Kevlar’s Contribution to Smart Infrastructure Solutions
JUL 10, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Kevlar in Smart Infrastructure: Background and Objectives
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s, has traditionally been associated with applications in protective gear and aerospace industries. However, its unique properties have recently garnered attention in the realm of smart infrastructure solutions. This technological shift represents a significant evolution in the material's application, aligning with the growing demand for innovative and sustainable infrastructure development.
The journey of Kevlar in smart infrastructure began with the recognition of its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. These characteristics make it an ideal candidate for reinforcing and enhancing various components of modern infrastructure systems. As urban populations continue to grow and climate change poses increasing challenges, the need for resilient and adaptive infrastructure has become paramount.
The primary objective of incorporating Kevlar into smart infrastructure solutions is to create more robust, efficient, and responsive systems that can withstand extreme conditions while providing enhanced functionality. This includes improving the structural integrity of buildings, bridges, and roads, as well as integrating smart sensing capabilities for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
One of the key goals is to leverage Kevlar's properties to develop self-healing materials that can automatically repair minor damages, thereby extending the lifespan of infrastructure and reducing maintenance costs. Additionally, researchers aim to exploit Kevlar's potential in creating flexible and adaptive structures that can respond to environmental changes or seismic activities, enhancing overall safety and resilience.
The integration of Kevlar into smart infrastructure also aligns with sustainability objectives. By improving the durability and performance of infrastructure components, the use of Kevlar can potentially reduce the need for frequent replacements and repairs, thereby minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact over the long term.
Furthermore, the development of Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions seeks to address the growing need for intelligent urban management systems. This includes the creation of sensor-embedded materials that can provide real-time data on structural health, traffic patterns, and environmental conditions, enabling more efficient and proactive infrastructure management.
As research in this field progresses, the ultimate aim is to establish Kevlar as a cornerstone material in the next generation of smart cities. This vision encompasses not only enhancing the physical robustness of urban structures but also contributing to the creation of interconnected, responsive, and sustainable urban environments that can adapt to the evolving needs of their inhabitants.
The journey of Kevlar in smart infrastructure began with the recognition of its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. These characteristics make it an ideal candidate for reinforcing and enhancing various components of modern infrastructure systems. As urban populations continue to grow and climate change poses increasing challenges, the need for resilient and adaptive infrastructure has become paramount.
The primary objective of incorporating Kevlar into smart infrastructure solutions is to create more robust, efficient, and responsive systems that can withstand extreme conditions while providing enhanced functionality. This includes improving the structural integrity of buildings, bridges, and roads, as well as integrating smart sensing capabilities for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
One of the key goals is to leverage Kevlar's properties to develop self-healing materials that can automatically repair minor damages, thereby extending the lifespan of infrastructure and reducing maintenance costs. Additionally, researchers aim to exploit Kevlar's potential in creating flexible and adaptive structures that can respond to environmental changes or seismic activities, enhancing overall safety and resilience.
The integration of Kevlar into smart infrastructure also aligns with sustainability objectives. By improving the durability and performance of infrastructure components, the use of Kevlar can potentially reduce the need for frequent replacements and repairs, thereby minimizing resource consumption and environmental impact over the long term.
Furthermore, the development of Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions seeks to address the growing need for intelligent urban management systems. This includes the creation of sensor-embedded materials that can provide real-time data on structural health, traffic patterns, and environmental conditions, enabling more efficient and proactive infrastructure management.
As research in this field progresses, the ultimate aim is to establish Kevlar as a cornerstone material in the next generation of smart cities. This vision encompasses not only enhancing the physical robustness of urban structures but also contributing to the creation of interconnected, responsive, and sustainable urban environments that can adapt to the evolving needs of their inhabitants.
Market Analysis for Kevlar-Enhanced Smart Infrastructure
The market for Kevlar-enhanced smart infrastructure solutions is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for durable, lightweight, and intelligent construction materials. Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont, has found its way into various applications beyond its traditional use in personal protective equipment and aerospace industries. In the context of smart infrastructure, Kevlar's unique properties offer substantial benefits in terms of structural reinforcement, sensor integration, and overall system performance.
