Optimizing Chiller Performance in Power Plants
JAN 23, 20269 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Chiller Technology Background and Performance Goals
Chiller systems have been integral to power plant operations since the mid-20th century, evolving from basic mechanical refrigeration units to sophisticated, computer-controlled systems that play a critical role in maintaining optimal operating conditions. In power generation facilities, chillers primarily serve to cool auxiliary equipment, control room environments, and support turbine efficiency by managing condenser water temperatures. The technology has progressed through several generations, from absorption chillers utilizing waste heat to modern centrifugal and screw compressor designs that offer superior energy efficiency and precise temperature control.
The fundamental challenge in power plant chiller applications lies in balancing cooling capacity with energy consumption, as chillers themselves can account for significant parasitic loads that reduce overall plant efficiency. Traditional chiller systems often operate at fixed capacities regardless of actual cooling demand, leading to substantial energy waste during partial load conditions. This inefficiency becomes particularly pronounced in power plants where cooling requirements fluctuate based on ambient conditions, load variations, and operational modes.
Contemporary performance goals for power plant chillers center on achieving coefficient of performance values exceeding 6.0 for electric chillers and 1.3 for absorption systems, while maintaining stable operation across varying load profiles. The industry increasingly emphasizes real-time optimization capabilities that can dynamically adjust chiller operation based on multiple variables including outdoor temperature, humidity, cooling load distribution, and electricity pricing structures. Advanced control strategies aim to minimize total plant auxiliary power consumption while ensuring equipment reliability and extending operational lifespan.
Emerging objectives also include integration with plant-wide energy management systems, enabling chillers to participate in demand response programs and optimize their operation in coordination with other auxiliary systems. The target is to reduce chiller-related energy consumption by 20-30% compared to conventional fixed-speed systems while improving temperature stability to within ±0.5°C of setpoints. Additionally, there is growing focus on reducing environmental impact through the adoption of low global warming potential refrigerants and improving part-load efficiency ratios to better match actual operating profiles in power generation environments.
The fundamental challenge in power plant chiller applications lies in balancing cooling capacity with energy consumption, as chillers themselves can account for significant parasitic loads that reduce overall plant efficiency. Traditional chiller systems often operate at fixed capacities regardless of actual cooling demand, leading to substantial energy waste during partial load conditions. This inefficiency becomes particularly pronounced in power plants where cooling requirements fluctuate based on ambient conditions, load variations, and operational modes.
Contemporary performance goals for power plant chillers center on achieving coefficient of performance values exceeding 6.0 for electric chillers and 1.3 for absorption systems, while maintaining stable operation across varying load profiles. The industry increasingly emphasizes real-time optimization capabilities that can dynamically adjust chiller operation based on multiple variables including outdoor temperature, humidity, cooling load distribution, and electricity pricing structures. Advanced control strategies aim to minimize total plant auxiliary power consumption while ensuring equipment reliability and extending operational lifespan.
Emerging objectives also include integration with plant-wide energy management systems, enabling chillers to participate in demand response programs and optimize their operation in coordination with other auxiliary systems. The target is to reduce chiller-related energy consumption by 20-30% compared to conventional fixed-speed systems while improving temperature stability to within ±0.5°C of setpoints. Additionally, there is growing focus on reducing environmental impact through the adoption of low global warming potential refrigerants and improving part-load efficiency ratios to better match actual operating profiles in power generation environments.
Power Plant Cooling System Market Demand Analysis
The global power generation sector is experiencing a fundamental shift in cooling system requirements, driven by multiple converging factors including stricter environmental regulations, rising energy costs, and increasing demands for operational efficiency. Power plants, whether fossil-fueled, nuclear, or renewable-based hybrid facilities, rely heavily on chiller systems to maintain optimal operating temperatures for turbines, condensers, and auxiliary equipment. The performance of these cooling systems directly impacts overall plant efficiency, with even marginal improvements translating to significant economic and environmental benefits across large-scale operations.
Market demand for optimized chiller performance solutions has intensified as aging power infrastructure in developed economies requires modernization while emerging markets simultaneously expand their generation capacity. Utilities and independent power producers face mounting pressure to reduce water consumption, minimize thermal pollution, and lower operational expenditures. These challenges have created substantial demand for advanced chiller optimization technologies that can deliver measurable improvements in coefficient of performance, reduce parasitic loads, and extend equipment lifespan through predictive maintenance capabilities.
The regulatory landscape further amplifies market demand, particularly in regions implementing carbon pricing mechanisms and water usage restrictions. Environmental compliance costs have become a critical factor in plant economics, making efficient cooling systems not merely operational assets but strategic necessities. This regulatory pressure has accelerated adoption timelines for optimization technologies that were previously considered optional upgrades.
