Optimizing Chiller Operation in Variable Climate Zones
JAN 23, 20269 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chiller Tech Evolution and Climate Adaptation Goals
Chiller technology has undergone substantial transformation since its inception in the early 20th century, evolving from basic mechanical refrigeration systems to sophisticated, digitally controlled equipment capable of responding to dynamic environmental conditions. The earliest chillers relied on simple vapor-compression cycles with limited efficiency and manual operation. By the mid-20th century, advancements in compressor technology and refrigerant chemistry significantly improved performance metrics, though these systems remained largely static in their operational parameters.
The emergence of variable-speed drive technology in the 1980s marked a pivotal shift, enabling chillers to modulate capacity in response to cooling load variations. This development laid the groundwork for adaptive operation strategies that would become essential for climate-responsive systems. Subsequent decades witnessed the integration of microprocessor-based controls, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustment of operational parameters based on ambient conditions.
Contemporary chiller systems represent a convergence of multiple technological streams, including advanced heat exchanger designs, magnetic bearing compressors, and intelligent control algorithms. The integration of IoT sensors and machine learning capabilities has enabled predictive maintenance and optimization strategies that were previously unattainable. These systems can now process vast amounts of climate data to anticipate cooling demands and adjust operations proactively.
The primary technical objective driving current research focuses on achieving optimal energy efficiency across diverse and fluctuating climate conditions. Variable climate zones present unique challenges, as chillers must maintain consistent performance despite significant temperature swings, humidity variations, and seasonal transitions. Traditional fixed-parameter systems often operate inefficiently under such conditions, consuming excessive energy during partial-load scenarios or mild weather periods.
Key goals include developing adaptive control strategies that can seamlessly transition between operational modes based on real-time climate data, minimizing energy consumption while maintaining thermal comfort requirements. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on refrigerant selection and system design that can accommodate extreme weather events becoming more frequent due to climate change. The ultimate aim is to create resilient, self-optimizing chiller systems that deliver consistent performance and maximum efficiency regardless of external climate variability, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact across diverse geographical deployments.
The emergence of variable-speed drive technology in the 1980s marked a pivotal shift, enabling chillers to modulate capacity in response to cooling load variations. This development laid the groundwork for adaptive operation strategies that would become essential for climate-responsive systems. Subsequent decades witnessed the integration of microprocessor-based controls, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustment of operational parameters based on ambient conditions.
Contemporary chiller systems represent a convergence of multiple technological streams, including advanced heat exchanger designs, magnetic bearing compressors, and intelligent control algorithms. The integration of IoT sensors and machine learning capabilities has enabled predictive maintenance and optimization strategies that were previously unattainable. These systems can now process vast amounts of climate data to anticipate cooling demands and adjust operations proactively.
The primary technical objective driving current research focuses on achieving optimal energy efficiency across diverse and fluctuating climate conditions. Variable climate zones present unique challenges, as chillers must maintain consistent performance despite significant temperature swings, humidity variations, and seasonal transitions. Traditional fixed-parameter systems often operate inefficiently under such conditions, consuming excessive energy during partial-load scenarios or mild weather periods.
Key goals include developing adaptive control strategies that can seamlessly transition between operational modes based on real-time climate data, minimizing energy consumption while maintaining thermal comfort requirements. Additionally, there is growing emphasis on refrigerant selection and system design that can accommodate extreme weather events becoming more frequent due to climate change. The ultimate aim is to create resilient, self-optimizing chiller systems that deliver consistent performance and maximum efficiency regardless of external climate variability, thereby reducing operational costs and environmental impact across diverse geographical deployments.
Market Demand for Climate-Adaptive Cooling Systems
The global demand for climate-adaptive cooling systems has intensified significantly as building operators and facility managers confront the dual challenges of rising energy costs and increasingly unpredictable weather patterns. Traditional chiller systems, designed for relatively stable climate conditions, are proving inadequate in regions experiencing substantial seasonal variations and extreme temperature fluctuations. This gap between existing infrastructure capabilities and operational requirements has created a substantial market opportunity for advanced cooling solutions that can dynamically adjust to variable climate zones.
Commercial and industrial sectors represent the primary demand drivers for optimized chiller systems. Large-scale facilities such as data centers, hospitals, manufacturing plants, and commercial office complexes require continuous cooling operations while facing mounting pressure to reduce operational expenditures and meet stringent environmental regulations. The escalating frequency of heat waves and shifting seasonal patterns have exposed the inefficiencies of conventional fixed-capacity systems, prompting facility managers to seek intelligent solutions capable of maintaining performance across diverse climatic conditions.
The hospitality and retail industries have emerged as particularly receptive markets for climate-adaptive cooling technologies. These sectors operate facilities across multiple geographic regions with varying climate profiles, making standardized cooling approaches economically unfeasible. The ability to optimize chiller performance based on real-time climate data and predictive analytics offers substantial cost savings while ensuring consistent indoor environmental quality across diverse locations.