The global smart infrastructure market is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) that outpaces many other sectors. This growth is fueled by urbanization trends, the need for sustainable development, and the integration of digital technologies in physical infrastructure. Kevlar-enhanced solutions are positioned to capture a significant portion of this market, particularly in areas where high strength-to-weight ratio and durability are critical factors.
Key market segments for Kevlar-enhanced smart infrastructure include transportation, energy, water management, and building construction. In transportation, Kevlar is being utilized in smart road systems, where its durability and ability to integrate with sensors make it ideal for creating long-lasting, responsive road surfaces. The energy sector is exploring Kevlar-enhanced materials for smart grid components and renewable energy installations, leveraging its resistance to environmental factors and potential for embedding smart technologies.
Water management systems are another promising area, with Kevlar-reinforced pipes and structures offering improved longevity and the capability to incorporate leak detection and flow monitoring sensors. In building construction, Kevlar-enhanced materials are being developed for smart facades, structural health monitoring systems, and advanced insulation solutions that can adapt to environmental conditions.
The market demand for these solutions is driven by several factors, including the need for infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, the push for more energy-efficient buildings and systems, and the desire for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. Governments and private sector entities are increasingly recognizing the long-term cost benefits of investing in smart, durable infrastructure solutions, which is creating a favorable market environment for Kevlar-enhanced products.
However, challenges exist in terms of initial cost considerations and the need for specialized knowledge in working with advanced materials like Kevlar. The market is also influenced by regulatory frameworks and standards for smart infrastructure, which are still evolving in many regions. Despite these challenges, the overall trend indicates a growing acceptance and demand for Kevlar-enhanced smart infrastructure solutions, with potential for significant market expansion in the coming years.
The global smart infrastructure market is projected to reach substantial value in the coming years, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) that outpaces many other sectors. This growth is fueled by urbanization trends, the need for sustainable development, and the integration of digital technologies in physical infrastructure. Kevlar-enhanced solutions are positioned to capture a significant portion of this market, particularly in areas where high strength-to-weight ratio and durability are critical factors.
Key market segments for Kevlar-enhanced smart infrastructure include transportation, energy, water management, and building construction. In transportation, Kevlar is being utilized in smart road systems, where its durability and ability to integrate with sensors make it ideal for creating long-lasting, responsive road surfaces. The energy sector is exploring Kevlar-enhanced materials for smart grid components and renewable energy installations, leveraging its resistance to environmental factors and potential for embedding smart technologies.
Water management systems are another promising area, with Kevlar-reinforced pipes and structures offering improved longevity and the capability to incorporate leak detection and flow monitoring sensors. In building construction, Kevlar-enhanced materials are being developed for smart facades, structural health monitoring systems, and advanced insulation solutions that can adapt to environmental conditions.
The market demand for these solutions is driven by several factors, including the need for infrastructure that can withstand extreme weather events, the push for more energy-efficient buildings and systems, and the desire for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities. Governments and private sector entities are increasingly recognizing the long-term cost benefits of investing in smart, durable infrastructure solutions, which is creating a favorable market environment for Kevlar-enhanced products.
However, challenges exist in terms of initial cost considerations and the need for specialized knowledge in working with advanced materials like Kevlar. The market is also influenced by regulatory frameworks and standards for smart infrastructure, which are still evolving in many regions. Despite these challenges, the overall trend indicates a growing acceptance and demand for Kevlar-enhanced smart infrastructure solutions, with potential for significant market expansion in the coming years.
Current Challenges in Kevlar-Based Smart Infrastructure
Despite the remarkable properties of Kevlar in enhancing infrastructure resilience, several challenges persist in its widespread adoption for smart infrastructure solutions. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost associated with Kevlar production and implementation. The complex manufacturing process and specialized equipment required for Kevlar-based materials contribute to elevated expenses, limiting its use in large-scale infrastructure projects where cost-effectiveness is crucial.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of smart technologies with Kevlar-reinforced structures. While Kevlar provides excellent mechanical properties, incorporating sensors, data transmission systems, and other smart components into Kevlar-based materials without compromising their structural integrity remains a technical hurdle. Engineers must develop innovative methods to seamlessly embed smart technologies within Kevlar composites while maintaining their strength and durability.