Industrial trends indicate growing preference for integrated digital solutions that combine real-time monitoring, artificial intelligence-driven control algorithms, and automated adjustment capabilities. Plant operators increasingly seek systems that can dynamically respond to variable load conditions, ambient temperature fluctuations, and grid demand patterns. The shift toward flexible generation to support intermittent renewable sources has further elevated the importance of responsive cooling systems capable of rapid load following without efficiency penalties.
Market segmentation reveals distinct demand patterns across plant types and geographical regions. Combined cycle gas turbine facilities demonstrate particularly strong demand due to their sensitivity to condenser performance, while nuclear plants prioritize reliability and safety-critical cooling functions. Geographically, regions with water scarcity issues show accelerated adoption of dry cooling and hybrid optimization solutions, whereas areas with abundant water resources focus primarily on energy efficiency improvements and emissions reduction technologies.
Market demand for optimized chiller performance solutions has intensified as aging power infrastructure in developed economies requires modernization while emerging markets simultaneously expand their generation capacity. Utilities and independent power producers face mounting pressure to reduce water consumption, minimize thermal pollution, and lower operational expenditures. These challenges have created substantial demand for advanced chiller optimization technologies that can deliver measurable improvements in coefficient of performance, reduce parasitic loads, and extend equipment lifespan through predictive maintenance capabilities.
The regulatory landscape further amplifies market demand, particularly in regions implementing carbon pricing mechanisms and water usage restrictions. Environmental compliance costs have become a critical factor in plant economics, making efficient cooling systems not merely operational assets but strategic necessities. This regulatory pressure has accelerated adoption timelines for optimization technologies that were previously considered optional upgrades.
Industrial trends indicate growing preference for integrated digital solutions that combine real-time monitoring, artificial intelligence-driven control algorithms, and automated adjustment capabilities. Plant operators increasingly seek systems that can dynamically respond to variable load conditions, ambient temperature fluctuations, and grid demand patterns. The shift toward flexible generation to support intermittent renewable sources has further elevated the importance of responsive cooling systems capable of rapid load following without efficiency penalties.
Market segmentation reveals distinct demand patterns across plant types and geographical regions. Combined cycle gas turbine facilities demonstrate particularly strong demand due to their sensitivity to condenser performance, while nuclear plants prioritize reliability and safety-critical cooling functions. Geographically, regions with water scarcity issues show accelerated adoption of dry cooling and hybrid optimization solutions, whereas areas with abundant water resources focus primarily on energy efficiency improvements and emissions reduction technologies.
Current Chiller Efficiency Challenges in Power Plants
Power plants worldwide face mounting pressure to enhance chiller efficiency as energy costs escalate and environmental regulations tighten. Chillers constitute one of the most energy-intensive components in power generation facilities, typically accounting for 30-50% of auxiliary power consumption. Despite technological advances, numerous operational and technical challenges continue to impede optimal performance, resulting in significant energy waste and reduced overall plant efficiency.
Fouling and scaling represent persistent obstacles in chiller operation. Heat exchanger surfaces accumulate mineral deposits, biological growth, and particulate matter over time, creating insulating layers that drastically reduce heat transfer efficiency. This degradation can decrease chiller performance by 10-30% annually if left unaddressed. Traditional cleaning methods prove labor-intensive and require extended downtime, directly impacting plant availability and revenue generation.
Refrigerant degradation and leakage pose additional technical constraints. Many existing power plant chillers still operate with older refrigerants that exhibit suboptimal thermodynamic properties and face regulatory phase-out pressures. Micro-leaks in aging systems lead to gradual performance deterioration that often goes undetected until efficiency losses become substantial. The transition to environmentally compliant refrigerants introduces compatibility issues with existing equipment and requires careful system modifications.
Variable load conditions create operational complexity that standard chiller designs struggle to accommodate efficiently. Power plants experience significant fluctuations in cooling demand based on ambient conditions, generation schedules, and seasonal variations. Conventional chillers operate most efficiently at or near full load, suffering dramatic efficiency penalties during partial load operation, which represents the majority of actual operating hours in many facilities.
Control system limitations further compound efficiency challenges. Legacy control architectures lack the sophistication to optimize chiller performance dynamically across changing conditions. These systems typically employ simple on-off or staged control strategies that fail to leverage advanced optimization algorithms. Integration gaps between chiller controls and broader plant management systems prevent holistic efficiency optimization and coordinated operation of multiple chillers.
Inadequate monitoring and diagnostic capabilities hinder proactive maintenance and performance optimization. Many facilities lack real-time performance tracking systems capable of detecting gradual efficiency degradation or identifying root causes of suboptimal operation. This reactive maintenance approach allows problems to persist and compound, resulting in cumulative efficiency losses and unexpected equipment failures that disrupt plant operations.