Regulatory frameworks and sustainability mandates are accelerating market adoption of adaptive cooling systems. Governments worldwide have implemented progressively stringent energy efficiency standards and carbon reduction targets for commercial buildings. Organizations seeking compliance with green building certifications and corporate sustainability commitments are actively investing in technologies that demonstrate measurable improvements in energy performance and environmental impact.
The integration of smart building technologies and Internet of Things platforms has further stimulated market demand. Building automation systems increasingly require cooling solutions that can seamlessly interface with broader energy management infrastructures, enabling holistic optimization strategies. This convergence of cooling technology with digital building management represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach thermal comfort and energy efficiency, creating sustained demand for sophisticated climate-adaptive solutions that deliver both operational flexibility and measurable performance improvements.
Commercial and industrial sectors represent the primary demand drivers for optimized chiller systems. Large-scale facilities such as data centers, hospitals, manufacturing plants, and commercial office complexes require continuous cooling operations while facing mounting pressure to reduce operational expenditures and meet stringent environmental regulations. The escalating frequency of heat waves and shifting seasonal patterns have exposed the inefficiencies of conventional fixed-capacity systems, prompting facility managers to seek intelligent solutions capable of maintaining performance across diverse climatic conditions.
The hospitality and retail industries have emerged as particularly receptive markets for climate-adaptive cooling technologies. These sectors operate facilities across multiple geographic regions with varying climate profiles, making standardized cooling approaches economically unfeasible. The ability to optimize chiller performance based on real-time climate data and predictive analytics offers substantial cost savings while ensuring consistent indoor environmental quality across diverse locations.
Regulatory frameworks and sustainability mandates are accelerating market adoption of adaptive cooling systems. Governments worldwide have implemented progressively stringent energy efficiency standards and carbon reduction targets for commercial buildings. Organizations seeking compliance with green building certifications and corporate sustainability commitments are actively investing in technologies that demonstrate measurable improvements in energy performance and environmental impact.
The integration of smart building technologies and Internet of Things platforms has further stimulated market demand. Building automation systems increasingly require cooling solutions that can seamlessly interface with broader energy management infrastructures, enabling holistic optimization strategies. This convergence of cooling technology with digital building management represents a fundamental shift in how organizations approach thermal comfort and energy efficiency, creating sustained demand for sophisticated climate-adaptive solutions that deliver both operational flexibility and measurable performance improvements.
Current Chiller Challenges in Variable Climate Conditions
Chiller systems operating in variable climate zones face multifaceted challenges that significantly impact their efficiency, reliability, and operational costs. The primary difficulty stems from the inherent unpredictability of weather patterns, which creates substantial fluctuations in cooling loads throughout different seasons and even within single days. Traditional chiller control strategies, typically designed for stable operating conditions, struggle to maintain optimal performance when confronted with rapid temperature swings, varying humidity levels, and inconsistent solar radiation patterns characteristic of transitional climate regions.
Energy efficiency degradation represents a critical concern in these environments. Conventional chillers are engineered to operate most efficiently at or near their design point, which corresponds to peak load conditions. However, in variable climates, systems frequently operate at partial loads, where efficiency curves deteriorate significantly. This mismatch between design capacity and actual demand results in excessive energy consumption, with studies indicating efficiency losses ranging from fifteen to thirty percent during off-peak periods. The situation intensifies when multiple chillers operate in parallel configurations, as load distribution algorithms often fail to account for real-time climate variations.
Equipment wear and maintenance issues escalate under variable climate conditions. Frequent cycling between different operational modes accelerates mechanical stress on compressors, pumps, and control valves. Temperature fluctuations cause thermal expansion and contraction cycles that compromise seals, gaskets, and heat exchanger integrity. Additionally, condensation problems emerge during transitional periods when outdoor conditions shift rapidly, potentially leading to corrosion and reduced component lifespan. These factors collectively increase maintenance frequency and operational downtime.
Control system limitations further compound operational challenges. Most existing building management systems employ static setpoints and rule-based control logic that cannot dynamically adapt to changing environmental conditions. The lack of predictive capabilities prevents proactive adjustments based on weather forecasts, resulting in reactive rather than anticipatory control strategies. Furthermore, inadequate sensor networks and data integration capabilities hinder real-time performance monitoring and optimization, leaving operators without sufficient visibility into system inefficiencies until problems manifest as comfort complaints or equipment failures.
Energy efficiency degradation represents a critical concern in these environments. Conventional chillers are engineered to operate most efficiently at or near their design point, which corresponds to peak load conditions. However, in variable climates, systems frequently operate at partial loads, where efficiency curves deteriorate significantly. This mismatch between design capacity and actual demand results in excessive energy consumption, with studies indicating efficiency losses ranging from fifteen to thirty percent during off-peak periods. The situation intensifies when multiple chillers operate in parallel configurations, as load distribution algorithms often fail to account for real-time climate variations.
