Product Slate Optimization: Naphtha, Diesel, And Lubricant-Range Fractions
AUG 22, 20259 MIN READ
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Patsnap Eureka helps you evaluate technical feasibility & market potential.
Petroleum Refining Background and Optimization Goals
Petroleum refining has evolved significantly since its inception in the mid-19th century, transforming from simple distillation processes to complex integrated systems capable of converting crude oil into a wide range of valuable products. The modern refinery represents a sophisticated network of interconnected processes designed to maximize the value extracted from each barrel of crude oil. These processes include atmospheric and vacuum distillation, catalytic cracking, hydrocracking, reforming, and various treatment technologies that collectively enable refiners to meet market demands for specific petroleum products.
The optimization of product slates—specifically naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions—has become increasingly critical in today's competitive refining landscape. Naphtha serves as a key feedstock for petrochemical production and gasoline blending, diesel fuels transportation sectors globally, and lubricant-range fractions provide high-value specialty products essential for industrial applications. The ability to adjust the yield and quality of these fractions in response to market conditions represents a significant competitive advantage.
Current technological trends in refinery optimization focus on advanced process control systems, real-time optimization algorithms, and integrated planning tools that enable refiners to make data-driven decisions about crude selection, processing conditions, and product blending. Machine learning and artificial intelligence applications are increasingly being deployed to predict equipment performance, optimize energy consumption, and enhance yield prediction accuracy.
The primary technical goals for product slate optimization include maximizing the yield of high-value products from available crude feedstocks, minimizing production costs through energy efficiency and process integration, meeting increasingly stringent product specifications, and reducing environmental impact. These goals must be achieved while maintaining operational flexibility to respond to market volatility and changing regulatory requirements.
Refiners face significant challenges in balancing short-term profitability with long-term sustainability objectives. The industry is experiencing pressure to reduce carbon footprint while maintaining economic viability, driving innovation in process technologies and catalysts. Additionally, the increasing complexity of crude oil feedstocks, particularly the processing of opportunity crudes with higher levels of contaminants, necessitates more sophisticated approaches to slate optimization.
The evolution of refinery configurations reflects these challenges, with modern facilities incorporating more conversion capacity to transform lower-value heavy fractions into premium products. This trend is expected to continue as refiners seek to maximize the production of transportation fuels and petrochemical feedstocks while minimizing the output of lower-value fuel oil products.
The optimization of product slates—specifically naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions—has become increasingly critical in today's competitive refining landscape. Naphtha serves as a key feedstock for petrochemical production and gasoline blending, diesel fuels transportation sectors globally, and lubricant-range fractions provide high-value specialty products essential for industrial applications. The ability to adjust the yield and quality of these fractions in response to market conditions represents a significant competitive advantage.
Current technological trends in refinery optimization focus on advanced process control systems, real-time optimization algorithms, and integrated planning tools that enable refiners to make data-driven decisions about crude selection, processing conditions, and product blending. Machine learning and artificial intelligence applications are increasingly being deployed to predict equipment performance, optimize energy consumption, and enhance yield prediction accuracy.
The primary technical goals for product slate optimization include maximizing the yield of high-value products from available crude feedstocks, minimizing production costs through energy efficiency and process integration, meeting increasingly stringent product specifications, and reducing environmental impact. These goals must be achieved while maintaining operational flexibility to respond to market volatility and changing regulatory requirements.
Refiners face significant challenges in balancing short-term profitability with long-term sustainability objectives. The industry is experiencing pressure to reduce carbon footprint while maintaining economic viability, driving innovation in process technologies and catalysts. Additionally, the increasing complexity of crude oil feedstocks, particularly the processing of opportunity crudes with higher levels of contaminants, necessitates more sophisticated approaches to slate optimization.
The evolution of refinery configurations reflects these challenges, with modern facilities incorporating more conversion capacity to transform lower-value heavy fractions into premium products. This trend is expected to continue as refiners seek to maximize the production of transportation fuels and petrochemical feedstocks while minimizing the output of lower-value fuel oil products.