The long-term durability and performance of Kevlar in diverse environmental conditions also present ongoing challenges. Although Kevlar exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to many forms of degradation, its behavior under prolonged exposure to UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures in various infrastructure applications requires further investigation. Ensuring the longevity of Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions in harsh environments is critical for their widespread adoption.
Moreover, the limited recyclability of Kevlar poses environmental concerns. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in infrastructure development, the difficulty in recycling Kevlar-based materials at the end of their lifecycle presents a challenge. Developing eco-friendly disposal or recycling methods for Kevlar composites is essential to align with circular economy principles and reduce the environmental impact of smart infrastructure solutions.
The need for specialized skills and knowledge in working with Kevlar-based materials also presents a challenge in the construction and maintenance of smart infrastructure. The unique properties of Kevlar require specific handling, installation, and repair techniques that may not be widely available among construction professionals. This skills gap necessitates extensive training and education programs to ensure proper implementation and maintenance of Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of advanced materials like Kevlar in infrastructure projects remains complex and often unclear. The lack of standardized guidelines and certifications for Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions can hinder their adoption in conservative industries such as civil engineering and construction. Developing comprehensive standards and obtaining necessary approvals from regulatory bodies is crucial for the widespread acceptance of Kevlar in smart infrastructure applications.
Another significant challenge lies in the integration of smart technologies with Kevlar-reinforced structures. While Kevlar provides excellent mechanical properties, incorporating sensors, data transmission systems, and other smart components into Kevlar-based materials without compromising their structural integrity remains a technical hurdle. Engineers must develop innovative methods to seamlessly embed smart technologies within Kevlar composites while maintaining their strength and durability.
The long-term durability and performance of Kevlar in diverse environmental conditions also present ongoing challenges. Although Kevlar exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to many forms of degradation, its behavior under prolonged exposure to UV radiation, moisture, and extreme temperatures in various infrastructure applications requires further investigation. Ensuring the longevity of Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions in harsh environments is critical for their widespread adoption.
Moreover, the limited recyclability of Kevlar poses environmental concerns. As sustainability becomes increasingly important in infrastructure development, the difficulty in recycling Kevlar-based materials at the end of their lifecycle presents a challenge. Developing eco-friendly disposal or recycling methods for Kevlar composites is essential to align with circular economy principles and reduce the environmental impact of smart infrastructure solutions.
The need for specialized skills and knowledge in working with Kevlar-based materials also presents a challenge in the construction and maintenance of smart infrastructure. The unique properties of Kevlar require specific handling, installation, and repair techniques that may not be widely available among construction professionals. This skills gap necessitates extensive training and education programs to ensure proper implementation and maintenance of Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions.
Lastly, the regulatory landscape surrounding the use of advanced materials like Kevlar in infrastructure projects remains complex and often unclear. The lack of standardized guidelines and certifications for Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions can hinder their adoption in conservative industries such as civil engineering and construction. Developing comprehensive standards and obtaining necessary approvals from regulatory bodies is crucial for the widespread acceptance of Kevlar in smart infrastructure applications.
Existing Kevlar-Based Smart Infrastructure Solutions
01 Kevlar-reinforced composite materials
Kevlar fibers are used to reinforce various composite materials, enhancing their strength, durability, and impact resistance. These composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, and protective equipment industries.- Kevlar-reinforced composite materials: Kevlar fibers are used to reinforce various composite materials, enhancing their strength, durability, and impact resistance. These composites find applications in aerospace, automotive, and protective equipment industries.
- Kevlar in protective gear and clothing: Kevlar is utilized in the manufacture of protective gear and clothing, such as bulletproof vests, helmets, and cut-resistant gloves. Its high tensile strength and lightweight properties make it ideal for personal protection equipment.
- Kevlar-based fire-resistant materials: Kevlar is incorporated into fire-resistant materials and fabrics, providing enhanced thermal protection and flame retardancy. These materials are used in firefighting equipment, industrial safety gear, and high-temperature applications.
- Kevlar in automotive components: Kevlar is used in various automotive components to reduce weight while maintaining strength and durability. Applications include reinforced tires, brake pads, and engine components, improving overall vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- Kevlar in sports equipment: Kevlar is incorporated into sports equipment to enhance performance and durability. It is used in products such as tennis rackets, bicycle frames, and kayaks, providing strength and lightweight properties for improved athletic performance.