Equipment wear and maintenance issues escalate under variable climate conditions. Frequent cycling between different operational modes accelerates mechanical stress on compressors, pumps, and control valves. Temperature fluctuations cause thermal expansion and contraction cycles that compromise seals, gaskets, and heat exchanger integrity. Additionally, condensation problems emerge during transitional periods when outdoor conditions shift rapidly, potentially leading to corrosion and reduced component lifespan. These factors collectively increase maintenance frequency and operational downtime.
Control system limitations further compound operational challenges. Most existing building management systems employ static setpoints and rule-based control logic that cannot dynamically adapt to changing environmental conditions. The lack of predictive capabilities prevents proactive adjustments based on weather forecasts, resulting in reactive rather than anticipatory control strategies. Furthermore, inadequate sensor networks and data integration capabilities hinder real-time performance monitoring and optimization, leaving operators without sufficient visibility into system inefficiencies until problems manifest as comfort complaints or equipment failures.
Mainstream Climate-Responsive Chiller Control Strategies
01 Control systems and methods for optimizing chiller performance
Advanced control systems can be implemented to optimize chiller operation by monitoring and adjusting various parameters in real-time. These systems utilize sensors and algorithms to continuously evaluate operating conditions and make automatic adjustments to improve efficiency. The control methods may include predictive algorithms, feedback loops, and adaptive control strategies that respond to changing load conditions and environmental factors to maintain optimal performance while minimizing energy consumption.- Control systems and algorithms for chiller optimization: Advanced control systems and algorithms can be implemented to optimize chiller operation by monitoring and adjusting various parameters in real-time. These systems utilize sensors, controllers, and computational methods to analyze operating conditions and make automatic adjustments to improve efficiency. Machine learning and artificial intelligence techniques can be incorporated to predict optimal operating points and adapt to changing load conditions. The control systems can coordinate multiple chillers in a plant to achieve optimal overall performance while minimizing energy consumption.
- Variable speed drive and compressor control: Variable speed drives can be integrated with chiller compressors to enable dynamic adjustment of cooling capacity based on actual demand. By modulating compressor speed rather than using on-off cycling, energy efficiency can be significantly improved during partial load conditions. The variable speed control allows the chiller to operate closer to optimal efficiency points across a wider range of load conditions. Advanced control strategies can coordinate multiple compressors with variable speed capabilities to match cooling requirements while minimizing power consumption.
- Condenser and evaporator optimization: Optimization of heat exchanger components, including condensers and evaporators, can significantly enhance chiller performance. This includes controlling water flow rates, temperatures, and pressure differentials to maintain optimal heat transfer conditions. Fouling detection and cleaning strategies can be implemented to maintain heat exchanger efficiency over time. Advanced designs and materials for heat exchangers can improve thermal performance while reducing pressure drops and pumping energy requirements.
- Load prediction and demand-based operation: Predictive algorithms can forecast cooling load requirements based on historical data, weather conditions, occupancy patterns, and other relevant factors. By anticipating future cooling demands, chiller systems can be pre-adjusted to operate more efficiently and avoid unnecessary energy consumption during low-demand periods. Demand-based control strategies can automatically adjust chiller capacity and sequencing to match actual cooling requirements. Integration with building management systems enables coordinated optimization across multiple HVAC components.
- Energy monitoring and performance analytics: Comprehensive monitoring systems can track energy consumption, efficiency metrics, and operational parameters to identify optimization opportunities. Real-time data analytics can detect performance degradation, inefficient operating modes, and maintenance needs before they significantly impact energy consumption. Benchmarking tools can compare actual performance against design specifications or industry standards to quantify improvement potential. Historical data analysis can reveal patterns and trends that inform long-term optimization strategies and equipment upgrade decisions.