Market Analysis for Refined Petroleum Products
The global refined petroleum products market has demonstrated significant volatility in recent years, with the naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions experiencing distinct demand patterns. The refined products market reached approximately $2.7 trillion in 2022, with projections indicating growth to $3.2 trillion by 2027, representing a compound annual growth rate of 3.5%.
Naphtha demand has been primarily driven by the petrochemical industry, which accounts for over 70% of global naphtha consumption. Asia-Pacific dominates this segment, with China and India collectively representing nearly 40% of global demand growth. The petrochemical feedstock market has shown resilience despite economic fluctuations, supported by increasing plastic production and expanding manufacturing sectors in emerging economies.
Diesel remains the backbone of the transportation sector, particularly in commercial and industrial applications. The global diesel market volume exceeded 29 million barrels per day in 2022, with road transportation accounting for approximately 50% of consumption. However, the market faces significant challenges from increasingly stringent emissions regulations and the gradual shift toward electrification in certain segments, particularly in Europe and North America.
Lubricant-range fractions represent a smaller but higher-value segment of refined products. The global lubricants market was valued at $164 billion in 2022, with automotive applications comprising roughly 60% of demand. Industrial lubricants account for most of the remainder, with steady growth driven by manufacturing expansion in developing regions.
Regional disparities in demand patterns are pronounced. While North America and Europe show plateauing or declining demand for conventional fuels, developing economies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America continue to exhibit robust growth trajectories. China and India together are expected to account for approximately 45% of the incremental global demand for refined petroleum products through 2030.
The competitive landscape features both integrated oil majors and specialized refiners. Companies with advanced optimization capabilities for product slate adjustment have demonstrated superior profit margins, averaging 2-3 percentage points higher than industry standards. This advantage becomes particularly significant during periods of market volatility or rapid demand shifts between product categories.
Pricing dynamics vary significantly across product categories. Diesel has maintained a premium over gasoline in most markets, with seasonal variations affecting the spread. Naphtha pricing correlates strongly with crude oil benchmarks but experiences additional volatility due to its linkage with petrochemical markets. Lubricant base oils command substantial premiums, with Group II and Group III base oils seeing growing demand due to higher performance requirements.
Naphtha demand has been primarily driven by the petrochemical industry, which accounts for over 70% of global naphtha consumption. Asia-Pacific dominates this segment, with China and India collectively representing nearly 40% of global demand growth. The petrochemical feedstock market has shown resilience despite economic fluctuations, supported by increasing plastic production and expanding manufacturing sectors in emerging economies.
Diesel remains the backbone of the transportation sector, particularly in commercial and industrial applications. The global diesel market volume exceeded 29 million barrels per day in 2022, with road transportation accounting for approximately 50% of consumption. However, the market faces significant challenges from increasingly stringent emissions regulations and the gradual shift toward electrification in certain segments, particularly in Europe and North America.
Lubricant-range fractions represent a smaller but higher-value segment of refined products. The global lubricants market was valued at $164 billion in 2022, with automotive applications comprising roughly 60% of demand. Industrial lubricants account for most of the remainder, with steady growth driven by manufacturing expansion in developing regions.
Regional disparities in demand patterns are pronounced. While North America and Europe show plateauing or declining demand for conventional fuels, developing economies in Asia, Africa, and Latin America continue to exhibit robust growth trajectories. China and India together are expected to account for approximately 45% of the incremental global demand for refined petroleum products through 2030.
The competitive landscape features both integrated oil majors and specialized refiners. Companies with advanced optimization capabilities for product slate adjustment have demonstrated superior profit margins, averaging 2-3 percentage points higher than industry standards. This advantage becomes particularly significant during periods of market volatility or rapid demand shifts between product categories.
Pricing dynamics vary significantly across product categories. Diesel has maintained a premium over gasoline in most markets, with seasonal variations affecting the spread. Naphtha pricing correlates strongly with crude oil benchmarks but experiences additional volatility due to its linkage with petrochemical markets. Lubricant base oils command substantial premiums, with Group II and Group III base oils seeing growing demand due to higher performance requirements.
Current Challenges in Product Slate Optimization
Product slate optimization in refining operations faces significant challenges due to the complex interplay between feedstock variability, processing constraints, and market demands. Refiners must continuously balance the production of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions while navigating volatile market conditions and increasingly stringent regulatory requirements.