Fouling and scaling represent persistent obstacles in chiller operation. Heat exchanger surfaces accumulate mineral deposits, biological growth, and particulate matter over time, creating insulating layers that drastically reduce heat transfer efficiency. This degradation can decrease chiller performance by 10-30% annually if left unaddressed. Traditional cleaning methods prove labor-intensive and require extended downtime, directly impacting plant availability and revenue generation.
Refrigerant degradation and leakage pose additional technical constraints. Many existing power plant chillers still operate with older refrigerants that exhibit suboptimal thermodynamic properties and face regulatory phase-out pressures. Micro-leaks in aging systems lead to gradual performance deterioration that often goes undetected until efficiency losses become substantial. The transition to environmentally compliant refrigerants introduces compatibility issues with existing equipment and requires careful system modifications.
Variable load conditions create operational complexity that standard chiller designs struggle to accommodate efficiently. Power plants experience significant fluctuations in cooling demand based on ambient conditions, generation schedules, and seasonal variations. Conventional chillers operate most efficiently at or near full load, suffering dramatic efficiency penalties during partial load operation, which represents the majority of actual operating hours in many facilities.
Control system limitations further compound efficiency challenges. Legacy control architectures lack the sophistication to optimize chiller performance dynamically across changing conditions. These systems typically employ simple on-off or staged control strategies that fail to leverage advanced optimization algorithms. Integration gaps between chiller controls and broader plant management systems prevent holistic efficiency optimization and coordinated operation of multiple chillers.
Inadequate monitoring and diagnostic capabilities hinder proactive maintenance and performance optimization. Many facilities lack real-time performance tracking systems capable of detecting gradual efficiency degradation or identifying root causes of suboptimal operation. This reactive maintenance approach allows problems to persist and compound, resulting in cumulative efficiency losses and unexpected equipment failures that disrupt plant operations.
Mainstream Chiller Optimization Solutions
01 Advanced control systems and optimization methods for chiller operation
Implementation of sophisticated control algorithms and optimization techniques to enhance chiller performance through real-time monitoring and adjustment of operating parameters. These systems utilize sensors, processors, and feedback mechanisms to automatically regulate compressor speed, refrigerant flow, and temperature settings based on load conditions. Advanced control strategies include predictive algorithms, adaptive control, and machine learning approaches that continuously optimize energy consumption while maintaining desired cooling capacity.- Advanced control systems and optimization methods for chiller operation: Implementation of sophisticated control algorithms and optimization techniques to enhance chiller performance through improved operational efficiency. These systems utilize predictive control, machine learning, and real-time monitoring to adjust operating parameters dynamically. The control methods focus on optimizing energy consumption while maintaining desired cooling capacity and temperature setpoints across varying load conditions.
- Heat exchanger design improvements and enhanced heat transfer mechanisms: Innovations in heat exchanger configurations and surface treatments to improve thermal transfer efficiency in chiller systems. These advancements include novel tube geometries, enhanced surface coatings, and optimized flow patterns that reduce thermal resistance. The improvements result in better heat rejection and absorption capabilities, leading to increased coefficient of performance and reduced energy consumption.
- Variable speed drive integration and compressor optimization: Application of variable frequency drives and advanced compressor technologies to match cooling output with actual demand. These systems enable precise capacity modulation through speed control, reducing energy waste during partial load operations. The integration includes inverter-driven compressors, magnetic bearing systems, and multi-stage compression arrangements that enhance overall system efficiency across the operating range.
- Refrigerant management and thermodynamic cycle enhancements: Developments in refrigerant selection, charge optimization, and cycle modifications to improve thermodynamic performance. These innovations encompass the use of low global warming potential refrigerants, subcooling and superheating optimization, and advanced expansion devices. The enhancements focus on maximizing the thermodynamic efficiency of the refrigeration cycle while ensuring environmental compliance and system reliability.
- Monitoring systems and predictive maintenance technologies: Implementation of sensor networks and diagnostic tools for continuous performance monitoring and fault detection in chiller systems. These technologies enable early identification of degradation patterns, refrigerant leaks, and component failures before they significantly impact performance. The systems utilize data analytics and condition-based monitoring to schedule maintenance activities optimally, reducing downtime and maintaining peak efficiency throughout the equipment lifecycle.