02 Energy efficiency optimization through variable speed drives and component control
Optimization of chiller operation can be achieved through the implementation of variable speed drives for compressors, pumps, and fans. By adjusting the speed of these components based on actual cooling demand, significant energy savings can be realized. This approach allows the system to operate at partial load conditions more efficiently, reducing power consumption during periods of lower cooling requirements while maintaining adequate cooling capacity during peak demand periods.Expand Specific Solutions03 Intelligent load management and demand-based optimization
Chiller systems can be optimized by implementing intelligent load management strategies that distribute cooling loads efficiently across multiple chillers or optimize single chiller operation based on actual demand. These strategies involve analyzing building occupancy patterns, weather conditions, and cooling requirements to predict and adjust chiller operation accordingly. Load balancing algorithms can determine the most efficient combination of chillers to operate and at what capacity levels to meet cooling demands while minimizing overall energy consumption.Expand Specific Solutions04 Monitoring and diagnostic systems for performance optimization
Implementation of comprehensive monitoring and diagnostic systems enables continuous assessment of chiller performance and identification of optimization opportunities. These systems collect and analyze operational data including temperatures, pressures, flow rates, and power consumption to detect inefficiencies, predict maintenance needs, and recommend operational adjustments. Advanced diagnostic capabilities can identify degraded performance, refrigerant issues, or component failures before they significantly impact efficiency, allowing for proactive maintenance and optimization interventions.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integration with building management systems for holistic optimization
Chiller optimization can be enhanced through integration with broader building management systems that coordinate cooling operations with other building systems and environmental factors. This integrated approach allows for optimization based on overall building energy consumption patterns, occupancy schedules, and external weather conditions. The system can implement strategies such as pre-cooling, thermal storage utilization, and coordinated operation with other HVAC components to achieve maximum efficiency across the entire facility while maintaining comfort requirements.Expand Specific Solutions
Leading Chiller Manufacturers and Solution Providers
The chiller optimization market in variable climate zones represents a mature yet rapidly evolving sector driven by energy efficiency demands and smart building integration. Major HVAC manufacturers including Carrier Corp., Johnson Controls, Gree Electric Appliances, and Haier Smart Home dominate the competitive landscape, leveraging decades of thermal management expertise. Technology maturity varies significantly across players: established giants like Mitsubishi Electric and LG Electronics deploy advanced IoT-enabled predictive controls, while Vertiv Corp. and Hoffman Enclosures focus on precision cooling for data centers. Chinese manufacturers such as Qingdao Hisense Hitachi and BSH Hausgeräte GmbH are rapidly advancing through AI-driven optimization algorithms. Research institutions including Tianjin University and Nanjing Tech University contribute fundamental innovations in adaptive control strategies. The market shows consolidation trends with component suppliers like SMC Corp. and Semiconductor Components Industries enabling next-generation variable-speed compressor technologies, positioning the industry at the intersection of traditional HVAC expertise and emerging digital transformation capabilities.
Carrier Corp.
Technical Solution: Carrier has developed advanced chiller optimization systems that utilize predictive algorithms and real-time weather data integration to adjust cooling capacity dynamically across variable climate zones. Their AquaEdge centrifugal chillers incorporate variable speed drive technology with magnetic bearings, enabling precise capacity modulation from 10% to 100% load conditions. The system employs machine learning algorithms to analyze historical climate patterns and building load profiles, automatically adjusting setpoints for optimal efficiency. Their BluEdge platform provides cloud-based monitoring and control, allowing remote optimization based on local weather forecasts and utility rate structures. The technology includes adaptive control strategies that account for ambient temperature swings, humidity variations, and seasonal transitions typical in variable climate regions, achieving energy savings of 30-50% compared to fixed-speed systems.
Strengths: Industry-leading efficiency ratings, comprehensive IoT integration, proven track record in diverse climate applications. Weaknesses: Higher initial capital investment, complexity requiring specialized maintenance personnel.
Gree Electric Appliances, Inc. of Zhuhai
Technical Solution: Gree has developed intelligent chiller systems with adaptive climate control technology specifically targeting variable climate zone applications. Their centrifugal chiller series incorporates variable frequency drive (VFD) technology on compressors, condenser fans, and pumps, enabling comprehensive system optimization. The control system utilizes artificial intelligence algorithms to analyze ambient temperature patterns, humidity levels, and building load variations, automatically adjusting operational parameters to maintain optimal efficiency across different climate conditions. Gree's solution includes a self-learning capability that adapts to seasonal transitions, with fuzzy logic control managing the balance between capacity, efficiency, and equipment wear. Their systems feature advanced heat recovery options that can be activated during transitional climate periods to improve overall system COP. The technology incorporates real-time monitoring of refrigerant conditions and automatic adjustment of expansion valve settings to optimize performance during temperature fluctuations typical in variable climate zones.
Strengths: Cost-competitive solutions, strong performance in Asian climate conditions, integrated heat recovery capabilities. Weaknesses: Limited market presence in Western regions, less extensive documentation in English.