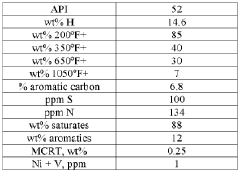
One of the primary challenges is the inherent uncertainty in crude oil composition. Refineries process crudes with varying properties, including API gravity, sulfur content, and molecular composition, which directly impact the yield and quality of different product fractions. This variability makes consistent optimization difficult, particularly when refineries must switch between crude sources due to supply chain disruptions or economic considerations.
Process unit constraints represent another significant hurdle. Refineries operate within the limitations of existing equipment capacities, conversion efficiencies, and operational parameters. These constraints often create bottlenecks that restrict the flexibility to adjust product slates in response to market signals. For instance, maximizing diesel production might require operating hydrocrackers at capacity limits, potentially causing accelerated equipment deterioration or increased maintenance requirements.
Energy consumption optimization presents a dual challenge of economic and environmental significance. The processes required to convert heavier fractions into more valuable products like diesel or to improve the quality of lubricant base stocks are energy-intensive. As energy costs rise and carbon regulations tighten, refiners must balance product slate adjustments against their energy and emissions footprint.
Market volatility adds another layer of complexity. Seasonal demand patterns, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic factors cause significant fluctuations in the relative values of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant products. Refiners must forecast these changes accurately while accounting for the lag time between production decisions and product availability in the market.
Regulatory compliance requirements continue to evolve, particularly regarding product specifications. Increasingly stringent sulfur limits, aromatics restrictions, and performance parameters for fuels and lubricants necessitate additional processing steps or limit blending options, constraining the optimization space.
Integration challenges between planning and operations further complicate optimization efforts. While sophisticated linear programming models can generate theoretically optimal product slates, translating these plans into operational reality often encounters practical difficulties due to process dynamics, transition costs, and operational constraints not fully captured in planning models.
Finally, the industry faces a knowledge gap as experienced personnel retire. The intuitive understanding of refinery operations that complements mathematical optimization is becoming scarcer, potentially limiting the effective implementation of optimization strategies in real-world scenarios.
One of the primary challenges is the inherent uncertainty in crude oil composition. Refineries process crudes with varying properties, including API gravity, sulfur content, and molecular composition, which directly impact the yield and quality of different product fractions. This variability makes consistent optimization difficult, particularly when refineries must switch between crude sources due to supply chain disruptions or economic considerations.
Process unit constraints represent another significant hurdle. Refineries operate within the limitations of existing equipment capacities, conversion efficiencies, and operational parameters. These constraints often create bottlenecks that restrict the flexibility to adjust product slates in response to market signals. For instance, maximizing diesel production might require operating hydrocrackers at capacity limits, potentially causing accelerated equipment deterioration or increased maintenance requirements.
Energy consumption optimization presents a dual challenge of economic and environmental significance. The processes required to convert heavier fractions into more valuable products like diesel or to improve the quality of lubricant base stocks are energy-intensive. As energy costs rise and carbon regulations tighten, refiners must balance product slate adjustments against their energy and emissions footprint.
Market volatility adds another layer of complexity. Seasonal demand patterns, geopolitical events, and macroeconomic factors cause significant fluctuations in the relative values of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant products. Refiners must forecast these changes accurately while accounting for the lag time between production decisions and product availability in the market.
Regulatory compliance requirements continue to evolve, particularly regarding product specifications. Increasingly stringent sulfur limits, aromatics restrictions, and performance parameters for fuels and lubricants necessitate additional processing steps or limit blending options, constraining the optimization space.
Integration challenges between planning and operations further complicate optimization efforts. While sophisticated linear programming models can generate theoretically optimal product slates, translating these plans into operational reality often encounters practical difficulties due to process dynamics, transition costs, and operational constraints not fully captured in planning models.
Finally, the industry faces a knowledge gap as experienced personnel retire. The intuitive understanding of refinery operations that complements mathematical optimization is becoming scarcer, potentially limiting the effective implementation of optimization strategies in real-world scenarios.