02 Variable speed drive technology for compressor efficiency
Integration of variable frequency drives and variable speed compressor systems to match cooling output with actual demand, reducing energy waste during partial load conditions. This technology allows the compressor to operate at optimal speeds rather than cycling on and off, resulting in improved coefficient of performance and reduced wear on mechanical components. The variable speed approach enables smooth modulation of cooling capacity across a wide range of operating conditions.Expand Specific Solutions03 Enhanced heat exchanger design and configuration
Improved heat exchanger geometries, materials, and arrangements to maximize heat transfer efficiency in both evaporator and condenser sections. Innovations include optimized fin designs, enhanced tube surfaces, microchannel configurations, and advanced coatings that promote better thermal conductivity and reduce fouling. These enhancements increase the overall heat transfer coefficient, allowing chillers to achieve higher performance with reduced refrigerant charge and smaller footprint.Expand Specific Solutions04 Refrigerant management and alternative refrigerant systems
Development of improved refrigerant circulation strategies and adoption of next-generation refrigerants with better thermodynamic properties and environmental profiles. This includes optimized refrigerant charging methods, subcooling and superheating control, and the use of refrigerant mixtures or natural refrigerants that offer higher efficiency and lower global warming potential. Proper refrigerant management ensures optimal phase change characteristics and minimizes pressure drops throughout the refrigeration cycle.Expand Specific Solutions05 Integrated monitoring and diagnostic systems for performance maintenance
Implementation of comprehensive monitoring frameworks that track key performance indicators, detect anomalies, and provide predictive maintenance capabilities to sustain optimal chiller performance over time. These systems collect data on temperatures, pressures, flow rates, power consumption, and vibration patterns to identify degradation trends before they result in significant efficiency losses. Diagnostic algorithms can pinpoint specific component issues such as fouled heat exchangers, refrigerant leaks, or compressor wear, enabling timely interventions.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Chiller Manufacturers and Power Plant Operators
The chiller performance optimization market in power plants is experiencing steady maturation, driven by increasing energy efficiency demands and sustainability regulations. Major industrial players like Siemens Industry, Trane International, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Thermal Systems, and Vertiv Corp. dominate with established HVAC and thermal management solutions, demonstrating high technological maturity through integrated control systems and IoT-enabled monitoring. Chinese state-owned enterprises including State Grid Corp., China Shenhua Energy, and Huadian Electric Power Research Institute represent significant regional market presence, particularly in Asia's expanding power generation sector. Specialized firms like Tekworx LLC and Green Revolution Cooling are advancing niche innovations in real-time optimization and immersion cooling technologies. The market shows consolidation trends with established manufacturers like Johnson Controls, Honeywell, and Hitachi leveraging comprehensive building management ecosystems, while emerging players focus on AI-driven predictive maintenance and adaptive control algorithms to achieve 30-50% energy reduction targets.
Siemens Industry, Inc.
Technical Solution: Siemens provides comprehensive chiller optimization solutions through their SICAM (Siemens Substation Automation and Communication) platform integrated with advanced process control systems. Their approach utilizes digital twin technology to create virtual models of chiller systems, enabling simulation-based optimization before implementation. The solution employs model predictive control (MPC) algorithms that forecast cooling demand based on historical data, weather patterns, and power generation schedules to pre-emptively adjust chiller operations. Siemens integrates IoT sensors throughout the cooling system to monitor parameters including refrigerant pressure, temperature differentials, flow rates, and power consumption in real-time. Their analytics platform applies artificial intelligence to identify inefficiencies and recommend operational adjustments. The system supports multi-chiller coordination, automatically determining optimal load distribution and sequencing to minimize total energy consumption while maintaining required cooling capacity for power generation equipment.
Strengths: Comprehensive digitalization capabilities, seamless integration with power plant automation systems, strong predictive analytics and AI-driven optimization. Weaknesses: Complex implementation requiring significant system integration effort, dependency on robust data infrastructure and connectivity.
Honeywell International Technologies Ltd.
Technical Solution: Honeywell's chiller optimization solution centers on their Forge platform combined with advanced process control technologies specifically designed for power plant applications. The system employs real-time optimization algorithms that continuously calculate the most efficient operating points for chillers based on ambient conditions, cooling load requirements, and electricity costs. Their technology includes advanced compressor control strategies that optimize capacity modulation through variable speed drives and digital scroll technology. Honeywell integrates condenser water optimization by dynamically adjusting cooling tower fan speeds and water flow rates to maintain optimal approach temperatures. The platform features fault detection and diagnostics (FDD) capabilities that identify issues such as refrigerant leaks, fouled heat exchangers, or degraded compressor performance before they significantly impact efficiency. Their solution provides comprehensive energy management by coordinating chiller plant operations with overall power plant thermal management systems, ensuring cooling systems support rather than detract from generation efficiency.
Strengths: Robust fault detection capabilities, excellent integration with diverse equipment manufacturers, strong focus on total plant energy optimization. Weaknesses: Requires continuous calibration and tuning for optimal performance, subscription-based software model increases long-term operational costs.