Core Patents in Variable Load Chiller Optimization
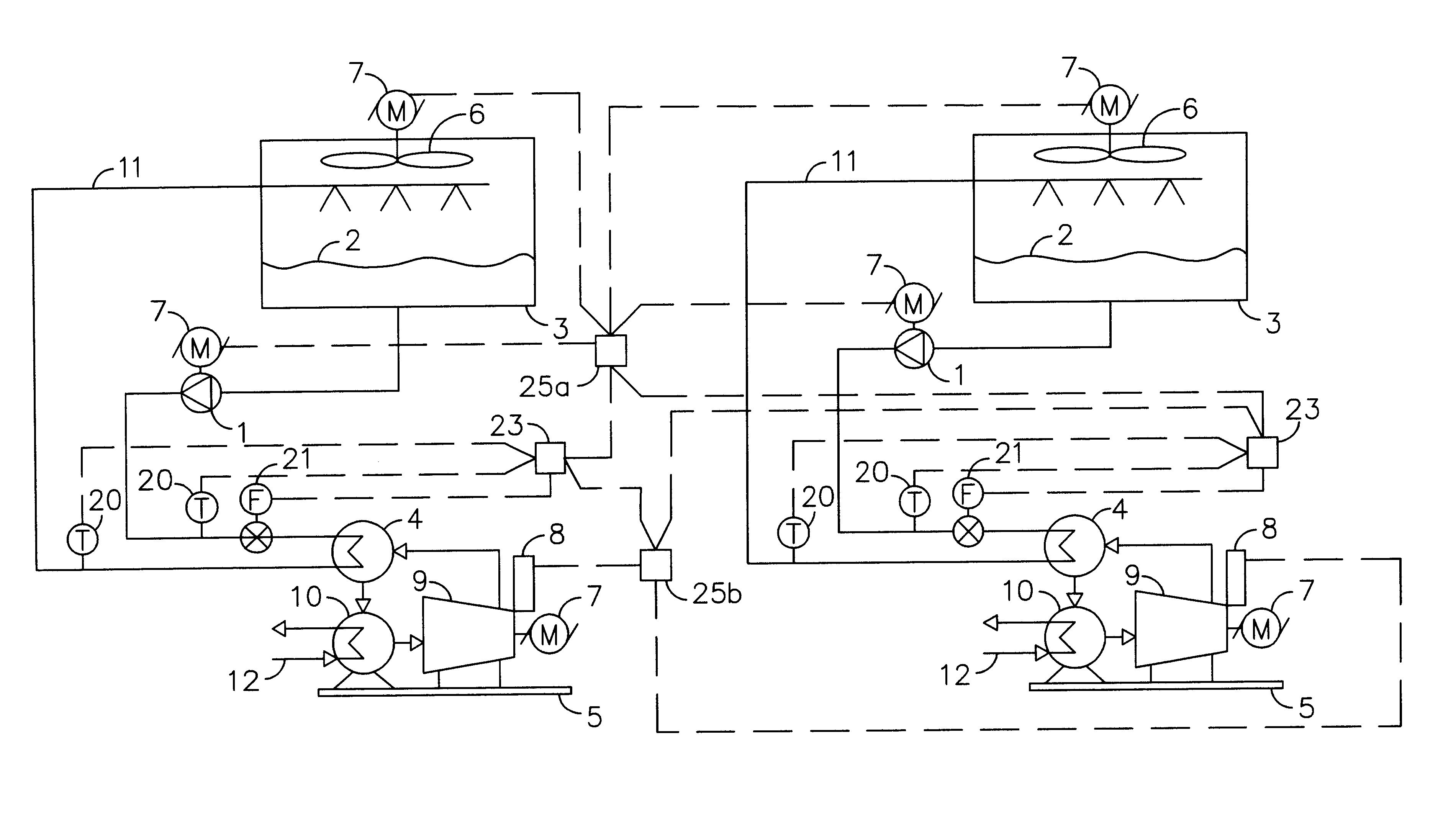
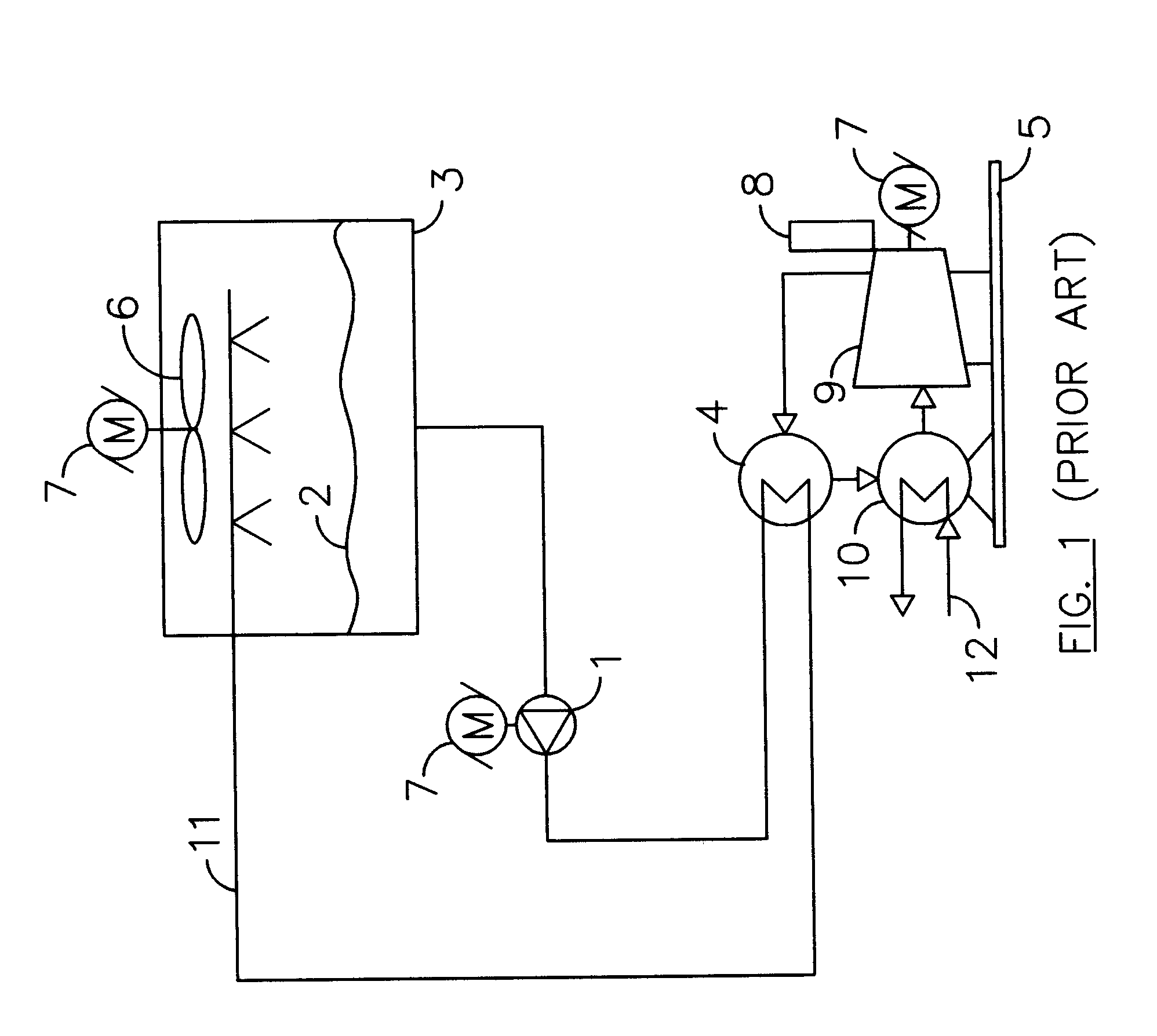
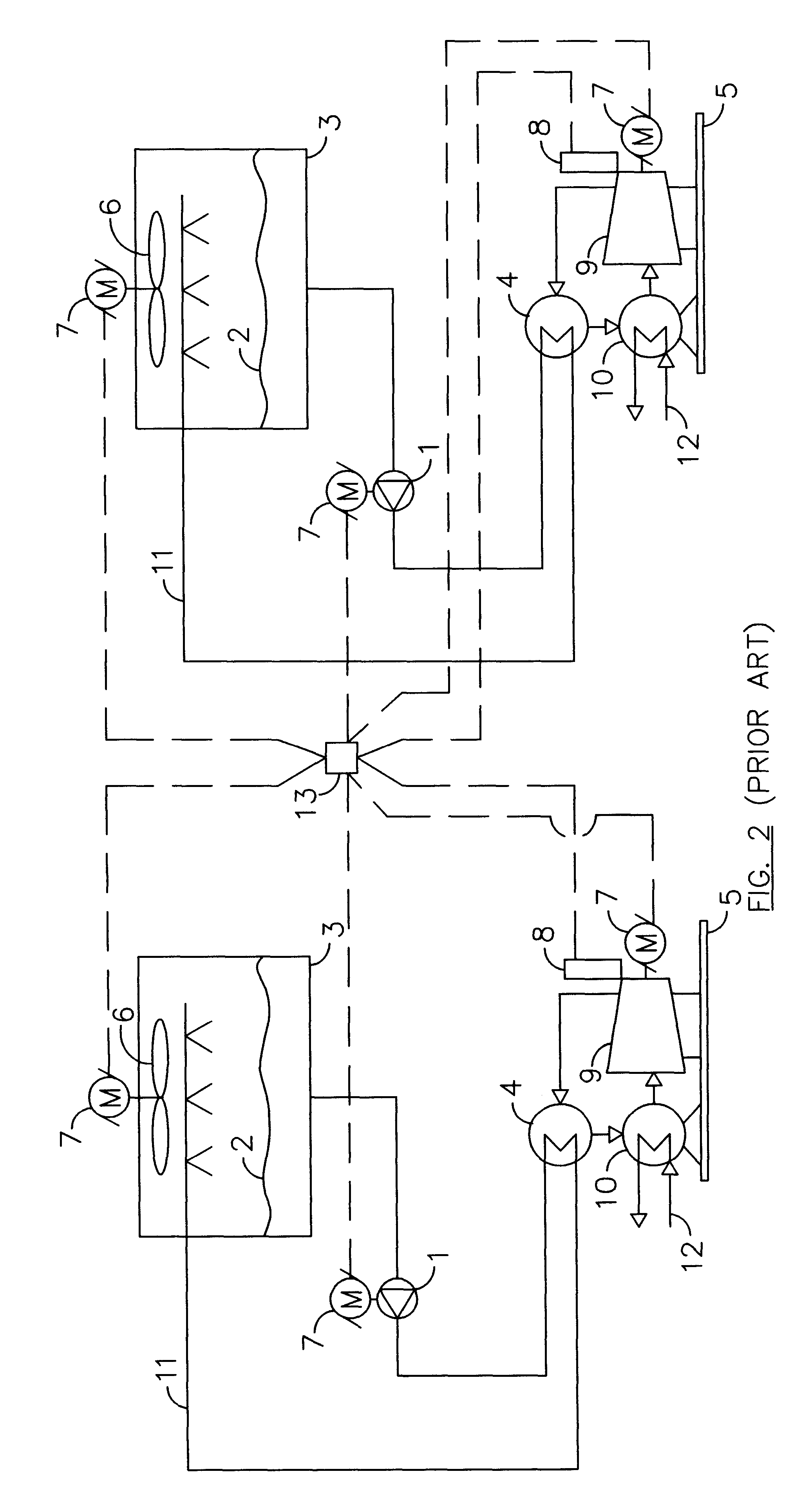
Multi-layer optimal chiller operation management framework
PatentInactiveUS20170219233A1
Innovation
- A multi-layer framework for chiller operation management that includes a day-ahead MILP-based optimization layer for 24-hour planning and a real-time dispatch layer for load adjustments, using rule-based chiller load sharing and MILP-based rolling optimization to address uncertainty, ensuring optimal chiller scheduling and continuous dispatching.
Method to optimize chiller plant operation
PatentInactiveUS6718779B1
Innovation
- A computerized controller system that uses temperature sensors and flow meters to maintain a constant temperature difference across the refrigerant condenser, controlling cooling fluid pump and cooling tower fan speeds based on measured parameters, allowing for flexible operation and integration with existing chiller plants without requiring proprietary access or complex setups.
Energy Efficiency Standards and Environmental Regulations
The optimization of chiller operation in variable climate zones is increasingly shaped by stringent energy efficiency standards and environmental regulations worldwide. These regulatory frameworks establish minimum performance requirements for chiller systems while addressing broader environmental concerns such as refrigerant management and carbon emissions reduction. Understanding these standards is essential for developing compliant and competitive chiller optimization strategies that balance operational efficiency with environmental responsibility.