02 Kevlar in protective gear and clothing
Kevlar is utilized in the manufacture of protective gear and clothing, including bulletproof vests, helmets, and cut-resistant gloves. Its high tensile strength and lightweight properties make it ideal for personal protection equipment.Expand Specific Solutions03 Kevlar-based fire-resistant materials
Kevlar is incorporated into fire-resistant materials and fabrics, providing enhanced thermal protection and flame retardancy. These materials are used in firefighting equipment, industrial safety gear, and high-temperature applications.Expand Specific Solutions04 Kevlar in automotive applications
Kevlar is used in various automotive components, such as tires, belts, and hoses, to improve their strength, durability, and heat resistance. It also finds applications in lightweight body panels and structural reinforcements for vehicles.Expand Specific Solutions05 Kevlar in aerospace and marine applications
Kevlar is employed in aerospace and marine industries for its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to environmental factors. It is used in aircraft components, spacecraft structures, and boat hulls to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity.Expand Specific Solutions
Key Players in Kevlar and Smart Infrastructure Industry
The Kevlar-based smart infrastructure solutions market is in a growth phase, driven by increasing demand for durable and intelligent construction materials. The global market size is expanding, with projections indicating significant growth potential in the coming years. Technologically, the field is advancing rapidly, with companies like Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson and NEC Asia Pacific Pte Ltd. leading innovations in integrating Kevlar with smart technologies. Traditional infrastructure players such as Colas SA and China Oil & Gas Pipeline Network Corp. are also adapting to incorporate these advanced materials, while research institutions like Indian Institutes of Technology and Lawrence Livermore National Security LLC are pushing the boundaries of Kevlar applications in smart infrastructure.
Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
Technical Solution: Ericsson has incorporated Kevlar into its smart infrastructure solutions for 5G and IoT networks. The company has developed Kevlar-reinforced antenna systems that offer improved durability and weather resistance for outdoor deployments[8]. These antennas integrate sensors that leverage the Kevlar components to monitor structural health and environmental conditions, enabling predictive maintenance and optimized performance[10]. Ericsson's smart infrastructure approach also includes Kevlar-enhanced protective enclosures for sensitive network equipment, which incorporate smart monitoring capabilities to ensure the integrity and security of critical infrastructure components[12].
Strengths: Enhanced durability of network components, integrated health monitoring, and improved security for critical infrastructure. Weaknesses: Potential increase in component costs and challenges in retrofitting existing network infrastructure.
AFL Telecommunications LLC
Technical Solution: AFL has leveraged Kevlar's properties in developing smart infrastructure solutions for the telecommunications industry. Their approach involves incorporating Kevlar strength members into fiber optic cables, enhancing both the physical protection and data transmission capabilities of network infrastructure[7]. AFL's Kevlar-reinforced cables are designed to withstand extreme environmental conditions and provide superior tensile strength, making them ideal for challenging installation scenarios such as long-span aerial deployments or underground conduits[9]. The company has also developed smart monitoring systems that utilize the Kevlar components to detect and locate physical disturbances along the cable route, enhancing network security and maintenance efficiency[11].
Strengths: Enhanced physical protection of network infrastructure, improved data transmission reliability, and integrated monitoring capabilities. Weaknesses: Potentially higher production costs and limited applicability in certain legacy network upgrades.
Innovative Kevlar Technologies for Infrastructure
Cognitive interoperable inquisitive source agnostic infrastructure omni-specifics intelligence process and system for collaborative infra super diligence
PatentPendingIN202141022044A
Innovation
- A unified, context-aware IoT-based analytics platform using advanced Machine Learning models and cognitive intelligence to process diverse data sources, provide prescriptive advisories, and automate workflows across IT/OT/IOT domains, enabling cross-disciplinary decision support and infrastructure optimization.