Key Patents in Advanced Chiller Control Systems
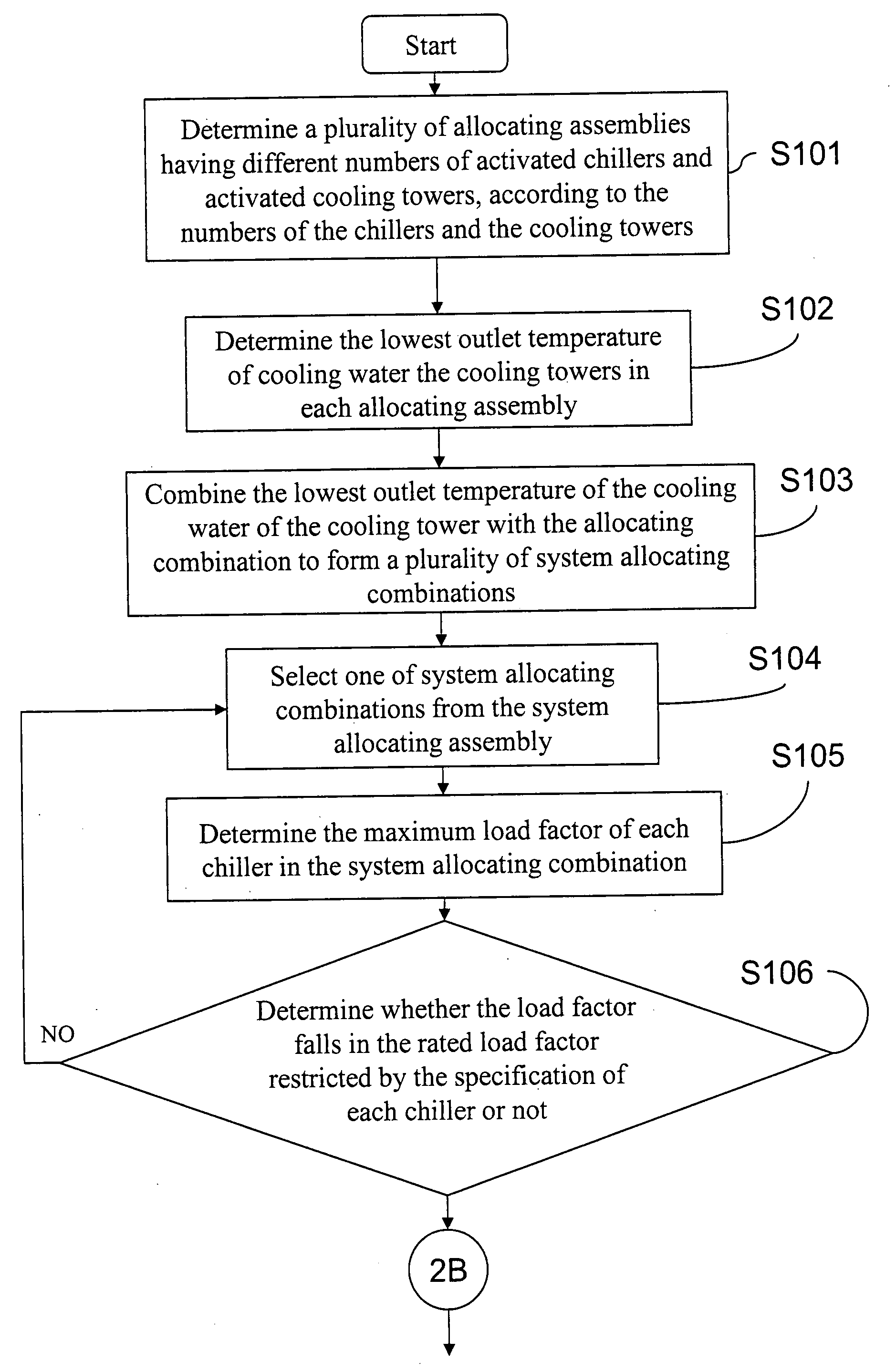
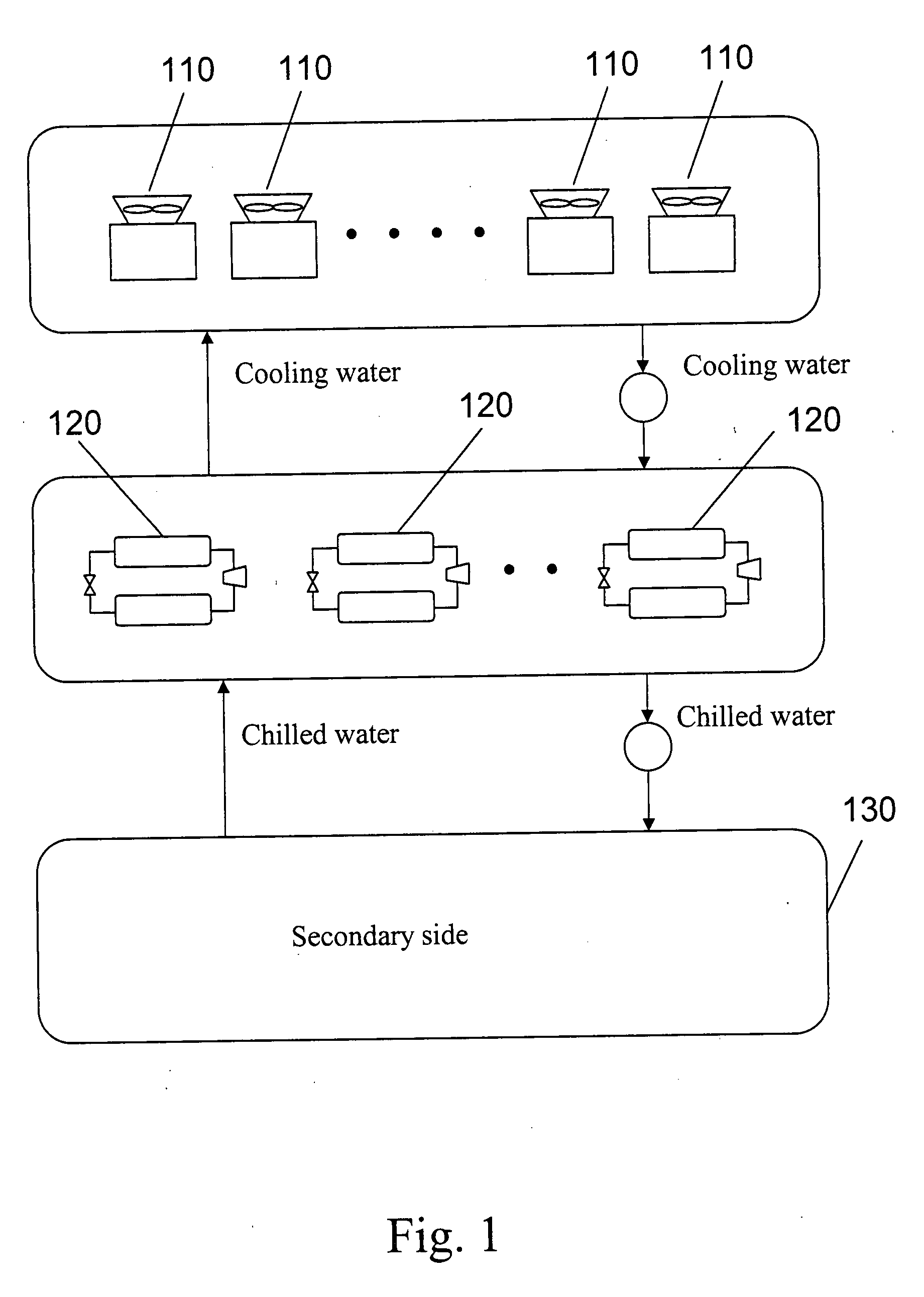
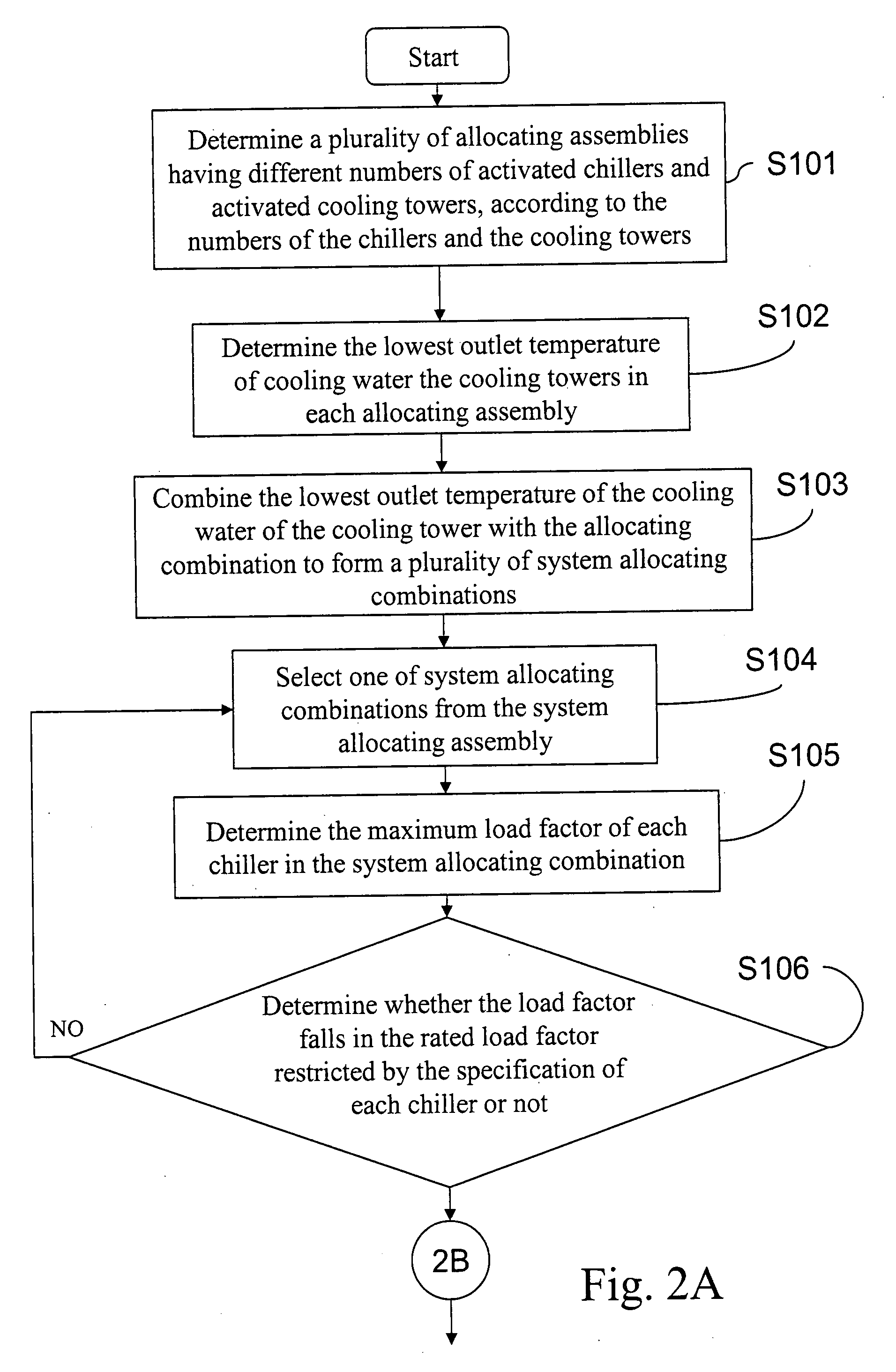
Method for evaluating and optimizing performance of chiller system
PatentInactiveUS20080162077A1
Innovation
- A method to evaluate and optimize the performance of chiller systems by determining the optimal number of activated chillers and cooling towers, and the lowest outlet temperature of cooling water, which allows for the selection of system configurations that minimize total power consumption without requiring physical changes to the chiller system.
Method and system for optimization of combined cycle power plant
PatentActiveEP2910743A1
Innovation
- A method involving digital modeling of power plant components using artificial neural networks and Kalman filters to simulate and optimize operations, determining an optimal operating set point by correlating thermodynamic and economic performance, and adjusting models based on actual plant data to reduce differences between simulated and actual performance.
Energy Efficiency Regulations for Power Plant Chillers
