, webinars, and demonstrations to showcase the benefits of LDAC technology in broadcast applications. These initiatives aim to educate industry professionals about the advantages of LDAC over traditional audio codecs, particularly in scenarios where high-quality wireless audio transmission is critical.
For broadcast solution providers, a phased approach to LDAC adoption can be beneficial. This may involve initially incorporating LDAC into high-end products or specific broadcast segments where audio quality is paramount. As the technology gains traction and becomes more cost-effective, it can be gradually integrated into a broader range of broadcast equipment.
Lastly, staying informed about updates to LDAC technology and licensing terms is crucial for long-term adoption strategies. As the technology evolves, new features or improvements may be introduced, potentially affecting licensing agreements and implementation requirements. Broadcast solution providers must maintain open communication channels with Sony and stay agile in their approach to fully leverage the benefits of LDAC in their audio solutions.
For broadcast audio solutions, adopting LDAC requires careful consideration of licensing terms and costs. Manufacturers must evaluate the potential benefits of improved audio quality against the associated licensing expenses. The licensing strategy often includes tiered options, allowing for different levels of integration based on the specific needs of broadcast equipment manufacturers.
To facilitate adoption, Sony has implemented a certification process for LDAC-enabled devices. This certification ensures that products meet the required technical standards and can deliver the promised audio quality. For broadcast equipment manufacturers, obtaining this certification can be a key differentiator in the market, demonstrating their commitment to high-quality audio transmission.
Collaboration with industry partners is another essential aspect of LDAC adoption strategies. Sony has been actively working with various audio equipment manufacturers, chipset providers, and software developers to expand the LDAC ecosystem. This collaborative approach helps in creating a more diverse range of LDAC-compatible products and solutions for the broadcast industry.
Education and awareness campaigns form an integral part of the adoption strategy. Sony and its partners often conduct workshops, webinars, and demonstrations to showcase the benefits of LDAC technology in broadcast applications. These initiatives aim to educate industry professionals about the advantages of LDAC over traditional audio codecs, particularly in scenarios where high-quality wireless audio transmission is critical.
For broadcast solution providers, a phased approach to LDAC adoption can be beneficial. This may involve initially incorporating LDAC into high-end products or specific broadcast segments where audio quality is paramount. As the technology gains traction and becomes more cost-effective, it can be gradually integrated into a broader range of broadcast equipment.
Lastly, staying informed about updates to LDAC technology and licensing terms is crucial for long-term adoption strategies. As the technology evolves, new features or improvements may be introduced, potentially affecting licensing agreements and implementation requirements. Broadcast solution providers must maintain open communication channels with Sony and stay agile in their approach to fully leverage the benefits of LDAC in their audio solutions.
LDAC Interoperability Standards
LDAC interoperability standards play a crucial role in ensuring seamless integration and compatibility of LDAC technology across various broadcast audio solutions. These standards define the protocols, interfaces, and specifications necessary for different devices and systems to effectively communicate and operate using LDAC codec.
One of the key aspects of LDAC interoperability standards is the implementation of a unified communication protocol. This protocol establishes a common language for devices to negotiate and establish LDAC connections, ensuring that transmitters and receivers can effectively communicate regardless of manufacturer or device type. The standardized protocol includes handshake procedures, connection parameters, and error handling mechanisms.
Another important component of LDAC interoperability standards is the definition of audio format specifications. These specifications outline the supported audio formats, sampling rates, and bit depths that can be transmitted using LDAC. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can ensure that their devices can encode and decode LDAC streams consistently, maintaining high-quality audio reproduction across different platforms.
LDAC interoperability standards also address the issue of metadata handling. They define how additional information, such as track titles, artist names, and album artwork, should be embedded and transmitted alongside the audio stream. This standardization enables consistent display and management of metadata across various broadcast audio solutions, enhancing the user experience.
Furthermore, the standards include provisions for adaptive bitrate streaming. This feature allows LDAC-enabled devices to dynamically adjust the audio quality based on available bandwidth and network conditions. The interoperability standards define the mechanisms for negotiating and switching between different bitrates, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted listening experience in varying network environments.
Security and encryption protocols are also integral to LDAC interoperability standards. These protocols define the methods for securing LDAC audio streams, protecting content from unauthorized access or tampering. By implementing standardized security measures, broadcast audio solutions can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of transmitted audio content.
Lastly, LDAC interoperability standards address compatibility with existing audio systems and protocols. They provide guidelines for integrating LDAC technology with established broadcast audio standards, such as AES67 and RAVENNA, facilitating seamless adoption in professional audio environments. This backward compatibility ensures that LDAC can be effectively utilized in a wide range of broadcast scenarios without disrupting existing workflows.
One of the key aspects of LDAC interoperability standards is the implementation of a unified communication protocol. This protocol establishes a common language for devices to negotiate and establish LDAC connections, ensuring that transmitters and receivers can effectively communicate regardless of manufacturer or device type. The standardized protocol includes handshake procedures, connection parameters, and error handling mechanisms.
Another important component of LDAC interoperability standards is the definition of audio format specifications. These specifications outline the supported audio formats, sampling rates, and bit depths that can be transmitted using LDAC. By adhering to these standards, manufacturers can ensure that their devices can encode and decode LDAC streams consistently, maintaining high-quality audio reproduction across different platforms.
LDAC interoperability standards also address the issue of metadata handling. They define how additional information, such as track titles, artist names, and album artwork, should be embedded and transmitted alongside the audio stream. This standardization enables consistent display and management of metadata across various broadcast audio solutions, enhancing the user experience.
Furthermore, the standards include provisions for adaptive bitrate streaming. This feature allows LDAC-enabled devices to dynamically adjust the audio quality based on available bandwidth and network conditions. The interoperability standards define the mechanisms for negotiating and switching between different bitrates, ensuring a smooth and uninterrupted listening experience in varying network environments.
Security and encryption protocols are also integral to LDAC interoperability standards. These protocols define the methods for securing LDAC audio streams, protecting content from unauthorized access or tampering. By implementing standardized security measures, broadcast audio solutions can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of transmitted audio content.
Lastly, LDAC interoperability standards address compatibility with existing audio systems and protocols. They provide guidelines for integrating LDAC technology with established broadcast audio standards, such as AES67 and RAVENNA, facilitating seamless adoption in professional audio environments. This backward compatibility ensures that LDAC can be effectively utilized in a wide range of broadcast scenarios without disrupting existing workflows.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!