International standards such as ISO 50001 for energy management systems and ASHRAE Standard 90.1 provide foundational guidelines for chiller efficiency requirements. These standards define minimum Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Coefficient of Performance (COP) values that chillers must achieve under specified operating conditions. In variable climate zones, compliance becomes more complex as systems must maintain efficiency across diverse temperature and humidity ranges, requiring adaptive control strategies that respond to changing environmental conditions while meeting baseline performance thresholds.
Regional regulatory variations significantly impact chiller optimization approaches. The European Union's Ecodesign Directive and F-Gas Regulation impose strict requirements on refrigerant selection and leakage prevention, driving adoption of low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants. Similarly, regulations in California and other progressive jurisdictions mandate advanced monitoring systems and regular efficiency audits. These requirements necessitate sophisticated control algorithms capable of optimizing performance while ensuring continuous regulatory compliance across different operational scenarios.
Environmental regulations increasingly focus on lifecycle impacts beyond operational efficiency. Refrigerant phase-down schedules under the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol are accelerating transitions to alternative refrigerants with lower environmental impact. This regulatory pressure influences chiller design and optimization strategies, as systems must accommodate new refrigerants with different thermodynamic properties while maintaining efficiency in variable climates. Additionally, carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions reporting requirements are incentivizing operators to prioritize optimization strategies that minimize overall environmental footprint rather than focusing solely on energy consumption metrics.
Compliance verification and documentation requirements are becoming more rigorous, with many jurisdictions mandating real-time monitoring and automated reporting systems. These regulatory demands are driving integration of advanced sensors, IoT connectivity, and data analytics platforms into chiller systems, creating opportunities for more sophisticated optimization approaches that leverage continuous performance data to demonstrate regulatory compliance while identifying efficiency improvement opportunities.
International standards such as ISO 50001 for energy management systems and ASHRAE Standard 90.1 provide foundational guidelines for chiller efficiency requirements. These standards define minimum Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) and Coefficient of Performance (COP) values that chillers must achieve under specified operating conditions. In variable climate zones, compliance becomes more complex as systems must maintain efficiency across diverse temperature and humidity ranges, requiring adaptive control strategies that respond to changing environmental conditions while meeting baseline performance thresholds.