Current Optimization Methodologies for Product Slate
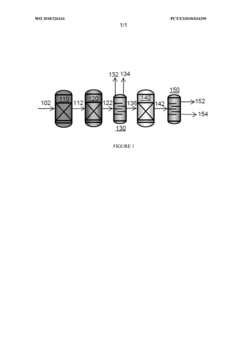
01 Catalytic processes for petroleum fraction optimization
Various catalytic processes can be employed to optimize petroleum fractions such as naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions. These processes involve the use of specific catalysts to enhance the quality and yield of desired products. Catalytic cracking, hydrocracking, and isomerization are common techniques that help in converting heavier fractions into lighter, more valuable products. The selection of appropriate catalysts and operating conditions plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency of these processes and the properties of the final products.- Catalytic processes for petroleum fraction optimization: Various catalytic processes can be employed to optimize petroleum fractions such as naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions. These processes involve the use of specific catalysts to enhance the quality and yield of desired petroleum products. Catalytic cracking, hydrocracking, and isomerization are common techniques that help in converting heavier fractions into lighter, more valuable products. These processes can improve properties like octane number for naphtha, cetane number for diesel, and viscosity index for lubricants.
- Hydrotreatment and desulfurization techniques: Hydrotreatment processes are essential for removing impurities from petroleum fractions, particularly sulfur compounds. These techniques involve treating the petroleum fractions with hydrogen under high pressure and temperature in the presence of catalysts. Desulfurization is crucial for meeting environmental regulations and improving the quality of final products. Advanced hydrotreatment methods can significantly reduce sulfur content in diesel and naphtha fractions while preserving or enhancing their performance characteristics.
- Fractionation and separation technologies: Efficient fractionation and separation technologies are fundamental to petroleum fraction optimization. These include advanced distillation techniques, solvent extraction, and membrane separation processes that allow for precise separation of different petroleum components based on their boiling points and other physical properties. Improved separation technologies can lead to higher purity fractions, reduced energy consumption, and better overall process economics in refinery operations.
- Additives and blending strategies: The use of specific additives and blending strategies can significantly enhance the properties of petroleum fractions. Various chemical additives can improve the stability, performance, and environmental characteristics of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant fractions. Blending different petroleum streams in optimal ratios can also help achieve desired specifications while maximizing the utilization of available feedstocks. Advanced blending models and algorithms enable refiners to optimize product quality while minimizing production costs.
- Process integration and optimization techniques: Comprehensive process integration and optimization techniques can maximize the efficiency of petroleum fraction production. These approaches involve integrating various refinery processes, heat recovery systems, and control strategies to minimize energy consumption and maximize product yields. Advanced modeling, simulation, and artificial intelligence tools can be employed to identify optimal operating conditions for complex refinery systems. Process integration can lead to significant improvements in both economic and environmental performance of petroleum fraction production.
02 Hydrotreatment and hydroprocessing techniques
Hydrotreatment and hydroprocessing are essential techniques for removing impurities and improving the quality of petroleum fractions. These processes involve treating petroleum fractions with hydrogen under high pressure and temperature in the presence of catalysts. The main objectives include sulfur and nitrogen removal, saturation of olefins and aromatics, and improvement of cetane number for diesel fractions. Advanced hydroprocessing techniques can significantly enhance the properties of lubricant-range fractions by removing unwanted components and improving oxidation stability.Expand Specific Solutions03 Fractionation and separation methods
Efficient fractionation and separation methods are crucial for optimizing petroleum fractions. These methods involve techniques such as distillation, extraction, and adsorption to separate different components based on their boiling points, molecular weights, or chemical properties. Advanced separation technologies can improve the yield and purity of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions. Optimization of operating parameters such as temperature, pressure, and reflux ratio in distillation columns can significantly enhance the separation efficiency and product quality.Expand Specific Solutions04 Additives and blending strategies
The use of additives and strategic blending approaches can significantly improve the properties of petroleum fractions. Various additives such as cetane improvers, pour point depressants, and antioxidants can enhance the performance characteristics of diesel and lubricant-range fractions. Blending different petroleum streams with complementary properties can help achieve desired specifications while optimizing resource utilization. Advanced blending models and algorithms can predict the properties of final products and optimize the blending ratios to meet specific requirements.Expand Specific Solutions05 Process integration and energy efficiency