Energy efficiency regulations for power plant chillers have become increasingly stringent worldwide as governments and international organizations prioritize carbon reduction and sustainable energy consumption. These regulatory frameworks establish mandatory performance standards that directly impact chiller selection, operation, and maintenance strategies in power generation facilities. The regulatory landscape encompasses both prescriptive requirements specifying minimum efficiency levels and performance-based standards that mandate overall energy consumption targets.
In the United States, the Department of Energy enforces efficiency standards under the Energy Policy and Conservation Act, which sets minimum Energy Efficiency Ratio requirements for commercial chillers exceeding certain capacity thresholds. The European Union implements the Ecodesign Directive and Energy Efficiency Directive, establishing Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio benchmarks and requiring regular energy audits for large industrial facilities including power plants. Similarly, China's GB19577 standard mandates coefficient of performance thresholds for water-cooled and air-cooled chillers, with progressive tightening of requirements in recent revisions.
Compliance mechanisms vary across jurisdictions but typically include certification testing, periodic performance verification, and documentation requirements. Many regulations incorporate tiered efficiency levels, with baseline standards representing minimum acceptable performance and higher tiers offering incentives or preferential treatment. The International Energy Agency estimates that implementing best-practice efficiency standards globally could reduce chiller energy consumption by approximately thirty percent by 2030.
Recent regulatory trends emphasize lifecycle assessment approaches, considering refrigerant global warming potential alongside operational efficiency. The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol accelerates hydrofluorocarbon phase-down schedules, compelling power plants to transition toward low-GWP refrigerants while maintaining efficiency compliance. Additionally, emerging regulations increasingly mandate real-time monitoring systems and data reporting to verify continuous compliance rather than relying solely on design-stage certification.
Non-compliance penalties range from financial sanctions to operational restrictions, making regulatory adherence a critical consideration in chiller optimization strategies. Forward-looking power plant operators must anticipate regulatory evolution, as standards typically tighten every three to five years, requiring proactive technology adoption and operational adjustments to maintain compliance margins.