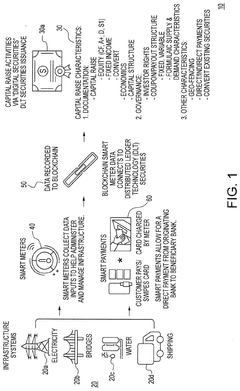
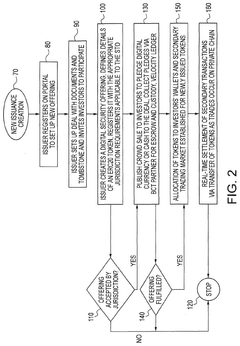
Securitization of assets utilizing distributed-ledgers & smart meters and a user permission framework for information flow
PatentPendingUS20250069144A1
Innovation
- The use of blockchain distributed ledgers in conjunction with smart meters and smart contracts to facilitate the issuance, administration, and management of digital securities for infrastructure projects, providing transparent and predictable returns to investors and efficient capital formation.
Environmental Impact of Kevlar in Infrastructure
The integration of Kevlar into smart infrastructure solutions presents both opportunities and challenges from an environmental perspective. As a high-performance synthetic fiber, Kevlar offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and durability, potentially reducing the overall material consumption in infrastructure projects. This reduction in material usage can lead to decreased energy consumption during manufacturing and transportation processes, thereby lowering the carbon footprint associated with infrastructure development.
However, the production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical-based raw materials, which raises concerns about its environmental impact. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of energy and generates chemical waste, necessitating careful management and disposal practices. Despite these challenges, advancements in production technologies and waste management systems have been implemented to mitigate these environmental concerns.
In the context of smart infrastructure, Kevlar's durability and resistance to environmental degradation contribute to extended lifespans of structures and components. This longevity reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, ultimately decreasing the long-term environmental impact associated with maintenance activities. Additionally, Kevlar's lightweight nature allows for more efficient transportation and installation of infrastructure elements, further reducing fuel consumption and emissions during the construction phase.
The use of Kevlar in smart infrastructure also enables the development of more resilient and adaptive systems. For instance, Kevlar-reinforced sensors and monitoring devices can withstand harsh environmental conditions, providing reliable data for optimizing infrastructure performance and resource utilization. This enhanced monitoring capability contributes to more efficient energy management and reduced waste in smart city applications.
Furthermore, Kevlar's potential in enhancing the recyclability and end-of-life management of infrastructure components is an area of ongoing research. While the material itself poses challenges in terms of recyclability, innovative approaches are being explored to repurpose and recycle Kevlar-containing composites, aligning with circular economy principles and reducing the environmental impact of infrastructure decommissioning.
As smart infrastructure solutions continue to evolve, the environmental impact of Kevlar integration must be carefully balanced against its performance benefits. Ongoing efforts in sustainable manufacturing practices, lifecycle assessment, and innovative recycling technologies are crucial in maximizing the positive environmental contributions of Kevlar while minimizing its negative impacts in the context of smart infrastructure development.
However, the production of Kevlar involves energy-intensive processes and the use of petrochemical-based raw materials, which raises concerns about its environmental impact. The manufacturing process requires significant amounts of energy and generates chemical waste, necessitating careful management and disposal practices. Despite these challenges, advancements in production technologies and waste management systems have been implemented to mitigate these environmental concerns.
In the context of smart infrastructure, Kevlar's durability and resistance to environmental degradation contribute to extended lifespans of structures and components. This longevity reduces the frequency of repairs and replacements, ultimately decreasing the long-term environmental impact associated with maintenance activities. Additionally, Kevlar's lightweight nature allows for more efficient transportation and installation of infrastructure elements, further reducing fuel consumption and emissions during the construction phase.
The use of Kevlar in smart infrastructure also enables the development of more resilient and adaptive systems. For instance, Kevlar-reinforced sensors and monitoring devices can withstand harsh environmental conditions, providing reliable data for optimizing infrastructure performance and resource utilization. This enhanced monitoring capability contributes to more efficient energy management and reduced waste in smart city applications.
Furthermore, Kevlar's potential in enhancing the recyclability and end-of-life management of infrastructure components is an area of ongoing research. While the material itself poses challenges in terms of recyclability, innovative approaches are being explored to repurpose and recycle Kevlar-containing composites, aligning with circular economy principles and reducing the environmental impact of infrastructure decommissioning.