Process integration and energy efficiency improvements are essential aspects of petroleum fraction optimization. Heat integration, waste heat recovery, and process intensification techniques can significantly reduce energy consumption and operational costs. Advanced control systems and optimization algorithms can help maintain optimal operating conditions and respond to changes in feedstock properties. Integration of different processing units can create synergies and improve overall efficiency. Implementation of energy-efficient technologies can also reduce the environmental footprint of petroleum processing operations.Expand Specific Solutions
Major Players in Petroleum Refining Industry
Product slate optimization in the petroleum industry is currently in a mature growth phase, with a global market size estimated at $3-5 billion annually. The competitive landscape is dominated by established oil majors and specialized technology providers. Sinopec, ExxonMobil, and Saudi Aramco lead with advanced optimization technologies for naphtha, diesel, and lubricant fractions, leveraging their integrated operations. UOP LLC and IFP Energies Nouvelles provide specialized optimization solutions as technology licensors. The technology has reached high maturity levels with companies like Shell, PetroChina, and Indian Oil Corporation implementing AI-driven optimization systems. Regional players such as Idemitsu Kosan and Repsol are developing niche applications, while research institutions like Sinopec Research Institute and East China University contribute to technological advancement through collaborative innovation.
China Petroleum & Chemical Corp.
Technical Solution: China Petroleum & Chemical Corp. (Sinopec) has developed an integrated Product Slate Optimization system that combines advanced mathematical modeling with real-time process monitoring. Their approach utilizes multi-objective optimization algorithms to balance the production of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant fractions based on market demand and refinery capabilities. The system incorporates machine learning models that analyze historical production data, market trends, and feedstock properties to predict optimal operating conditions. Sinopec's technology employs a two-stage optimization process: first optimizing crude selection and blending, then determining the optimal processing parameters across various refinery units to maximize value-added products while minimizing energy consumption. Their solution also features dynamic scheduling capabilities that can adjust production targets in response to changing market conditions or equipment constraints, ensuring continuous optimization of the product slate.
Strengths: Comprehensive integration with existing refinery infrastructure; robust adaptation to feedstock quality variations; strong market-responsive capabilities. Weaknesses: High implementation complexity requiring significant technical expertise; substantial initial investment in monitoring and control systems; potential challenges in smaller refineries with limited technological infrastructure.
ExxonMobil Technology & Engineering Co.
Technical Solution: ExxonMobil's Product Slate Optimization technology centers on their proprietary Molecular Management approach, which tracks hydrocarbon molecules throughout the refining process to optimize product yields. Their system employs detailed kinetic modeling of catalytic processes to predict and control the transformation of specific molecular structures, allowing precise tailoring of naphtha, diesel, and lubricant fractions. The technology incorporates advanced process control systems with real-time optimization capabilities that continuously adjust operating parameters to maximize value across the entire refinery. ExxonMobil's approach is distinguished by its integration of molecular-level understanding with economic optimization models that account for market dynamics, energy costs, and environmental constraints. Their system also features sophisticated blending optimization tools that ensure final products meet all specifications while minimizing quality giveaway, effectively balancing the production of various fractions based on their relative market values and production costs.
Strengths: Superior molecular-level control leading to higher-value products; excellent integration between technical and economic optimization; proven track record across diverse refinery configurations. Weaknesses: Requires extensive analytical capabilities and specialized expertise; higher implementation and maintenance costs compared to conventional approaches; significant computational resources needed for real-time molecular tracking.
Key Technical Innovations in Fractionation Processes
Production of diesel and base stocks from crude oil
PatentWO2018226416A1
Innovation
- A process that hydroprocesses whole waxy crude oil without vacuum distillation, using hydrotreating and catalytic dewaxing to produce Group III base oils, naphtha, and diesel products, with dewaxing catalysts isomerizing naphtha and diesel range molecules to enhance octane value and reduce cloud point, and hydrofinishing to remove polynuclear aromatics.