Regional regulatory variations significantly impact chiller optimization approaches. The European Union's Ecodesign Directive and F-Gas Regulation impose strict requirements on refrigerant selection and leakage prevention, driving adoption of low Global Warming Potential (GWP) refrigerants. Similarly, regulations in California and other progressive jurisdictions mandate advanced monitoring systems and regular efficiency audits. These requirements necessitate sophisticated control algorithms capable of optimizing performance while ensuring continuous regulatory compliance across different operational scenarios.
Environmental regulations increasingly focus on lifecycle impacts beyond operational efficiency. Refrigerant phase-down schedules under the Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol are accelerating transitions to alternative refrigerants with lower environmental impact. This regulatory pressure influences chiller design and optimization strategies, as systems must accommodate new refrigerants with different thermodynamic properties while maintaining efficiency in variable climates. Additionally, carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions reporting requirements are incentivizing operators to prioritize optimization strategies that minimize overall environmental footprint rather than focusing solely on energy consumption metrics.
Compliance verification and documentation requirements are becoming more rigorous, with many jurisdictions mandating real-time monitoring and automated reporting systems. These regulatory demands are driving integration of advanced sensors, IoT connectivity, and data analytics platforms into chiller systems, creating opportunities for more sophisticated optimization approaches that leverage continuous performance data to demonstrate regulatory compliance while identifying efficiency improvement opportunities.
IoT Integration for Real-Time Climate-Based Control
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies represents a transformative approach to optimizing chiller operations across variable climate zones. By deploying interconnected sensors and smart devices throughout HVAC systems, facilities can achieve unprecedented levels of real-time monitoring and adaptive control. IoT-enabled chillers can continuously collect data on ambient temperature, humidity levels, occupancy patterns, and energy consumption, transmitting this information to centralized or cloud-based platforms for immediate analysis and response.
Real-time climate-based control systems leverage IoT infrastructure to dynamically adjust chiller parameters based on instantaneous weather conditions and forecasted climate patterns. Advanced sensor networks positioned both inside facilities and at external locations provide granular environmental data that feeds into intelligent control algorithms. These systems can automatically modulate cooling capacity, adjust water flow rates, and optimize compressor speeds in response to rapid climate fluctuations, ensuring energy efficiency while maintaining thermal comfort across diverse operational scenarios.
The communication protocols underlying IoT integration, including MQTT, CoAP, and BACnet/IP, enable seamless data exchange between distributed sensors, actuators, and control systems. Edge computing capabilities allow for localized processing of sensor data, reducing latency in control responses and minimizing bandwidth requirements for cloud connectivity. This distributed intelligence architecture proves particularly valuable in facilities spanning multiple climate zones, where localized environmental conditions may vary significantly within short distances.
Machine learning algorithms integrated with IoT platforms can identify complex patterns in climate data and chiller performance metrics that traditional control systems might overlook. These predictive models continuously refine their understanding of how specific climate variables impact cooling demands, enabling proactive adjustments before environmental changes affect indoor conditions. The combination of real-time data streams and predictive analytics creates a self-optimizing system that improves operational efficiency over time while adapting to seasonal climate variations and long-term climate trends.
Security considerations and data management protocols remain critical components of IoT implementation, requiring robust encryption standards and secure authentication mechanisms to protect operational data and prevent unauthorized system access in increasingly connected industrial environments.
Real-time climate-based control systems leverage IoT infrastructure to dynamically adjust chiller parameters based on instantaneous weather conditions and forecasted climate patterns. Advanced sensor networks positioned both inside facilities and at external locations provide granular environmental data that feeds into intelligent control algorithms. These systems can automatically modulate cooling capacity, adjust water flow rates, and optimize compressor speeds in response to rapid climate fluctuations, ensuring energy efficiency while maintaining thermal comfort across diverse operational scenarios.
The communication protocols underlying IoT integration, including MQTT, CoAP, and BACnet/IP, enable seamless data exchange between distributed sensors, actuators, and control systems. Edge computing capabilities allow for localized processing of sensor data, reducing latency in control responses and minimizing bandwidth requirements for cloud connectivity. This distributed intelligence architecture proves particularly valuable in facilities spanning multiple climate zones, where localized environmental conditions may vary significantly within short distances.
Machine learning algorithms integrated with IoT platforms can identify complex patterns in climate data and chiller performance metrics that traditional control systems might overlook. These predictive models continuously refine their understanding of how specific climate variables impact cooling demands, enabling proactive adjustments before environmental changes affect indoor conditions. The combination of real-time data streams and predictive analytics creates a self-optimizing system that improves operational efficiency over time while adapting to seasonal climate variations and long-term climate trends.
Security considerations and data management protocols remain critical components of IoT implementation, requiring robust encryption standards and secure authentication mechanisms to protect operational data and prevent unauthorized system access in increasingly connected industrial environments.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!