As smart infrastructure solutions continue to evolve, the environmental impact of Kevlar integration must be carefully balanced against its performance benefits. Ongoing efforts in sustainable manufacturing practices, lifecycle assessment, and innovative recycling technologies are crucial in maximizing the positive environmental contributions of Kevlar while minimizing its negative impacts in the context of smart infrastructure development.
Regulatory Framework for Advanced Materials in Construction
The regulatory framework for advanced materials in construction, particularly concerning Kevlar's integration into smart infrastructure solutions, is a complex and evolving landscape. Governments and industry bodies worldwide are working to establish comprehensive guidelines that balance innovation with safety and sustainability.
In the United States, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) has been at the forefront of developing standards for the use of advanced materials in infrastructure. They have issued guidelines for the use of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites, which include Kevlar-based materials, in bridge construction and rehabilitation. These guidelines address design considerations, material specifications, and quality control measures to ensure the long-term performance and safety of structures incorporating these advanced materials.
The European Union has taken a similar approach through the Construction Products Regulation (CPR), which sets harmonized rules for the marketing of construction products across EU member states. This regulation includes provisions for innovative materials like Kevlar-based composites, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with essential requirements related to mechanical strength, fire safety, and environmental impact.
In Japan, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) has developed specific guidelines for the use of advanced composite materials in infrastructure projects. These guidelines cover the design, construction, and maintenance of structures incorporating materials like Kevlar, with a focus on seismic resilience and durability in harsh environmental conditions.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and ASTM International, have also played crucial roles in developing global standards for advanced materials in construction. ISO 14484, for instance, provides guidelines for the design and construction of FRP-reinforced concrete structures, which can include Kevlar-based reinforcements.
As smart infrastructure solutions continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges. For example, the integration of sensors and data collection systems into Kevlar-reinforced structures has raised questions about data privacy and cybersecurity. Regulatory bodies are now working to develop standards that address these concerns while promoting the benefits of smart infrastructure.
The regulatory landscape also reflects a growing emphasis on sustainability and lifecycle assessment. Many jurisdictions now require environmental impact assessments for construction projects using advanced materials, considering factors such as energy consumption during production, potential for recycling, and long-term environmental effects.
As Kevlar and other advanced materials become more prevalent in smart infrastructure solutions, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve. This ongoing development aims to strike a balance between fostering innovation, ensuring public safety, and promoting sustainable construction practices.
In the United States, the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) has been at the forefront of developing standards for the use of advanced materials in infrastructure. They have issued guidelines for the use of fiber-reinforced polymer (FRP) composites, which include Kevlar-based materials, in bridge construction and rehabilitation. These guidelines address design considerations, material specifications, and quality control measures to ensure the long-term performance and safety of structures incorporating these advanced materials.
The European Union has taken a similar approach through the Construction Products Regulation (CPR), which sets harmonized rules for the marketing of construction products across EU member states. This regulation includes provisions for innovative materials like Kevlar-based composites, requiring manufacturers to demonstrate compliance with essential requirements related to mechanical strength, fire safety, and environmental impact.
In Japan, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) has developed specific guidelines for the use of advanced composite materials in infrastructure projects. These guidelines cover the design, construction, and maintenance of structures incorporating materials like Kevlar, with a focus on seismic resilience and durability in harsh environmental conditions.
International standards organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and ASTM International, have also played crucial roles in developing global standards for advanced materials in construction. ISO 14484, for instance, provides guidelines for the design and construction of FRP-reinforced concrete structures, which can include Kevlar-based reinforcements.
As smart infrastructure solutions continue to evolve, regulatory frameworks are adapting to address new challenges. For example, the integration of sensors and data collection systems into Kevlar-reinforced structures has raised questions about data privacy and cybersecurity. Regulatory bodies are now working to develop standards that address these concerns while promoting the benefits of smart infrastructure.
The regulatory landscape also reflects a growing emphasis on sustainability and lifecycle assessment. Many jurisdictions now require environmental impact assessments for construction projects using advanced materials, considering factors such as energy consumption during production, potential for recycling, and long-term environmental effects.
As Kevlar and other advanced materials become more prevalent in smart infrastructure solutions, it is likely that regulatory frameworks will continue to evolve. This ongoing development aims to strike a balance between fostering innovation, ensuring public safety, and promoting sustainable construction practices.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!