Increasing hydrocracker diesel yield, total liquid yield and pour point properties by ammonia or amine spiking
PatentActiveUS10550334B1
Innovation
- Selectively using a naphtha-selective catalyst and introducing a basic compound, such as ammonia, to partially passivate the catalyst, thereby increasing diesel production while maintaining the ability to revert to original product ratios when needed.
Environmental Regulations Impact on Product Slate
Environmental regulations have become increasingly stringent worldwide, significantly impacting refinery operations and product slate optimization strategies. The regulatory landscape governing petroleum products has evolved dramatically over the past two decades, with particular focus on reducing sulfur content, aromatics, and overall emissions profiles of transportation fuels.
In the European Union, the implementation of Euro VI standards has mandated ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) with maximum sulfur content of 10 ppm, while also restricting polyaromatic hydrocarbon content to less than 8%. These requirements have forced refineries to invest heavily in hydrotreatment capacity and reconfigure their operations to meet these specifications while maintaining economic viability.
Similarly, the United States EPA Tier 3 regulations have progressively tightened gasoline sulfur limits to 10 ppm annual average, creating significant challenges for naphtha processing units. California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) has further pushed refineries toward producing lower carbon intensity fuels, directly affecting product slate decisions and processing pathways.
The International Maritime Organization's IMO 2020 regulation, limiting marine fuel sulfur content to 0.5% from the previous 3.5%, has dramatically altered the market dynamics for high-sulfur fuel oil and created new demand patterns for low-sulfur blending components. This has particularly impacted the optimization of diesel and lubricant-range fractions, as refiners must now divert more middle distillates to the marine fuel pool.
Emerging regulations on biofuel blending mandates across various jurisdictions have introduced additional complexity to product slate optimization. The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) in the US and the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) in Europe require increasing percentages of renewable content in transportation fuels, necessitating adjustments in conventional petroleum product slates and blending strategies.
Carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes in various regions have created economic incentives that directly influence product slate decisions. Refineries must now factor carbon costs into their optimization models, potentially favoring less carbon-intensive processing routes and product mixes.
Looking forward, proposed regulations targeting plastic waste and single-use petrochemicals may significantly impact naphtha utilization pathways, potentially shifting optimization strategies away from petrochemical feedstock production toward transportation fuels or other applications. Additionally, emerging regulations on lubricant biodegradability and toxicity are reshaping requirements for lubricant-range fractions.
These regulatory pressures collectively necessitate more sophisticated and dynamic approaches to product slate optimization, incorporating regulatory compliance costs, market premiums for cleaner products, and strategic investments in processing capabilities that provide flexibility to adapt to evolving requirements.
In the European Union, the implementation of Euro VI standards has mandated ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) with maximum sulfur content of 10 ppm, while also restricting polyaromatic hydrocarbon content to less than 8%. These requirements have forced refineries to invest heavily in hydrotreatment capacity and reconfigure their operations to meet these specifications while maintaining economic viability.
Similarly, the United States EPA Tier 3 regulations have progressively tightened gasoline sulfur limits to 10 ppm annual average, creating significant challenges for naphtha processing units. California's Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) has further pushed refineries toward producing lower carbon intensity fuels, directly affecting product slate decisions and processing pathways.
The International Maritime Organization's IMO 2020 regulation, limiting marine fuel sulfur content to 0.5% from the previous 3.5%, has dramatically altered the market dynamics for high-sulfur fuel oil and created new demand patterns for low-sulfur blending components. This has particularly impacted the optimization of diesel and lubricant-range fractions, as refiners must now divert more middle distillates to the marine fuel pool.
Emerging regulations on biofuel blending mandates across various jurisdictions have introduced additional complexity to product slate optimization. The Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) in the US and the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) in Europe require increasing percentages of renewable content in transportation fuels, necessitating adjustments in conventional petroleum product slates and blending strategies.
Carbon pricing mechanisms and emissions trading schemes in various regions have created economic incentives that directly influence product slate decisions. Refineries must now factor carbon costs into their optimization models, potentially favoring less carbon-intensive processing routes and product mixes.
Looking forward, proposed regulations targeting plastic waste and single-use petrochemicals may significantly impact naphtha utilization pathways, potentially shifting optimization strategies away from petrochemical feedstock production toward transportation fuels or other applications. Additionally, emerging regulations on lubricant biodegradability and toxicity are reshaping requirements for lubricant-range fractions.