In the United States, the Department of Energy enforces efficiency standards under the Energy Policy and Conservation Act, which sets minimum Energy Efficiency Ratio requirements for commercial chillers exceeding certain capacity thresholds. The European Union implements the Ecodesign Directive and Energy Efficiency Directive, establishing Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio benchmarks and requiring regular energy audits for large industrial facilities including power plants. Similarly, China's GB19577 standard mandates coefficient of performance thresholds for water-cooled and air-cooled chillers, with progressive tightening of requirements in recent revisions.
Compliance mechanisms vary across jurisdictions but typically include certification testing, periodic performance verification, and documentation requirements. Many regulations incorporate tiered efficiency levels, with baseline standards representing minimum acceptable performance and higher tiers offering incentives or preferential treatment. The International Energy Agency estimates that implementing best-practice efficiency standards globally could reduce chiller energy consumption by approximately thirty percent by 2030.
Recent regulatory trends emphasize lifecycle assessment approaches, considering refrigerant global warming potential alongside operational efficiency. The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol accelerates hydrofluorocarbon phase-down schedules, compelling power plants to transition toward low-GWP refrigerants while maintaining efficiency compliance. Additionally, emerging regulations increasingly mandate real-time monitoring systems and data reporting to verify continuous compliance rather than relying solely on design-stage certification.
Non-compliance penalties range from financial sanctions to operational restrictions, making regulatory adherence a critical consideration in chiller optimization strategies. Forward-looking power plant operators must anticipate regulatory evolution, as standards typically tighten every three to five years, requiring proactive technology adoption and operational adjustments to maintain compliance margins.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Reduction Strategies
The optimization of chiller performance in power plants carries significant environmental implications, particularly in the context of global carbon reduction commitments. Chillers typically account for 30-50% of total power plant auxiliary power consumption, making them critical targets for emission reduction initiatives. Enhanced chiller efficiency directly translates to reduced fuel consumption in the primary generation cycle, thereby lowering carbon dioxide emissions per unit of electricity produced. Studies indicate that a 10% improvement in chiller coefficient of performance can reduce plant-level carbon emissions by approximately 2-3%, representing substantial environmental benefits when scaled across multiple facilities.
The implementation of advanced chiller optimization strategies aligns with international carbon neutrality frameworks and regulatory requirements. Many jurisdictions now mandate power plants to operate within specific carbon intensity thresholds, creating economic incentives for efficiency improvements. Variable speed drive technology, intelligent load distribution algorithms, and predictive maintenance systems not only enhance operational efficiency but also minimize refrigerant leakage risks. Modern low-global-warming-potential refrigerants, when combined with optimized system performance, can reduce the overall carbon footprint by up to 40% compared to legacy systems using high-GWP substances.
Waste heat recovery integration represents another crucial carbon reduction pathway. Optimized chillers can effectively utilize waste heat from turbine condensers or other plant processes, reducing the need for additional cooling tower operations and associated energy consumption. This circular approach to thermal management can decrease auxiliary power requirements by 15-20%, contributing to lower scope 2 emissions.
Furthermore, real-time monitoring and data analytics enable power plants to demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and participate in carbon trading schemes. Documented efficiency improvements provide verifiable carbon credits, creating additional revenue streams while supporting corporate sustainability objectives. The convergence of chiller optimization with renewable energy integration and energy storage systems positions power plants as more environmentally responsible entities, capable of meeting increasingly stringent emission reduction targets while maintaining operational reliability and economic viability.
The implementation of advanced chiller optimization strategies aligns with international carbon neutrality frameworks and regulatory requirements. Many jurisdictions now mandate power plants to operate within specific carbon intensity thresholds, creating economic incentives for efficiency improvements. Variable speed drive technology, intelligent load distribution algorithms, and predictive maintenance systems not only enhance operational efficiency but also minimize refrigerant leakage risks. Modern low-global-warming-potential refrigerants, when combined with optimized system performance, can reduce the overall carbon footprint by up to 40% compared to legacy systems using high-GWP substances.
Waste heat recovery integration represents another crucial carbon reduction pathway. Optimized chillers can effectively utilize waste heat from turbine condensers or other plant processes, reducing the need for additional cooling tower operations and associated energy consumption. This circular approach to thermal management can decrease auxiliary power requirements by 15-20%, contributing to lower scope 2 emissions.
Furthermore, real-time monitoring and data analytics enable power plants to demonstrate compliance with environmental standards and participate in carbon trading schemes. Documented efficiency improvements provide verifiable carbon credits, creating additional revenue streams while supporting corporate sustainability objectives. The convergence of chiller optimization with renewable energy integration and energy storage systems positions power plants as more environmentally responsible entities, capable of meeting increasingly stringent emission reduction targets while maintaining operational reliability and economic viability.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!