These regulatory pressures collectively necessitate more sophisticated and dynamic approaches to product slate optimization, incorporating regulatory compliance costs, market premiums for cleaner products, and strategic investments in processing capabilities that provide flexibility to adapt to evolving requirements.
Economic Modeling for Refinery Product Portfolio
Economic modeling for refinery product portfolio optimization requires sophisticated analytical frameworks that capture the complex interplay between market dynamics, production costs, and operational constraints. These models typically incorporate multiple variables including crude oil prices, processing costs, product demand forecasts, and regulatory requirements to determine the most profitable product slate configuration.
Financial simulation tools are essential components of these models, enabling refineries to project cash flows under various scenarios. Monte Carlo simulations are particularly valuable, as they account for price volatility and demand uncertainty by generating thousands of potential outcomes based on historical data patterns and market projections. This probabilistic approach provides decision-makers with a comprehensive risk assessment rather than a single-point forecast.
Linear and non-linear programming techniques form the mathematical backbone of optimization models, allowing refineries to maximize profit margins while respecting operational constraints. These algorithms can rapidly evaluate millions of potential product combinations to identify optimal production strategies for naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions based on current market conditions.
Sensitivity analysis represents another critical element in economic modeling, enabling refineries to understand how changes in key variables affect overall profitability. By systematically varying parameters such as crude oil prices, processing yields, and product premiums, refineries can identify which factors most significantly impact their bottom line and develop appropriate hedging strategies.
Integration of real-time market data feeds has revolutionized economic modeling capabilities. Modern systems continuously update pricing information, allowing refineries to adjust their product slate dynamically in response to market shifts. This capability is particularly valuable in volatile markets where the optimal balance between naphtha, diesel, and lubricant production can change rapidly.
Return on investment (ROI) calculations for capital projects represent the final critical component of comprehensive economic modeling. When considering investments in processing units that affect product slate flexibility, refineries must evaluate not only the initial capital expenditure but also the long-term strategic value of being able to adjust product ratios in response to changing market conditions. These analyses typically incorporate multiple scenarios spanning 10-20 year timeframes to capture the full lifecycle benefits of enhanced production flexibility.
Financial simulation tools are essential components of these models, enabling refineries to project cash flows under various scenarios. Monte Carlo simulations are particularly valuable, as they account for price volatility and demand uncertainty by generating thousands of potential outcomes based on historical data patterns and market projections. This probabilistic approach provides decision-makers with a comprehensive risk assessment rather than a single-point forecast.
Linear and non-linear programming techniques form the mathematical backbone of optimization models, allowing refineries to maximize profit margins while respecting operational constraints. These algorithms can rapidly evaluate millions of potential product combinations to identify optimal production strategies for naphtha, diesel, and lubricant-range fractions based on current market conditions.
Sensitivity analysis represents another critical element in economic modeling, enabling refineries to understand how changes in key variables affect overall profitability. By systematically varying parameters such as crude oil prices, processing yields, and product premiums, refineries can identify which factors most significantly impact their bottom line and develop appropriate hedging strategies.
Integration of real-time market data feeds has revolutionized economic modeling capabilities. Modern systems continuously update pricing information, allowing refineries to adjust their product slate dynamically in response to market shifts. This capability is particularly valuable in volatile markets where the optimal balance between naphtha, diesel, and lubricant production can change rapidly.
Return on investment (ROI) calculations for capital projects represent the final critical component of comprehensive economic modeling. When considering investments in processing units that affect product slate flexibility, refineries must evaluate not only the initial capital expenditure but also the long-term strategic value of being able to adjust product ratios in response to changing market conditions. These analyses typically incorporate multiple scenarios spanning 10-20 year timeframes to capture the full lifecycle benefits of enhanced production flexibility.
Unlock deeper insights with Patsnap Eureka Quick Research — get a full tech report to explore trends and direct your research. Try now!
Generate Your Research Report Instantly with AI Agent
Supercharge your innovation with Patsnap Eureka AI Agent Platform!